Difference between revisions of "Anwendungstabellen und Richtwerte für den Einsatz elektrischer Kontakte"
Doduco Admin (talk | contribs) (→Geschlossene Kontakte) |
Teitscheid (talk | contribs) |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
Probleme zu berücksichtigen, die bei den Schaltvorgängen und der | Probleme zu berücksichtigen, die bei den Schaltvorgängen und der | ||
Stromführung auftreten. | Stromführung auftreten. | ||
| + | |||
siehe Artikle: [[Hohe_elektrische_Last| Hohe elektrische Last]] | siehe Artikle: [[Hohe_elektrische_Last| Hohe elektrische Last]] | ||
| Line 24: | Line 25: | ||
Eine hohe Kontaktzuverlässigkeit und hohe Lebensdauer von elektromechanischen | Eine hohe Kontaktzuverlässigkeit und hohe Lebensdauer von elektromechanischen | ||
Bauelementen und Schaltgeräten wird nur dann erreicht, wenn den | Bauelementen und Schaltgeräten wird nur dann erreicht, wenn den | ||
| − | Anforderungen entsprechend der optimale Kontaktwerkstoff und die | + | Anforderungen entsprechend der optimale Kontaktwerkstoff und die geeignetste |
Kontaktform eingesetzt werden. Bei der Festlegung des Kontaktwerkstoffes | Kontaktform eingesetzt werden. Bei der Festlegung des Kontaktwerkstoffes | ||
und der technologischen Gestaltung der Kontaktstellen müssen allerdings | und der technologischen Gestaltung der Kontaktstellen müssen allerdings | ||
| Line 36: | Line 37: | ||
{| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px" | {| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! | + | !Type of Contacts or Devices |
| − | ! | + | !Characteristic Requirements for Contacts |
| − | ! | + | !Contact Material |
| − | ! | + | !Design Form of Contacts |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Contacts for dry circuits |
| − | | | + | |Reliable contacting at very low currents and voltages and mostly at also<br />low contact forces |
| − | + | |AuAg alloys, (AuPt), Au | |
| − | |AuAg | + | |Contact rivets, welded miniature profiles (tapes), electroplated Au, sputtered Au layers |
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Switching contacts in measuring devices |
| − | | | + | |Reliable switching at low voltages and currents at low contact forces |
| − | + | |Au and Pt alloys, (AgPd alloys) | |
| − | |Au | + | |Contact rivets, welded tips, clad parts |
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Keyboard contacts |
| − | | | + | |Defined contacting, close to bounce-free make, high reliability at low switching loads |
| − | + | |Au alloys, (AgPd), Au on Ni substrate | |
| − | |Au | + | |Au plated snap discs, Au clad wires and stamped parts, hard gold electroplated contact spots on printed circuit boards |
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Rotary switches on printed circuit boards |
| − | + | |Good frictional wear resistance, low contact résistance | |
| − | | | + | |Sliding track: hard gold on Ni substrate Slider: AgPd alloy, (Hard silver) |
| − | | | + | |Electroplated coatings on slide tracks; clad, welded, or riveted stamping parts |
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Slip rings with high reliability |
| − | | | + | |Low and consistent contact resistance at low contact forces |
| − | + | |Brushes: Au alloys, AgPd, AgPdCu; Slip rings: Au alloys, Ag alloys (Rh); For higher currents: Ag/C brushes against Ag slip rings | |
| − | | | + | |Brush wires, stamped brushes; solid, clad, or electroplated slip rings, Ag/C formed parts |
| − | Au | ||
| − | Ag/C | ||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | Ag/C | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Sliding contacts in miniature motors |
| − | | | + | |Very high frictional wear resistance, sure contacting even at very low contact forces |
| − | + | |Ag and Au alloys, Pd alloys, Au multi component alloys | |
| − | |Ag | + | |Brushes from flat rolled wire or stamped; collector hard gold electroplated or clad, or made from miniature profile segments |
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Centrifugal controllers for small motors |
| − | | | + | |Little shape changes, defined contacting at very low contact forces and high frequency of operation |
| − | + | |Pd alloys | |
| − | |Pd | + | |Contact rivets, contact screws, welded parts |
| − | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Connectors |
| − | | | + | |Low contact resistance, corrosion resistance, sufficient frictional wear resistance, good sliding capabilities |
| − | + | |Ag and Au alloys, Pd, PdNi; For automotive and consumer electronic at low operation numbers: Sn and Sn alloys | |
| − | |Ag | + | |Electroplated layers or clad, often Au flash plated, mostly with Ni substrate layer, stamped parts from hot tin dipped strip |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Telecommunication relays |
| − | | | + | |Reliable contacting even at high operational frequency |
| − | |Ag, AgPd, Au | + | |Ag, AgPd, Au alloys, PdRu |
| − | | | + | |Rivets, welded profile segments |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |Reed | + | |Reed relay contacts |
| − | | | + | |High reliability at low currents independent of atmospheric environment |
| − | + | |Au, (Rh) | |
| − | |Rh | + | |Switch paddles FeNi with partially diffused Au, (electroplated Rh) |
| − | | | ||
| − | Au, Rh | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Relays in electronic circuits |
| − | | | + | |High reliability at low switching loads and compact device design |
| − | + | |Au alloys, AgPd, Ag alloys | |
| − | |Au | + | |Stamped springs from seam-welded profiles, welded miniature profile (tape) segments, contact rivets |
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |GP relais (Elementary relays) |
| − | | | + | |Low arc erosion, high weld resistance, low and consistent contact resistance |
| − | |||
|Ag/Ni, Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub>, (Ag/CdO), Ag/ZnO,AgNi0.15, (Ag) | |Ag/Ni, Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub>, (Ag/CdO), Ag/ZnO,AgNi0.15, (Ag) | ||
| − | | | + | |Solid and composite contact rivets, welded miniature profile (tape) segments |
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Automotive relays |
| − | | | + | |Low material transfer, low contact resistance, high weld resistance |
| − | |||
|AgNi0.15, Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub>, Ag/Ni | |AgNi0.15, Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub>, Ag/Ni | ||
