Difference between revisions of "Precious Metal Powders and Preparations"
(→Precious Metal Powders) |
(→Precious Metal Powders) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
The measured densities of powders – both, the apparent density and the tap density – are low compared to the wrought metals because of the gaps between the particles. They vary in a wide range between 0.5 and 6 g/cm3 depending on the morphology of the particles and their tendency to agglomeration. Precious metal powders can be compacted by pressing and then sintered; a certain amount of porosity is however always retained. | The measured densities of powders – both, the apparent density and the tap density – are low compared to the wrought metals because of the gaps between the particles. They vary in a wide range between 0.5 and 6 g/cm3 depending on the morphology of the particles and their tendency to agglomeration. Precious metal powders can be compacted by pressing and then sintered; a certain amount of porosity is however always retained. | ||
| − | <figure id="fig:Different shapes of silver powders"> | + | <figure id="fig:Different shapes of silver powders"> |
[[File:Different shapes of silver powders.jpg|right|thumb|Different shapes of silver powders a) spherical b) rounded crystal applomerates]] | [[File:Different shapes of silver powders.jpg|right|thumb|Different shapes of silver powders a) spherical b) rounded crystal applomerates]] | ||
</figure> | </figure> | ||
Revision as of 12:34, 30 April 2014
Contents
Precious Metal Powders
Precious metal powders are used as raw materials for many technical products as well as for medical and decorative applications. Among these are the manufacture of composite silver materials for electrical contacts (Ag/Ni, Ag/metal oxides, Ag/C, Ag/W, etc), catalysts, electrodes, or dental products. Besides these precious metal powders are used as the base material in preparations as well as conductive paints and adhesives.
Precious metal powders consist of small particles of approx. 1 – 100 µm diameter which distinguish themselves by particle shape, particle size and particle size distribution. Depending on the manufacturing process, silver particles may be spherical, crystalline, or dentritic. Smaller particle size typically leads to a larger surface area.
The measured densities of powders – both, the apparent density and the tap density – are low compared to the wrought metals because of the gaps between the particles. They vary in a wide range between 0.5 and 6 g/cm3 depending on the morphology of the particles and their tendency to agglomeration. Precious metal powders can be compacted by pressing and then sintered; a certain amount of porosity is however always retained.
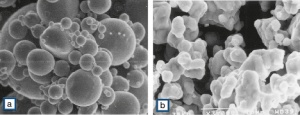
Precious metal powders are produced by various methods, such as for example electrolysis, atomizing from the molten phase, chemical precipitation, or by cementation with non-precious metals. Depending on the manufacturing process silver powders – as the by far largest volume precious metal powder used – have different properties as shown in Table 1 (Tab. 8.1) and Table 2.12 (Tab. 2.12). Atomizing from a melt results in a powder with high tap density composed of spherical particles. Using electrolytic deposition from a silver salt solution creates randomly shaped dentritic to crystalline particle structures. Chemical processes can result in rather fine particles with a large specific surface area. Figure 1 Fig. 8.1 shows typical SEM photo-graphs of atomized silver powder in spherical shapes (a) and a cementation powder composed of rounded crystal agglomerates (b).
Powder type | GE | GN1 | ES | V |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Manufacturing Process | chemical | chemical | electrolytic | atomized |
Particle shape | agglomerated | agglomerated | dentritic | spherical |
Avg. particle diameter (median) [µm] | 10 - 15 | 20 - 40 | - | 32 - 60 |
Medium particle size (FSS - Fisher Sub Sieve Size) [µm] | - | - | 4.0 - 6.0 | - |
Tap density (DIN/ISO 3953) [g/cm3] | 0.7 - 1.1 | 2.0 - 2.5 | 2.0 - 3.0 | 4.0 - 6.7 |
Specific surface area (B.E.T.) [m2/g] | 0.5 - 0.9 | - | - | - |
Precious Metal Preparations
While in the past mostly glass ware and ceramics (table china) were coated for decorative purposes with gold or platinum, precious metals have since quite a few years been applied to non-metallic substrates such as ceramics, glass, or plastics to make their surfaces electrically conductive. To coat these surfaces fine powders of the precious metal are dispersed in a carrier containing a paint basis and organic solvents. Such preparations can be applied by screen or tampon printing, by spraying, immersion, or with a paint brush.
Precious Metal Firing Preparations
The firing preparations in liquid or paste form are widely used in electrical and electronic engineering and especially in the thick-film technology Table 2 (Table 8.2). The precious metal filler material is mostly pure silver because of its high electrical conductivity. During firing in an oxidizing atmosphere at temperatures between 400 and 850°C a well adhering and highly conductive surface layer is formed. When utilizing screen printing techniques any shapes of conductive patterns can be created Figure 2 (Fig. 8.2) resulting in conductive paths with good electrical properties and high temperature stability.
