Difference between revisions of "Switching Contacts"
(→6.4.4 Switching Contacts) |
(→6.4.4 Switching Contacts) |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
*'''Influence of out-gasing from plastics''' | *'''Influence of out-gasing from plastics''' | ||
| − | Fig. 6.9: | + | |
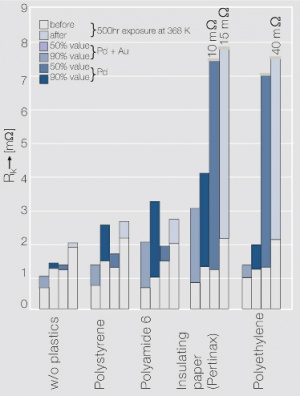
| − | Histogram of the contact | + | <xr id="fig:fig6.9"/> Fig. 6.9: Histogram of the contact resistance Rk of an electroplated palladium layer (3 μm) with and without hard gold flash plating (0.2 μm) after exposure with different plastic materials |
| − | resistance R of an electroplated | + | |
| − | palladium layer (3 μm) with and | + | <div class="multiple-images"> |
| − | without hard gold flash plating | + | <figure id="fig:fig6.9"> |
| − | (0.2 μm) after exposure with | + | [[File:Histogram of the contact resistance Rk.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Histogram of the contact resistance R<sub>K< /sub> of an electroplated palladium layer (3 μm) with and without hard gold flash plating (0.2 μm) after exposure with different plastic materials</caption>]] |
| − | different plastic materials | + | </figure> |
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div class="clear"></div> | ||
Fig. 6.10: Contact resistance with exposure to out-gasing from plastics as a function of numbers of | Fig. 6.10: Contact resistance with exposure to out-gasing from plastics as a function of numbers of | ||
Revision as of 13:41, 1 April 2014
6.4.4 Switching Contacts
- Effects during switching operations
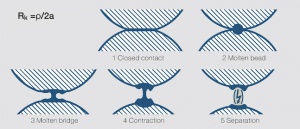
Figure 1 Fig. 6.7: Contact opening with arc formation schematic
- Influence of out-gasing from plastics
Figure 2 Fig. 6.9: Histogram of the contact resistance Rk of an electroplated palladium layer (3 μm) with and without hard gold flash plating (0.2 μm) after exposure with different plastic materials
Fig. 6.10: Contact resistance with exposure to out-gasing from plastics as a function of numbers of operations at 6 V ,100 mA: 1 Silicon containing plastic; 2 Plastics with strongly out-gasing DC components; 3 Plastics with minimal out-gasing components
- Influence of corrosive gases on the contact resistance
Fig. 6.11: Distribution of cumulative frequency H of the contact resistance for solid contact rivets after 10 days exposure in a three-component test environment with 400 ppb each of H2S, SO2 and NO2 at 25°C, 75% RH; Contact force 10cN; Measuring parameters: ≤ 40 mVDC,10 mA; Probing contact: Gold rivet
Fig. 6.8: Influences on contact areas in relays
- Contact Phenomena under the influence of arcing Matertia
- Material transfer
Fig. 6.12: Material transfer under DC load a) Cathode; b) Anode. 6 Material: AgNi0.15; Switching parameters: 12VDC, 3 A, 2x10 operations
- Arc erosion
Fig. 6.13 Arc erosion of a Ag/SnO2 contact pair after extreme arcing conditions a) Overall view; b) Partial detail view
- Contact welding
Fig. 6.14: Micro structure of a welded contact pair (Ag/SnO2 88/12 - Ag/CdO88/12) after extremely high current load. a) Ag/SnO2 88/12; b) Ag/CdO88/12