| − | | | + | |Contact rivets, welded miniature profile (tape) segments |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Flasher relays (automotive, > 3 Mio operations) |
| − | ( | + | |Low material transfer, high arc erosion resistance, low contact resistance |
| − | | | + | |PdCu15 and 40 (Anode) vs. AgNi0.15, AgCu3 (Cathode), Ag/ZnO, Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> |
| − | + | |Contact rivets, welded miniature profile (tape) and strip segments | |
| − | |PdCu15 and 40 (Anode) | ||
| − | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Breaker points (automotive ignition) |
| − | | | + | |Very high arc erosion resistance, high switching frequency |
|W | |W | ||
| − | | | + | |Tips or discs welded to formed parts or Fe supports |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Automotive horn contacts |
| − | | | + | |High arc erosion resistance at extremely high number of switching operations |
|W, Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> | |W, Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> | ||
| − | | | + | |Contact rivets, W weld buttons, springs or formed parts with brazed or welded tips |
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Appliance switches |
| − | | | + | |Low contact resistance, reasonable arc erosion and weld resistance |
| − | |||
|AgNi0.15, Ag/Ni, Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub>, (Ag/CdO) | |AgNi0.15, Ag/Ni, Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub>, (Ag/CdO) | ||
| − | | | + | |Contact rivets, welded contact parts |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Temperature controllers (Thermostats) |
| − | ( | + | |Defined contacting point even at slow motion make, high operating temperatures |
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
|AgNi0.15, Ag/Ni, Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub>, (Ag/CdO) | |AgNi0.15, Ag/Ni, Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub>, (Ag/CdO) | ||
| − | | | + | |Contact rivets, welded contact parts, weld buttons |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Wiring devices (Light switches) |
| − | | | + | |Low contact resistance, reasonable arc erosion and weld resistance |
| − | + | |AgNi0.15, AgCu, Ag/Ni, with make peaks also Ag/ZnO, (Ag/CdO) | |
| − | |AgNi0.15, AgCu, Ag/Ni, | + | |Contact rivets, welded contact parts |
| − | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
</figtable> | </figtable> | ||
| Line 183: | Line 144: | ||
{| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px" | {| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! | + | !Type of Contacts or Devices |
| − | ! | + | !Characteristic Requirements for Contacts |
| − | ! | + | !Contact Material |
| − | ! | + | !Design Form of Contacts |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Automatic staircase lighting switches |
| − | | | + | |High arc erosion and weld resistance |
| − | |Ag/Ni, Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub>, (Ag/CdO), Ag/C | + | |Ag/Ni, Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub>, (Ag/CdO), Ag/C against Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> |
| − | | | + | |Rivets, welded contact parts |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Miniature Circuit breakers |
| − | | | + | |Extremely high weld resistance, low temperature rise in use, sufficient arc erosion resistance |
| − | + | |I< 50 A: Ag/C97/3 (Cu/C) against Cu, I> 50 A : Ag/C97/3 o. 95/5 against AgCu3, Ag/Ni90/10 o. 80/20, Ag/W, Ag/WC (USA) | |
| − | |I< 50 A: Ag/C97/3 (Cu/C) | + | |Welded contact parts (Ag/C), clad stamped parts |
| − | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Fault current circuit breakers |
| − | | | + | |Extremely high weld resistance, low contact resistance, high arc erosion resistance |
| − | |||
|Stationary contact: Ag/C96/4 o. 95/5 Movable contact: Ag/Ni, Ag/MeO, Ag/W, Ag/WC, Ag/WC/C | |Stationary contact: Ag/C96/4 o. 95/5 Movable contact: Ag/Ni, Ag/MeO, Ag/W, Ag/WC, Ag/WC/C | ||
| − | | | + | |Welded and brazed contact parts |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Micro snap switches |
| − | | | + | |Low contact resistance, no sticking during make operation |
|AgNi 0,15, Ag/Ni, Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub>, (Ag/CdO) | |AgNi 0,15, Ag/Ni, Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub>, (Ag/CdO) | ||
| − | | | + | |Rivets, clad or welded contact parts |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Control and auxiliary switches |
| − | | | + | |Low contact resistance over extended life span |
|Ag, AgNi 0,15, AgCu, Ag/Ni | |Ag, AgNi 0,15, AgCu, Ag/Ni | ||
| − | | | + | |Rivets, clad stamped parts, (gold plated rivets), welded contact parts |
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Auxiliary and control relays |
| − | | | + | |High reliability over extended life span, low contact resistance |
| − | |||
|AgNi 0,15, Ag/Ni | |AgNi 0,15, Ag/Ni | ||
| − | | | + | |Rivets, clad profile parts, welded contact parts |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Cam switches (higher loads) |
| − | | | + | |High arc erosion and weld resistance, low contact resistance |
| − | |||
|AgCu, Ag/Ni, Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub>, Ag/ZnO, (Ag/CdO) | |AgCu, Ag/Ni, Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub>, Ag/ZnO, (Ag/CdO) | ||
| − | | | + | |Rivets, welded contact parts |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Contactors |
| − | | | + | |High arc erosion and weld resistance, low contact resistance |
| − | |||
|I< 20A : Ag/Ni, Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> I>20A : Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub>, (AgCdO) | |I< 20A : Ag/Ni, Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> I>20A : Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub>, (AgCdO) | ||
| − | | | + | |Welded and brazed contact tips |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |Motor- | + | |Motor -protective circuit breakers |
| − | | | + | |Extremely high weld resistance, low contact resistance |
| − | + | |Ag/ZnO, Ag/C against Ag/Ni | |
| − | |Ag/ZnO, Ag/C | + | |Welded contact parts, toplay stamping parts |
| − | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Power switches and circuit breakers |
| − | | | + | |Extremely high arc erosion and weld resistance, low contact resistance |