Preparation | Substrate Material | Application by | Firing Temperature [°C] | Properties | Silver Content [wt%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Argonor N92 | glass, ceramics | paint brush, spray gun | 530 - 650 | Viscosity 500 – 1.000 mPa·s, good solderability | 65 |
Argonor | glass, ceramics | screen printing | 530 - 650 | Viscosity 10 – 15.000 mPa·s, good solderability | 65 |
Conductive Paints and Adhesives
Conductive paints are precious metal preparations in liquid or paste form. They contain the metal filler material, fine silver particles as conductive pigments mostly in flake form, a paint compound on artificial resin basis, and an organic solvent Table 3 (Table 8.3). The solvent evaporates during drying in air or by aging at slightly elevated temperatures. This allows the silver particles to connect metallically and form conductive paths Figure 3 (Fig. 8.3).
Conductive adhesives are used mostly for mechanical bonding with low thermal impact. As the adhesive components high-polymer organic substances such as epoxy resins and mixed polymers are mostly used. They are made electrically filler materials such as flake shaped silver powders (70 – 80 wt%). Silver based conductive adhesives are available as single or two component adhesive systems. Both types are hardening without the application of pressure.
| Preparation | Substrate Material |
Application by | Drying [°C] |
Properties | Usage Amount [g/100 cm2] |
Area Resistance [Ω/m2] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AROMAL 38 | glass, plastics | spraying, immersion, paint brush |
RT, 30 min 100°C |
hard well conducting Ag layer for broad applications |
0.5 - 2 | < 0.1 |
| AROMAL 50 | glass, wax, plastics | spraying, immersion, paint brush |
10 min RT |
very flat surface, especially for electrolytic build-up |
0.5 - 2 | < 0.2 |
| AROMAL 70T | plastics | tampon printing | 60 min RT |
hard and well conductive coating | < 0.1 | |
| AROMAL 141 | plastics, paper- based plastics |
screen printing | 45 min 120°C |
mechanically very strong coatings |
< 0.05 | |
| AROMAL 170 | plastics | screen printing | 30 min 100°C |
flexible layers, well suited for foil materials |
< 0.05 | |
| AROMAL K 5 A+B | metal, glass | dispenser, screen printing |
24h RT, 3h 80°C |
mechanically very strong bond connection as alternative to soldering |
< 0.1 | |
| AROMAL K 20 | metal, plastics, ceramics |
dispenser, screen printing |
15 min 150°C |
flexible bonds which help decrease thermal stresses |
< 0.1 | |
| DOSILAC | Silver conductive paints in spray cans; can be spray painted; properties similar to those of AUROMAL 50 | |||||
Conductive paints and adhesives have broad applications in electrical and electronic engineering. They are used for example for the contacting of film resistors, mounting of terminal wires, conducting electrostatic electricity, or contacting components at low temperatures.
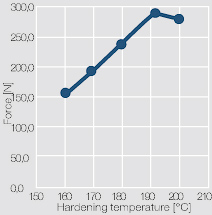
The mechanical strength of the bond connections depends mostly on the selected hardening temperature Figure 4 (Fig. 8.4).
Precious Metal Flakes
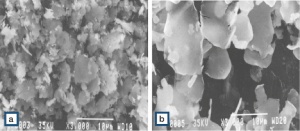
To obtain certain desired physical properties of preparations the dispersed precious metals in flat flake-like particles (generally called “flakes”) are needed. These are produced by milling fine metal powders in the presence of milling additives or agents. The properties of these metal flakes, i.e. silver flakes (ability to disperse easily, flow characteristics, electrical conductivity) are strongly dependent on the particle shape and size as well as on the type of milling agents used. Figure 5 Fig. 8.5 illustrates through SEM photos a type of rather fine silver flake (medium particle size 4 – 6 µm) (a) and another one with relatively large flat but thin flake shapes (particle size 8 – 11 µm) (b). Typical commercial silver flake types are listed with their respective properties in Table 4 (Tab. 8.4). Gold and platinum can also be produced as powder flakes. By volumes used they are however of lesser commercial importance.
| Type of Flake | F56 | B190 | ES4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Main characteristics | Low tap density | Very fine | Pure, wide grain size distribution |
| Silver content [wt%] | > 99.0 | > 99.0 | > 99.7 |
| Med. Grain size [μm] Tap density | 3 - 8 | 4 - 6 | 9 - 13 |
| DIN/ISO 3953 [g/cm3] | 0.7 - 1.1 | 2.1 - 2.7 | 2.7 - 3.6 |
| Spec. Surface area B.E.T. [m2/g] | 0.7 - 1.1 | 0.3 - 0.7 |