Schaltende Kontakte
Schaltende Kontakte
- Effekte bei Schaltvorgängen
- Einfluss von Kunststoffausgasungen
- Einfluss von Schadgasen auf den Kontaktwiderstand
- Contact Phenomena under the influence of arcing Matertia
- Material transfer
- Arc erosion
- Contact welding
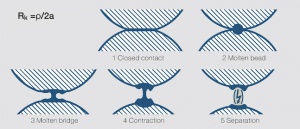
Figure 1 Kontaktöffnung unter Lichtbogenbildung (schematisch)
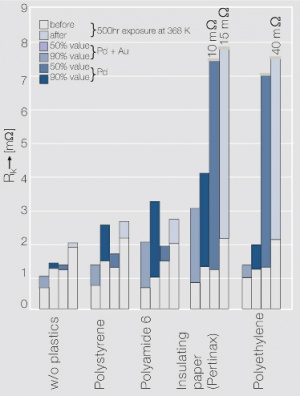
Figure 2 Histogramm des Kontaktwiderstandes RK einer galvanischen Palladiumschicht (3 μm) mit und ohne Hartgoldflash (0,2 μm) bei Auslagerung mit verschiedenen Kunststoffen
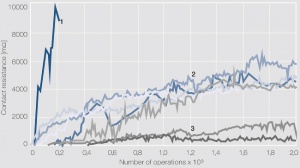
Figure 3 Kontaktwiderstand und Ausgasungen aus Kunststoffen in Abhängigkeit von der Schaltspielzahl bei 6 VDC , 100 mA: 1 silikonhaltiger Kunststoff; 2 Kunststoffe mit stark ausgasenden Komponenten; 3 Kunststoffe mit minimaler Ausgasung
Figure 4 Distribution of cumulative frequency H of the contact resistance for solid contact rivets after 10 days exposure in a three-component test environment with 400 ppb each of H2S, SO2 and NO2 at 25°C, 75% RH; Contact force 10cN; Measuring parameters: ≤ 40 mVDC,10 mA; Probing contact: Gold rivet
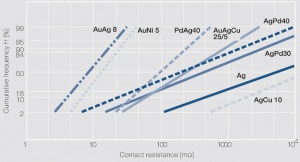
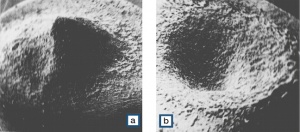
Figure 5 Material transfer under DC load a) Cathode; b) Anode.
Material: AgNi0.15; Switching parameters: 12VDC, 3 A, 2x106 operations
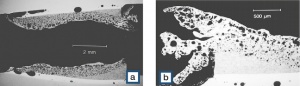
Figure 6 Arc erosion of a Ag/SnO2 contact pair after extreme arcing conditions a) Overall view; b) Partial detail view
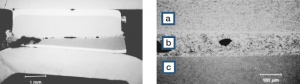
Figure 7 Micro structure of a welded contact pair (Ag/SnO288/12 - Ag/CdO88/12) after extremely high current load. a) Ag/SnO288/12; b) Ag/CdO88/12