| − | + | |Ag/ZnO, Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> , Ag/C against Ag/Ni o. Ag/W, Ag/W, Ag/WC/C, Ag/W against Ag/CdO | |
| − | |Ag/ZnO, Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> , Ag/C | + | |Brazed and welded contact tips and formed parts |
| − | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Power switches with arcing and main contacts |
| − | + | |High weld resistance, low contact resistance, high arc erosion resistance | |
| − | | | + | |Arcing contacts: W/Ag, W/Cu, (Cu) Main contacts: Ag/Ni, Ag/ZnO, Ag/W, Ag/WC |
| − | + | |Brazed and welded contact tips and formed parts | |
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Disconnect switches |
| − | | | + | |Low contact resistance, sufficient mechanical strength |
| − | + | |AgNi 0,15, Ag/Ni, Ag (electroplated) | |
| − | |AgNi 0,15, Ag/Ni, Ag ( | + | |Electroplated coatings, brazed contact parts |
| − | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |High voltage circuit breakers |
| − | + | |Arcing contacts: highest arc erosion resistance Main contacts: low contact resistance | |
| − | | | + | |Arcing contacts: W/Cu-infiltrated Main contact CuCrZr silver plated, |
| − | + | |Cast-on, electron-beam welded (or brazed) formed parts, percussion welded pins | |
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Load disconnect switches (medium and high voltage) |
| − | | | + | |Low contact resistance, sufficient mechanical strength, high arc erosion resistance of precontacts |
| − | + | |Arcing contact: W/Cu, Cu, Ag/C Main contact: Cu, CuCrZr silver plated, Ag/Ni, AgNi0,15, Ag/C | |
| − | | | + | |Arcing contacts: brazed or welded parts Main contacts: silver plated, brazed or welded parts |
| − | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Vacuum contactors |
| − | | | + | |Low chopping current, high arc erosion resistance, low contact resistance |
| − | | | + | |Low gas content W/Cu, W/CuSb, WC/Ag, CuCr |
| − | | | + | |Contact discs, shaped rings |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Vacuum circuit breakers |
| − | | | + | |High switching capacity, low contact resistance |
| − | + | |Low gas content CuCr | |
| − | | | + | |Contact discs |
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Transformer tab changers |
| − | | | + | |High arc erosion resistance in oil environment |
| − | |W/Cu | + | |W/Cu in filtrated with approx. 70% |
| − | | | + | |Brazed contact tips |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Disconnect switches in high voltage circuits |
| − | + | |Low contact resistance, low mechanical wear, sufficient arc erosion resistance during current commutation | |
| − | | | + | |Ag (electroplated), AgNi0,15, Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> |
| − | + | |Electroplated coatings, brazed parts, Toplay profile segments | |
| − | |Ag ( | ||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
'''Anmerkungen:''' | '''Anmerkungen:''' | ||
| Line 328: | Line 262: | ||
{| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px" | {| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! | + | !Contact Parts, Semi-finished Materials |
| − | ! | + | !Typical Contact Materials and Dimensions |
!Main Areas of Application | !Main Areas of Application | ||
!Remarks | !Remarks | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Contact rivets solid, inserted wire segments |
| − | + | |Ag, Ag alloys, Au alloys, Pd alloys, Ag/Ni, Ag/C97/3, Ag/MeO (1.2 – 8 mm Ø) | |
| − | |Ag, Ag | + | |All types of switches in the communications, automotive, or power distribution technology simple contact component, universally applied, selection through economic aspects |
| − | Ag/MeO (1 | + | |Secure rivet attachment only with sufficiently thick shank (shank Ø = 1⁄2 head Ø); change-over contacts by forming secondary head from longer shanks |
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Contact rivets, clad (Composite Rivets) |
| − | |Ag, Ag | + | |Ag, Ag alloys, Ag/Ni, Ag/MeO on Cu base (2 ~ 10 mm Ø) |
| − | (2 | + | |All types of switches in the communications, automotive, or power engineering |
| − | | | + | |Secure rivet attachment only with sufficiently thick shank (shank Ø = 1⁄2 head Ø) |
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Contact rivets with brazed surface layer |
| − | | | + | |Tungsten and difficult to form powder metallurgical materials (i.e. Ag/C) on Cu or Fe bases (1 ~ 12 mm Ø) |
| − | Ag/C) | + | |Switches for power engineering, W layers mostly for controls |
| − | | | + | |Tungsten contact to be staked (riveted) with moderate force or using orbital riveting; for Fe bases also warm-forming |
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Contact screws |
| − | | | + | |Any contact material on Fe and CuZn screws, brazed, (1 ~ 10 mm Ø, M 2 ~ M 10) |
| − | + | |Adjustable contacts for controls and horns | |
| − | | | + | |During brazing carrier may get soft |
| − | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Vertically welded wire segments |
| − | |Ag, Ag | + | |Ag, Ag alloys, Ag/Ni, AgPd, Au alloys (wire 0.6 ~ 5 mm Ø) |
| − | + | |Contact parts for control functions and power engine- ering; economical manufacturing at higher quantities | |
| − | | | + | |Welding and subsequently heading or orbital forming of head shape |
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Horizontally welded wire and profile segments |
| − | + | |Au alloys, Pd alloys, Ag, Ag alloys, Ag/Ni, Ag/MeO, Ag/C in strip or profile form, Miniature profiles - also multi-layered (profile width 0.2 ~ 5 mm) | |
| − | |Au | + | |Contact parts for communication, measurement, controls and power engineering; very economical with respect to precious metal usage |
| − | Ag/C in | + | |Welding synchronized to stamping / forming on special equipment |
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Weld buttons |
| − | |Ag, Ag | + | |Ag, Ag alloys, Ag/Ni, Ag/MeO on Steel, Ni, Monel; Ag/W, Ag/Mo (1.5 ~ 10 mm Ø) |
| − | + | |Welded for example to steel springs or thermostatic bimetals for temperature controls | |
| − | | | + | |Metallurgical bond through simple projection welding remains strong in temperature cycling applications |
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Tungsten weld buttons |
| − | |W | + | |W on Ni or Ni-plated Fe, (2 ~ 6 mm) with weld projections |
| − | + | |Contacts for controls, ignition points and horns; arcing contacts in special relays | |
