Difference between revisions of "General Rules for Dimensioning of Contacts"
From Electrical Contacts
(→6.4.6 General Rules for Dimensioning of Contacts) |
Doduco Admin (talk | contribs) |
||
| (26 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | ===6.4.6 General Rules for Dimensioning of Contacts=== | + | ===<!--6.4.6-->General Rules for Dimensioning of Contacts=== |
| − | + | '''Recommended Minimum Contact Forces at Slightly Sliding Contact Make:''' | |
| − | Contact Make:''' | ||
| − | {| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px;width: | + | <table class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px;width:40%"> |
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>Gold</td> | ||
| + | <td>0.03 N </td> | ||
| + | </tr><tr> | ||
| + | <td>Silver </td> | ||
| + | <td>0.1 N</td> | ||
| + | </tr><tr> | ||
| + | <td>Tungsten </td> | ||
| + | <td>0.5 N</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Contact Force Recommendations:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px;width:40%" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Signal relays | ||
| + | |≥ 3 cN | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |AC power relays | ||
| + | |≥ 20 cN | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Automotive relays | ||
| + | |≥ 20 cN | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Motor switches (Contactors)<br />(Silver – Metal oxide contacts) | ||
| + | |0.05 - 0.08 N/A | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Power switches |
| − | |0. | + | |0.1 - 0.2 N/A |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Connectors<br />(Gold coating) |
| − | | | + | |≥ 30 cN/contact element |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Connectors<br />(Silver coating) |
| − | | | + | |≥ 50 cN/contact element |
|- | |- | ||
| + | |Connectors<br />(Tin coating) | ||
| + | |≥ 1 N/contact element | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''General Rules for Dimensioning of Contact Rivets''' | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
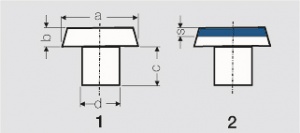
| − | + | [[File:General Rules for Dimensioning of Contact Rivets.jpg|left|thumb|Figure 1: General Rules for Dimensioning of Contact Rivets]] | |
| − | + | {| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px;width:100%" | |
| + | |- | ||
| + | !Dimensioning | ||
| + | !Solid Rivets (1) | ||
| + | !Composite Rivets (2) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |a : d | ||
| + | |1.5 : 1 bis 2.5 : 1 | ||
| + | |2 : 1 bis 2.5 : 1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |a : b | ||
| + | |2.5 : 1 bis 10 : 1 | ||
| + | |3 : 1 bis 5 : 1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |c : b | ||
| + | |≥ 1 : 1 | ||
| + | |≥ 1 : 1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |b : s | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |≥ 2 : 1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |s<sub>min</sub> | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |≈ 0.3 mm | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''Failure Probability of Single and Double (Bifurcated) Contacts''' (according to Thielecke) | |
| − | + | {| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px;width:100%" | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | !Contact force[N] | |
| + | !colspan="4" style="text-align:center"|'''Single contact''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! | ||
| + | !Ag | ||
| + | !AuNi 5, Pt | ||
| + | !Ag | ||
| + | !AuNi 5, Pt | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |0.04 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |1 x 10<sup>-4</sup> | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |2 x 10<sup>-8</sup> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |0.1 | ||
| + | |2 x 10<sup>-3</sup> | ||
| + | |4 x 10<sup>-5</sup> | ||
| + | |8 x 10<sup>-5</sup> | ||
| + | |8 x 10<sup>-9</sup> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |0.2 | ||
| + | |1 x 10<sup>-4</sup> | ||
| + | |8 x 10<sup>-6</sup> | ||
| + | |4 x 10<sup>-6</sup> | ||
| + | |4 x 10<sup>-8</sup> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |0.3 | ||
| + | |5.5 x 10<sup>-6</sup> | ||
| + | |1.5 x 10<sup>-6</sup> | ||
| + | |1.8 x 10<sup>-7</sup> | ||
| + | |3.2 x 10<sup>-10</sup> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | function of the current (according to | + | <div class="multiple-images"> |
| − | Kirchdorfer); Ag/Ni10; F = 0.45 N; U = 24 V | + | <figure id="fig:Failure probability of a contact as a function of the voitage"> |
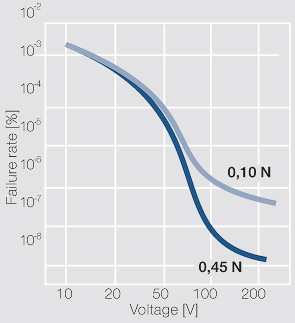
| + | [[File:Failure probability of a contact as a function of the voitage.jpg|left|thumb|Figure 2: Failure probability of a contact as a function of the voltage (according to Kirchdorfer); Ag/Ni10; 10 mA]] | ||
| + | </figure> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <figure id="fig:Failure probability of a contact as a function of the current"> | ||
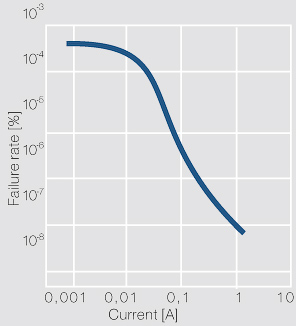
| + | [[File:Failure probability of a contact as a function of the current.jpg|left|thumb|Figure 3: Failure probability of a contact as a function of the current (according to Kirchdorfer); Ag/Ni10; F<sub>k</sub> = 0.45 N; U = 24 V]] | ||
| + | </figure> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div class="clear"></div> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
[[Application Tables and Guideline Data for Use of Electrical Contact Design#References|References]] | [[Application Tables and Guideline Data for Use of Electrical Contact Design#References|References]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[de:Faustregeln_für_die_Kontaktdimensionierung]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:01, 26 January 2023
General Rules for Dimensioning of Contacts
Recommended Minimum Contact Forces at Slightly Sliding Contact Make:
| Gold | 0.03 N |
| Silver | 0.1 N |
| Tungsten | 0.5 N |
Contact Force Recommendations:
| Signal relays | ≥ 3 cN |
| AC power relays | ≥ 20 cN |
| Automotive relays | ≥ 20 cN |
| Motor switches (Contactors) (Silver – Metal oxide contacts) |
0.05 - 0.08 N/A |
| Power switches | 0.1 - 0.2 N/A |
| Connectors (Gold coating) |
≥ 30 cN/contact element |
| Connectors (Silver coating) |
≥ 50 cN/contact element |
| Connectors (Tin coating) |
≥ 1 N/contact element |
General Rules for Dimensioning of Contact Rivets
| Dimensioning | Solid Rivets (1) | Composite Rivets (2) |
|---|---|---|
| a : d | 1.5 : 1 bis 2.5 : 1 | 2 : 1 bis 2.5 : 1 |
| a : b | 2.5 : 1 bis 10 : 1 | 3 : 1 bis 5 : 1 |
| c : b | ≥ 1 : 1 | ≥ 1 : 1 |
| b : s | ≥ 2 : 1 | |
| smin | ≈ 0.3 mm |
Failure Probability of Single and Double (Bifurcated) Contacts (according to Thielecke)
| Contact force[N] | Single contact | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag | AuNi 5, Pt | Ag | AuNi 5, Pt | |
| 0.04 | 1 x 10-4 | 2 x 10-8 | ||
| 0.1 | 2 x 10-3 | 4 x 10-5 | 8 x 10-5 | 8 x 10-9 |
| 0.2 | 1 x 10-4 | 8 x 10-6 | 4 x 10-6 | 4 x 10-8 |
| 0.3 | 5.5 x 10-6 | 1.5 x 10-6 | 1.8 x 10-7 | 3.2 x 10-10 |