Difference between revisions of "Contact Spring Calculations"
From Electrical Contacts
Doduco Admin (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
</figure> | </figure> | ||
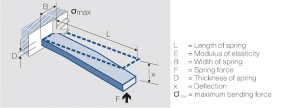
The influence of the dimensions can be illustrated best by using the single side fixed beam model <xr id="fig:One side fixed contact bending spring"/> (Fig. 6.20). For small deflections the following equation is valid: | The influence of the dimensions can be illustrated best by using the single side fixed beam model <xr id="fig:One side fixed contact bending spring"/> (Fig. 6.20). For small deflections the following equation is valid: | ||
| − | :<math>F = \frac{3 | + | :<math>F = \frac{3 \cdot E \cdot J}{L^3} \cdot </math> |
where J is the momentum of inertia of the rectangular cross section of the beam | where J is the momentum of inertia of the rectangular cross section of the beam | ||
Revision as of 14:08, 30 April 2014
6.4.7 Contact Spring Calculations
The influence of the dimensions can be illustrated best by using the single side fixed beam model Figure 1 (Fig. 6.20). For small deflections the following equation is valid:
where J is the momentum of inertia of the rectangular cross section of the beam
For springs with a circular cross-sectional area the momentum of inertia is
To avoid plastic deformation of the spring the max bending force σmax cannot be exceeded
The stress limit is defined through the fatigue limit and the 0.2% elongation limit resp.
and/or
- Triangular spring
- Trapezoidal spring
Deflection
Max. bending force
Deflection
Max. bending force