| − | | | + | |For change-over contact welded on both sides of carrier |
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Brazed contact tips |
| − | | | + | |All materials and dimensions, oxide and graphite containing materials with brazable backing, carrier parts from Fe, Cu and Cu alloys, at higher strength requirements also CuCrZr or CuBe |
| − | + | |Medium and higher load switching devices for power engineering | |
| − | + | |Braze alloy layer with low meting point, carriers may soften during brazing | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Clad contact materials (Contact Bimetals), totally covered or with inlayed strips |
| − | + | |Ductile precious metals on Cu and Cu alloys, minimum precious metal layer 2% of total strip thickness for Ag and Ag alloys, 0.5% of total strip thickness for Au alloys (with Ni intermediate layer), max. inlayed thickness 50% of total, strip width starting at 2 mm | |
| − | | | + | |Clad contact springs; stamped and formed parts for communications and power engineering; aluminum clad for bonding capability |
| − | + | |Metallurgical bond; inlayed strip stamped perpendicular or at angle to strip direction; avoid bends at the cladding edges | |
| − | Ag | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Strips or profiles with brazed contact material layers (Toplay material) |
| − | + | |Ag, Ag alloys, Ag/Ni, Ag/MeO on Cu and Cu alloy carriers, total width 10 ~ 100mm, carrier thickness 0.3 – 5 mm, Ag strip cross section from 0.3 x 3 mm<sup>2</sup>, strip thickn. to be ≤ carrier thickn. | |
| − | |Ag, Ag | + | |Stationary and moving contact bridges for power engineering switching devices |
| − | + | |Contact layers brazed with Ag brazing alloys; strips re-hardened during profile rolling | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Seam-welded contact strips or profiles |
| − | | | + | |Wire, strip, miniature profiles (solid or clad) welded to Cu alloy carrier strip (0.3 – 3 mm Ø or up to 5 mm width) |
| − | + | |Switches, pushbuttons, relays, auxiliary contactors, sliding contacts | |
| − | + | |Broad usability, highly economical, thin spring hard carriers can be used | |
| − | | | ||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Miniature profiles (Weld tapes) |
| − | | | + | |Mostly high precious contact materials, double or multi layer, Ni, Monel, or Cu alloy carrier; miniature-profile width 0.2 – 2 mm |
| − | + | |Welded profile segments for contact parts in communication, measurement and control engineering | |
| − | + | |Manufacturing of cross-directional contact spots; most economical precious metal usage | |
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 462: | Line 338: | ||
{| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px" | {| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! | + | !Contact Parts, Semi-finished Materials |
| − | ! | + | !Typical Contact Materials and Dimensions |
| − | ! | + | !Main Areas of Application |
| − | ! | + | !Remarks |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Clad profiles |
| − | |Ag, Ag | + | |Ag, Ag alloys, Ag/Ni, Ag/MeO, on Cu or Cu alloy carriers, all cross-sectional areas that can be drawn or rolled; Profile width: 2 ~ 10 mm |
| − | Cu | + | |Profile segments as contact areas for low and high voltage switching devices |
| − | + | |More complex shapes require costly tooling | |
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Sintered and infiltrated parts |
| − | | | + | |W-, WC-, Mo-based materials, in almost any contact shapes |
| − | + | |Contact parts for low and high voltage switching devices | |
| − | | | + | |Single parts pressing; mostly with weld projec- tions and braze alloy coating on underside |
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Formed arc erosion parts |
| − | |W/Cu | + | |W/Cu infiltration materials, parts in almost any shapes |
| − | + | |Arcing contacts for extreme duty switching devices, i.e. SF<sub>6</sub> circuit breakers | |
| − | | | + | |Attachment to Cu carriers by cast-on, percussion welding, electron-beam welding; rarely by brazing |
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Low gas content contact parts |
| − | |W/Cu-, WC/Ag-, CuCr- | + | |W/Cu-, WC/Ag-, CuCr-based materials, rings and discs in almost any shape |
| − | + | |Shaped contact parts for vacuum switches (contactors, power switches, circuit breakers) | |
| − | | | + | |Brazing to Cu carriers requires special brazing alloys |
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Cast-on contact parts |
| − | |W/Cu | + | |W/Cu cast on with Cu, shaped parts and rings up to 100 mm Ø |
| − | 100 | + | |Arcing contacts in high voltage switchgear |
| − | | | + | |Seamless bond interface, carriers get hardened through subsequent forming |
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Electron-beam welded contact parts |
| − | |W/Cu | + | |W/Cu on Cu or CuCrZr contact rods, tubes, tulips |
| − | + | |Arcing contacts in high voltage circuit breakers | |
| − | | | + | |Seamless bond interface, withstands high mechanical and thermal stresses |
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Silver electroplating |
| − | | | + | |Layer thickness up to 20 μm, mostly on Cu and Cu alloys |
| − | | | + | |Connecting areas and no-load switching contacts in power engineering; rotary switches, sliding contacts, connectors |
| − | + | |For switching contacts only under very low loads | |
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Gold electroplating |
| − | | | + | |Flash plating 0.1 – 0.2 μm on Ag alloys, and Cu alloys; contact layers 0.5 – 5 μm mostly with intermediate Ni layer |
| − | + | |Contacts with low current and voltage loads, connectors, rotary and sliding switches, contact areas on printed circuit boards | |
| − | Ni | + | |Flash plating only limited effective as corrosion resistant layer on silver contacts |
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Selectively electroplated strips |
| − | | | + | |Stripe coatings: Tin plating 1- 10 μm, Ag plating 1 – 20 μm, Au plating 0.2 – 5 μm; stripe width 2 mm min, stripe distance > 2 mm; carrier material: Cu and Cu alloys, Ni alloys, stainless steel; strip thickness: 0.1 ~ 1 mm; strip width: 5 ~ 100 mm |
| − | + | |Contact parts for connectors, keyboard switches, rotary and sliding switches; bondable areas (Au) for electronic components | |
