Physical Effects in Sliding and Connector Contacts
From Electrical Contacts
Revision as of 15:52, 1 April 2014 by Doduco Redaktion (talk | contribs) (→6.4.5 Physical Effects in Sliding and Connector Contacts)
6.4.5 Physical Effects in Sliding and Connector Contacts
- Mechanical wear of sliding contacts
| dV/dx = k x FK /3 HW |
| dV/dx Wear volume in mm3 per slide path length in mm |
| k Coefficient of frictional wear |
| HW Hardness of the softer material (Brinell or Vickers units) |
| FK Contact force in cN |
| Wear coefficient k during material transfer |
| Silver – Silver 120 x 10-4 |
| Platinum – Platinum 400 x 10-4 |
| Silver – Platinum 1.3 x 10-4 |
| Coefficient of fractional wear k during wear loss |
| Silver – silver 8 x 10-4 |
| Gold – gold 9 x 10-4 |
| Platinum – platinum 40 x 10-4 |
| Silver – gold 9 x 10-4 |
| Silver – platinum 5 x 10-4 |
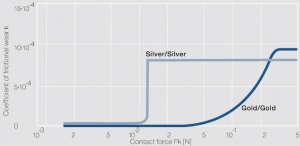
Fig. 6.15: Coefficient of frictional wear for the wear loss of sliding contacts Silver/Silver and hard gold/hard gold as a function of the contact force
- Contact behavior of connectors
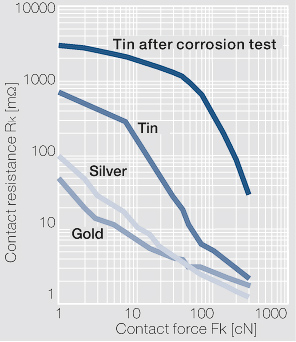
Fig. 6.16: Contact resistance R as a function k of the contact force F for different surface k coating materials. Measured against a spherical gold probe; I = 10 mA, U < 20 mV
Fig. 6.17: Contact resistance R as a function k of the fretting wear cycles for different surface coating materials
Tab.6.4: Surface Coating Materials for Connectors