| − | + | |Economic manufacturing for partially plated parts; hard gold with Ni intermediate layer possible but has limited formability | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Selectively electroplated pre-stamped strips, Spot gold plating |
| − | + | |Continuous partial electroplating of pre-stamped and coined contact spots; all | |
| − | | | + | precious metals; intermediate layers of Cu or Ni; selective tinning of connector contact areas and terminal ends; carrier materials up to 1 mm thick, strip width up to ~ 80 mm |
| − | + | |Precious metal plating of switching contacts, connector parts, and terminal pins in the communication technology | |
| − | + | |Crack-free and wear resistant layers possible since contact areas are already formed to final shape | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Sputtered profiles |
| − | |Au, Au | + | |Au, Au alloys in any composition; layer thickness 0.1 – 5 μm |
| − | + | |Contact profiles for relays, switches and keyboard contacts in the information and measuring technology | |
| − | + | |High purity contact layers for high reliability | |
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Hot-dip tinned strips |
| − | | | + | |All around or stripe tinning 1 ~ 15 μm |
| − | | | + | |Connectors for automotive and consumer technology; screw and crimp connectors |
| − | + | |Economic coating method; does not form (Sn) whiskers | |
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
</figtable> | </figtable> | ||
| Line 592: | Line 418: | ||
===<!--6.4.3-->Geschlossene Kontakte=== | ===<!--6.4.3-->Geschlossene Kontakte=== | ||
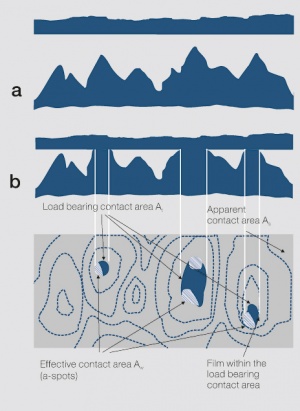
| + | <xr id="fig:Rough flat surface"/><!--Fig. 6.5:--> Raue ebene Oberfläche. a) vor und b) während der Berührung mit einer ideal glatten, ebenen Fläche; c) Darstellung der scheinbaren, tragenden und wirksamen Kontaktfläche (Maßstäbe willkürlich; gestrichelte Linien sind Höhenlinien) | ||
| + | |||
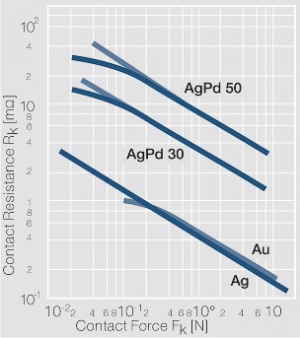
| + | <xr id="fig:Contact-resistance-of-crossed-rods"/><!--Fig. 6.6:--> Kontaktwiderstand gekreuzter Rundstäbe in Abhängigkeit von der Kontaktkraft für Gold, Silber und Silber-Palladium-Legierungen | ||
| + | <div class="multiple-images"> | ||
<figure id="fig:Rough flat surface"> | <figure id="fig:Rough flat surface"> | ||
| − | [[File:Rough flat surface.jpg|left|thumb| | + | [[File:Rough flat surface.jpg|left|thumb|Raue ebene Oberfläche. a) vor und b) während der Berührung mit einer ideal glatten, ebenen Fläche; c) Darstellung der scheinbaren, tragenden und wirksamen Kontaktfläche (Maßstäbe willkürlich; gestrichelte Linien sind Höhenlinien)]] |
</figure> | </figure> | ||
<figure id="fig:Contact-resistance-of-crossed-rods"> | <figure id="fig:Contact-resistance-of-crossed-rods"> | ||
| − | [[File:Contact-resistance-of-crossed-rods.jpg|left|thumb| | + | [[File:Contact-resistance-of-crossed-rods.jpg|left|thumb|Kontaktwiderstand gekreuzter Rundstäbe in Abhängigkeit von der Kontaktkraft für Gold, Silber und Silber-Palladium-Legierungen]] |
</figure> | </figure> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 610: | Line 440: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! | ! | ||
| − | ! | + | !Contact Materials |
| − | ! | + | !Thermo-electric Voltage (0 - 100°C) [mV] |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Pure metals |
|Ag<br />Au<br />Pt<br />Ir<br />Pd<br />Rh<br />Re<br />Cu<br />W<br />Mo | |Ag<br />Au<br />Pt<br />Ir<br />Pd<br />Rh<br />Re<br />Cu<br />W<br />Mo | ||
| + 0.04<br />+ 0.06<br />+ 0.78<br />+ 0.13<br />+ 1.35<br />+ 0.08<br />+ 0.78<br />0<br />- 0.46<br />- 0.73 | | + 0.04<br />+ 0.06<br />+ 0.78<br />+ 0.13<br />+ 1.35<br />+ 0.08<br />+ 0.78<br />0<br />- 0.46<br />- 0.73 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Alloys/Composite materials |
|AgCu 3<br />AgPd 30<br />AgPd 40<br />AgPd 50<br />AgPd 60<br />Ag/Ni 10<br />Ag/Ni 20<br />Ag/W 65<br />AuNi 5<br />AuAg 20<br />AuPt 10<br />PtW 5<br />Ptlr 10<br />Ptlr 20<br />PtRu 5<br />PtRu 10<br />PdCu 15<br />PdCu 40 | |AgCu 3<br />AgPd 30<br />AgPd 40<br />AgPd 50<br />AgPd 60<br />Ag/Ni 10<br />Ag/Ni 20<br />Ag/W 65<br />AuNi 5<br />AuAg 20<br />AuPt 10<br />PtW 5<br />Ptlr 10<br />Ptlr 20<br />PtRu 5<br />PtRu 10<br />PdCu 15<br />PdCu 40 | ||
| + 0.026<br />+ 0.125<br />+ 0.198<br />+ 0.321<br />+ 0.412<br />+ 0.23<br />+ 0.27<br />+ 0.01<br />+ 4.7<br />+ 2.76<br />+ 1.11<br />+ 0.67<br />+ 0.56<br />+ 0.60<br />+ 0.32<br />+ 0.13<br />+ 0.180<br />+ 0.247 | | + 0.026<br />+ 0.125<br />+ 0.198<br />+ 0.321<br />+ 0.412<br />+ 0.23<br />+ 0.27<br />+ 0.01<br />+ 4.7<br />+ 2.76<br />+ 1.11<br />+ 0.67<br />+ 0.56<br />+ 0.60<br />+ 0.32<br />+ 0.13<br />+ 0.180<br />+ 0.247 | ||
Revision as of 17:56, 25 September 2014
Contents
Anwendungsbereiche für schaltende Kontakte
Kleine und mittlere elektrische Last
Schaltvorgänge bei kleinen und mittleren elektrischen Lasten treten z.B. in Relais und Schaltern der Messtechnik, Informationstechnik, Kfz-Technik und Hausgerätetechnik auf. Die Schaltspannung liegt dabei üblicherweise zwischen μV und 400 V, der Schaltstrom zwischen μA und ca. 100 A.
siehe Artikle: Kleine und mittlere elektrische Last
Hohe elektrische Last
Bei hohen elektrischen Lasten, die überwiegend im Bereich der Energietechnik auftreten, sind die Schaltvorgänge weitgehend mit dem Auftreten von Lichtbögen verbunden. Die Beherrschung des Schaltlichtbogens ist in den meisten Anwendungen das zentrale Problem. Je nach Schaltgerätetyp stehen bestimmte Anforderungen im Vordergrund, nach denen die Wahl des Kontaktwerkstoffes erfolgt. Wie in der Informations- und Nachrichtentechnik sind dabei die Probleme zu berücksichtigen, die bei den Schaltvorgängen und der Stromführung auftreten.
siehe Artikle: Hohe elektrische Last
Werkstoffbestückung von Kontaktstellen
Eine hohe Kontaktzuverlässigkeit und hohe Lebensdauer von elektromechanischen Bauelementen und Schaltgeräten wird nur dann erreicht, wenn den Anforderungen entsprechend der optimale Kontaktwerkstoff und die geeignetste Kontaktform eingesetzt werden. Bei der Festlegung des Kontaktwerkstoffes und der technologischen Gestaltung der Kontaktstellen müssen allerdings auch wirtschaftliche Gesichtspunkte berücksichtigt werden. In der folgenden Tabelle (Table 1) sind anhand einiger Anwendungsbeispiele Vorschläge für die Wahl des Kontaktwerkstoffes und der Kontaktform aufgelistet.
| Type of Contacts or Devices | Characteristic Requirements for Contacts | Contact Material | Design Form of Contacts |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contacts for dry circuits | Reliable contacting at very low currents and voltages and mostly at also low contact forces |
AuAg alloys, (AuPt), Au | Contact rivets, welded miniature profiles (tapes), electroplated Au, sputtered Au layers |
| Switching contacts in measuring devices | Reliable switching at low voltages and currents at low contact forces | Au and Pt alloys, (AgPd alloys) | Contact rivets, welded tips, clad parts |
| Keyboard contacts | Defined contacting, close to bounce-free make, high reliability at low switching loads | Au alloys, (AgPd), Au on Ni substrate | Au plated snap discs, Au clad wires and stamped parts, hard gold electroplated contact spots on printed circuit boards |
| Rotary switches on printed circuit boards | Good frictional wear resistance, low contact résistance | Sliding track: hard gold on Ni substrate Slider: AgPd alloy, (Hard silver) | Electroplated coatings on slide tracks; clad, welded, or riveted stamping parts |
| Slip rings with high reliability | Low and consistent contact resistance at low contact forces | Brushes: Au alloys, AgPd, AgPdCu; Slip rings: Au alloys, Ag alloys (Rh); For higher currents: Ag/C brushes against Ag slip rings | Brush wires, stamped brushes; solid, clad, or electroplated slip rings, Ag/C formed parts |
| Sliding contacts in miniature motors | Very high frictional wear resistance, sure contacting even at very low contact forces | Ag and Au alloys, Pd alloys, Au multi component alloys | Brushes from flat rolled wire or stamped; collector hard gold electroplated or clad, or made from miniature profile segments |
| Centrifugal controllers for small motors | Little shape changes, defined contacting at very low contact forces and high frequency of operation | Pd alloys | Contact rivets, contact screws, welded parts |
| Connectors | Low contact resistance, corrosion resistance, sufficient frictional wear resistance, good sliding capabilities | Ag and Au alloys, Pd, PdNi; For automotive and consumer electronic at low operation numbers: Sn and Sn alloys | Electroplated layers or clad, often Au flash plated, mostly with Ni substrate layer, stamped parts from hot tin dipped strip |
| Telecommunication relays | Reliable contacting even at high operational frequency | Ag, AgPd, Au alloys, PdRu | Rivets, welded profile segments |
| Reed relay contacts | High reliability at low currents independent of atmospheric environment | Au, (Rh) | Switch paddles FeNi with partially diffused Au, (electroplated Rh) |
| Relays in electronic circuits | High reliability at low switching loads and compact device design | Au alloys, AgPd, Ag alloys | Stamped springs from seam-welded profiles, welded miniature profile (tape) segments, contact rivets |
| GP relais (Elementary relays) | Low arc erosion, high weld resistance, low and consistent contact resistance | Ag/Ni, Ag/SnO2, (Ag/CdO), Ag/ZnO,AgNi0.15, (Ag) | Solid and composite contact rivets, welded miniature profile (tape) segments |
| Automotive relays | Low material transfer, low contact resistance, high weld resistance | AgNi0.15, Ag/SnO2, Ag/Ni | Contact rivets, welded miniature profile (tape) segments |
| Flasher relays (automotive, > 3 Mio operations) | Low material transfer, high arc erosion resistance, low contact resistance | PdCu15 and 40 (Anode) vs. AgNi0.15, AgCu3 (Cathode), Ag/ZnO, Ag/SnO2 | Contact rivets, welded miniature profile (tape) and strip segments |
| Breaker points (automotive ignition) | Very high arc erosion resistance, high switching frequency | W | Tips or discs welded to formed parts or Fe supports |
| Automotive horn contacts | High arc erosion resistance at extremely high number of switching operations | W, Ag/SnO2 | Contact rivets, W weld buttons, springs or formed parts with brazed or welded tips |
| Appliance switches | Low contact resistance, reasonable arc erosion and weld resistance | AgNi0.15, Ag/Ni, Ag/SnO2, (Ag/CdO) | Contact rivets, welded contact parts |
| Temperature controllers (Thermostats) | Defined contacting point even at slow motion make, high operating temperatures | AgNi0.15, Ag/Ni, Ag/SnO2, (Ag/CdO) | Contact rivets, welded contact parts, weld buttons |
| Wiring devices (Light switches) | Low contact resistance, reasonable arc erosion and weld resistance | AgNi0.15, AgCu, Ag/Ni, with make peaks also Ag/ZnO, (Ag/CdO) | Contact rivets, welded contact parts |
Table 1: Werkstoffbestückung von Kontaktteilen (Fortsetzung)
| Type of Contacts or Devices | Characteristic Requirements for Contacts | Contact Material | Design Form of Contacts |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automatic staircase lighting switches | High arc erosion and weld resistance | Ag/Ni, Ag/SnO2, (Ag/CdO), Ag/C against Ag/SnO2 | Rivets, welded contact parts |
| Miniature Circuit breakers | Extremely high weld resistance, low temperature rise in use, sufficient arc erosion resistance | I< 50 A: Ag/C97/3 (Cu/C) against Cu, I> 50 A : Ag/C97/3 o. 95/5 against AgCu3, Ag/Ni90/10 o. 80/20, Ag/W, Ag/WC (USA) | Welded contact parts (Ag/C), clad stamped parts |
| Fault current circuit breakers | Extremely high weld resistance, low contact resistance, high arc erosion resistance | Stationary contact: Ag/C96/4 o. 95/5 Movable contact: Ag/Ni, Ag/MeO, Ag/W, Ag/WC, Ag/WC/C | Welded and brazed contact parts |
| Micro snap switches | Low contact resistance, no sticking during make operation | AgNi 0,15, Ag/Ni, Ag/SnO2, (Ag/CdO) | Rivets, clad or welded contact parts |
| Control and auxiliary switches | Low contact resistance over extended life span | Ag, AgNi 0,15, AgCu, Ag/Ni | Rivets, clad stamped parts, (gold plated rivets), welded contact parts |
| Auxiliary and control relays | High reliability over extended life span, low contact resistance | AgNi 0,15, Ag/Ni | Rivets, clad profile parts, welded contact parts |
| Cam switches (higher loads) | High arc erosion and weld resistance, low contact resistance | AgCu, Ag/Ni, Ag/SnO2, Ag/ZnO, (Ag/CdO) | Rivets, welded contact parts |
| Contactors | High arc erosion and weld resistance, low contact resistance | I< 20A : Ag/Ni, Ag/SnO2 I>20A : Ag/SnO2, (AgCdO) | Welded and brazed contact tips |
| Motor -protective circuit breakers | Extremely high weld resistance, low contact resistance | Ag/ZnO, Ag/C against Ag/Ni | Welded contact parts, toplay stamping parts |
| Power switches and circuit breakers | Extremely high arc erosion and weld resistance, low contact resistance | Ag/ZnO, Ag/SnO2 , Ag/C against Ag/Ni o. Ag/W, Ag/W, Ag/WC/C, Ag/W against Ag/CdO | Brazed and welded contact tips and formed parts |
| Power switches with arcing and main contacts | High weld resistance, low contact resistance, high arc erosion resistance | Arcing contacts: W/Ag, W/Cu, (Cu) Main contacts: Ag/Ni, Ag/ZnO, Ag/W, Ag/WC | Brazed and welded contact tips and formed parts |
| Disconnect switches | Low contact resistance, sufficient mechanical strength | AgNi 0,15, Ag/Ni, Ag (electroplated) | Electroplated coatings, brazed contact parts |
| High voltage circuit breakers | Arcing contacts: highest arc erosion resistance Main contacts: low contact resistance | Arcing contacts: W/Cu-infiltrated Main contact CuCrZr silver plated, | Cast-on, electron-beam welded (or brazed) formed parts, percussion welded pins |
| Load disconnect switches (medium and high voltage) | Low contact resistance, sufficient mechanical strength, high arc erosion resistance of precontacts | Arcing contact: W/Cu, Cu, Ag/C Main contact: Cu, CuCrZr silver plated, Ag/Ni, AgNi0,15, Ag/C | Arcing contacts: brazed or welded parts Main contacts: silver plated, brazed or welded parts |
| Vacuum contactors | Low chopping current, high arc erosion resistance, low contact resistance | Low gas content W/Cu, W/CuSb, WC/Ag, CuCr | Contact discs, shaped rings |
| Vacuum circuit breakers | High switching capacity, low contact resistance | Low gas content CuCr | Contact discs |
| Transformer tab changers | High arc erosion resistance in oil environment | W/Cu in filtrated with approx. 70% | Brazed contact tips |
| Disconnect switches in high voltage circuits | Low contact resistance, low mechanical wear, sufficient arc erosion resistance during current commutation | Ag (electroplated), AgNi0,15, Ag/SnO2 | Electroplated coatings, brazed parts, Toplay profile segments |
Anmerkungen: Table 1 soll Hinweise geben, welche Kontaktwerkstoffe grundsätzlich für den jeweiligen Gerätetyp eingesetzt werden. Bei den aufgeführten Kontaktwerkstoffen wurde teilweise bewusst auf die Angabe der genauen Zusammensetzung und, wie bei Ag/SnO2 und Ag/ZnO, der Art der Zusätze verzichtet, da eine endgültige Werkstofffestlegung auch von spezifischen konstruktiven Gegebenheiten des Gerätes abhängt. Hinweise auf spezielle Eigenschaften der Kontaktwerkstoffe sind aus Kap. 2 Kontaktwerkstoffe für die Elektrotechnik zu entnehmen.
Technologische Gestaltung von Kontaktstellen
Für die Herstellung von Kontaktteilen steht eine große Vielfalt an Technologien zur Verfügung (Kap. 3 Technologien für die Herstellung von Kontaktteilen). Die gewünschte Kontaktform setzt allerdings bestimmte Werkstoffeigenschaften z.B. Umform-, Schweißbarkeit usw. voraus, die nicht von allen Kontaktwerkstoffen gleich gut erfüllt werden. Darüber hinaus muss die Gestaltung der Kontaktstelle auf die Beanspruchung im jeweiligen Schaltgerät abgestimmt werden. Die nachfolgende Tabelle (Table 2) stellt eine Verknüpfung von Kontaktteil, Kontaktwerkstoff und Anwendung dar.
| Contact Parts, Semi-finished Materials | Typical Contact Materials and Dimensions | Main Areas of Application | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contact rivets solid, inserted wire segments | Ag, Ag alloys, Au alloys, Pd alloys, Ag/Ni, Ag/C97/3, Ag/MeO (1.2 – 8 mm Ø) | All types of switches in the communications, automotive, or power distribution technology simple contact component, universally applied, selection through economic aspects | Secure rivet attachment only with sufficiently thick shank (shank Ø = 1⁄2 head Ø); change-over contacts by forming secondary head from longer shanks |
| Contact rivets, clad (Composite Rivets) | Ag, Ag alloys, Ag/Ni, Ag/MeO on Cu base (2 ~ 10 mm Ø) | All types of switches in the communications, automotive, or power engineering | Secure rivet attachment only with sufficiently thick shank (shank Ø = 1⁄2 head Ø) |
| Contact rivets with brazed surface layer | Tungsten and difficult to form powder metallurgical materials (i.e. Ag/C) on Cu or Fe bases (1 ~ 12 mm Ø) | Switches for power engineering, W layers mostly for controls | Tungsten contact to be staked (riveted) with moderate force or using orbital riveting; for Fe bases also warm-forming |
| Contact screws | Any contact material on Fe and CuZn screws, brazed, (1 ~ 10 mm Ø, M 2 ~ M 10) | Adjustable contacts for controls and horns | During brazing carrier may get soft |
| Vertically welded wire segments | Ag, Ag alloys, Ag/Ni, AgPd, Au alloys (wire 0.6 ~ 5 mm Ø) | Contact parts for control functions and power engine- ering; economical manufacturing at higher quantities | Welding and subsequently heading or orbital forming of head shape |
| Horizontally welded wire and profile segments | Au alloys, Pd alloys, Ag, Ag alloys, Ag/Ni, Ag/MeO, Ag/C in strip or profile form, Miniature profiles - also multi-layered (profile width 0.2 ~ 5 mm) | Contact parts for communication, measurement, controls and power engineering; very economical with respect to precious metal usage | Welding synchronized to stamping / forming on special equipment |
| Weld buttons | Ag, Ag alloys, Ag/Ni, Ag/MeO on Steel, Ni, Monel; Ag/W, Ag/Mo (1.5 ~ 10 mm Ø) | Welded for example to steel springs or thermostatic bimetals for temperature controls | Metallurgical bond through simple projection welding remains strong in temperature cycling applications |
| Tungsten weld buttons | W on Ni or Ni-plated Fe, (2 ~ 6 mm) with weld projections | Contacts for controls, ignition points and horns; arcing contacts in special relays | For change-over contact welded on both sides of carrier |
| Brazed contact tips | All materials and dimensions, oxide and graphite containing materials with brazable backing, carrier parts from Fe, Cu and Cu alloys, at higher strength requirements also CuCrZr or CuBe | Medium and higher load switching devices for power engineering | Braze alloy layer with low meting point, carriers may soften during brazing |
| Clad contact materials (Contact Bimetals), totally covered or with inlayed strips | Ductile precious metals on Cu and Cu alloys, minimum precious metal layer 2% of total strip thickness for Ag and Ag alloys, 0.5% of total strip thickness for Au alloys (with Ni intermediate layer), max. inlayed thickness 50% of total, strip width starting at 2 mm | Clad contact springs; stamped and formed parts for communications and power engineering; aluminum clad for bonding capability | Metallurgical bond; inlayed strip stamped perpendicular or at angle to strip direction; avoid bends at the cladding edges |
| Strips or profiles with brazed contact material layers (Toplay material) | Ag, Ag alloys, Ag/Ni, Ag/MeO on Cu and Cu alloy carriers, total width 10 ~ 100mm, carrier thickness 0.3 – 5 mm, Ag strip cross section from 0.3 x 3 mm2, strip thickn. to be ≤ carrier thickn. | Stationary and moving contact bridges for power engineering switching devices | Contact layers brazed with Ag brazing alloys; strips re-hardened during profile rolling |
| Seam-welded contact strips or profiles | Wire, strip, miniature profiles (solid or clad) welded to Cu alloy carrier strip (0.3 – 3 mm Ø or up to 5 mm width) | Switches, pushbuttons, relays, auxiliary contactors, sliding contacts | Broad usability, highly economical, thin spring hard carriers can be used |
| Miniature profiles (Weld tapes) | Mostly high precious contact materials, double or multi layer, Ni, Monel, or Cu alloy carrier; miniature-profile width 0.2 – 2 mm | Welded profile segments for contact parts in communication, measurement and control engineering | Manufacturing of cross-directional contact spots; most economical precious metal usage |
Table 2: Technologische Gestaltung von Kontaktstellen (Fortsetzung)
| Contact Parts, Semi-finished Materials | Typical Contact Materials and Dimensions | Main Areas of Application | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clad profiles | Ag, Ag alloys, Ag/Ni, Ag/MeO, on Cu or Cu alloy carriers, all cross-sectional areas that can be drawn or rolled; Profile width: 2 ~ 10 mm | Profile segments as contact areas for low and high voltage switching devices | More complex shapes require costly tooling |
| Sintered and infiltrated parts | W-, WC-, Mo-based materials, in almost any contact shapes | Contact parts for low and high voltage switching devices | Single parts pressing; mostly with weld projec- tions and braze alloy coating on underside |
| Formed arc erosion parts | W/Cu infiltration materials, parts in almost any shapes | Arcing contacts for extreme duty switching devices, i.e. SF6 circuit breakers | Attachment to Cu carriers by cast-on, percussion welding, electron-beam welding; rarely by brazing |
| Low gas content contact parts | W/Cu-, WC/Ag-, CuCr-based materials, rings and discs in almost any shape | Shaped contact parts for vacuum switches (contactors, power switches, circuit breakers) | Brazing to Cu carriers requires special brazing alloys |
| Cast-on contact parts | W/Cu cast on with Cu, shaped parts and rings up to 100 mm Ø | Arcing contacts in high voltage switchgear | Seamless bond interface, carriers get hardened through subsequent forming |
| Electron-beam welded contact parts | W/Cu on Cu or CuCrZr contact rods, tubes, tulips | Arcing contacts in high voltage circuit breakers | Seamless bond interface, withstands high mechanical and thermal stresses |
| Silver electroplating | Layer thickness up to 20 μm, mostly on Cu and Cu alloys | Connecting areas and no-load switching contacts in power engineering; rotary switches, sliding contacts, connectors | For switching contacts only under very low loads |
| Gold electroplating | Flash plating 0.1 – 0.2 μm on Ag alloys, and Cu alloys; contact layers 0.5 – 5 μm mostly with intermediate Ni layer | Contacts with low current and voltage loads, connectors, rotary and sliding switches, contact areas on printed circuit boards | Flash plating only limited effective as corrosion resistant layer on silver contacts |
| Selectively electroplated strips | Stripe coatings: Tin plating 1- 10 μm, Ag plating 1 – 20 μm, Au plating 0.2 – 5 μm; stripe width 2 mm min, stripe distance > 2 mm; carrier material: Cu and Cu alloys, Ni alloys, stainless steel; strip thickness: 0.1 ~ 1 mm; strip width: 5 ~ 100 mm | Contact parts for connectors, keyboard switches, rotary and sliding switches; bondable areas (Au) for electronic components | Economic manufacturing for partially plated parts; hard gold with Ni intermediate layer possible but has limited formability |
| Selectively electroplated pre-stamped strips, Spot gold plating | Continuous partial electroplating of pre-stamped and coined contact spots; all
precious metals; intermediate layers of Cu or Ni; selective tinning of connector contact areas and terminal ends; carrier materials up to 1 mm thick, strip width up to ~ 80 mm |
Precious metal plating of switching contacts, connector parts, and terminal pins in the communication technology | Crack-free and wear resistant layers possible since contact areas are already formed to final shape |
| Sputtered profiles | Au, Au alloys in any composition; layer thickness 0.1 – 5 μm | Contact profiles for relays, switches and keyboard contacts in the information and measuring technology | High purity contact layers for high reliability |
| Hot-dip tinned strips | All around or stripe tinning 1 ~ 15 μm | Connectors for automotive and consumer technology; screw and crimp connectors | Economic coating method; does not form (Sn) whiskers |
Formeln und Regeln
Begriffe
siehe Artikel: Begriffe
Formeln aus der Kontaktphysik
Main Artikel: Formeln aus der Kontaktphysik
Geschlossene Kontakte
Figure 1 Raue ebene Oberfläche. a) vor und b) während der Berührung mit einer ideal glatten, ebenen Fläche; c) Darstellung der scheinbaren, tragenden und wirksamen Kontaktfläche (Maßstäbe willkürlich; gestrichelte Linien sind Höhenlinien)
Figure 2 Kontaktwiderstand gekreuzter Rundstäbe in Abhängigkeit von der Kontaktkraft für Gold, Silber und Silber-Palladium-Legierungen
| Contact Materials | Thermo-electric Voltage (0 - 100°C) [mV] | |
|---|---|---|
| Pure metals | Ag Au Pt Ir Pd Rh Re Cu W Mo |
+ 0.04 + 0.06 + 0.78 + 0.13 + 1.35 + 0.08 + 0.78 0 - 0.46 - 0.73 |
| Alloys/Composite materials | AgCu 3 AgPd 30 AgPd 40 AgPd 50 AgPd 60 Ag/Ni 10 Ag/Ni 20 Ag/W 65 AuNi 5 AuAg 20 AuPt 10 PtW 5 Ptlr 10 Ptlr 20 PtRu 5 PtRu 10 PdCu 15 PdCu 40 |
+ 0.026 + 0.125 + 0.198 + 0.321 + 0.412 + 0.23 + 0.27 + 0.01 + 4.7 + 2.76 + 1.11 + 0.67 + 0.56 + 0.60 + 0.32 + 0.13 + 0.180 + 0.247 |
Schaltende Kontakte
siehe Artikel: Schaltende Kontakte
Physikalische Effekte bei Gleit- und Steckkontakten
siehe Artikel: Physikalische Effekte bei Gleit- und Steckkontakten
Faustregeln für die Kontaktdimensionierung
siehe Artikel: Faustregeln für die Kontaktdimensionierung
Berechnung von Kontaktfedern
siehe Artikel: Berechnung von Kontaktfedern
Referenzen
Vinaricky, E. (Hrsg): Elektrische Kontakte-Werkstoffe und Anwendungen. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg 2002
Schröder, K.-H.: Grundlagen der Werkstoffauswahl für elektrische Kontakte. Buchreihe „Kontakt & Studium“, Band 366:zit. in „Werkstoffe für elektrische Kontakte und ihre Anwendungen“, Expert Verlag, Renningen, Bd. 366, (1997) 1-30
Horn, J.: „Steckverbinder“. zit. in Vinaricky, E. (Hrsg): „Elektrische Kontakte- Werkstoffe und Anwendungen“, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg 2002, 401- 419
Holm, R.: Electric Contacts, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York 1967
Sauer, H. (Hrsg): Relais-Lexikon. 2. Aufl. Hüthig-Verlag, Heidelberg 1985
Greenwood J.A.: Constriction Resistance and the Area of Contact, Brit.J.Appl.Phys. 17 (1966) 1621
Biefer, H.: Elektrische Kontakte, Technische Rundschau (Bern) (1954/10) 17
Thielecke, K.: Anwendung von Kontakten in Schwachstromschaltern, in “Kontaktwerkstoffe in der Elektrotechnik”, Akademie-Verlag Berlin 1962, 107
Kirchdorfer, J.: Schalter für elektrische Steuerkreise, Blaue TR-Reihe, Heft 91, Verlag Hallwag, Bern und Stuttgart 1969