Difference between revisions of "Physical Effects in Sliding and Connector Contacts"
From Electrical Contacts
Doduco Admin (talk | contribs) (→Physical Effects in Sliding and Connector Contacts) |
Doduco Admin (talk | contribs) (→Physical Effects in Sliding and Connector Contacts) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
===<!--6.4.5-->Physical Effects in Sliding and Connector Contacts=== | ===<!--6.4.5-->Physical Effects in Sliding and Connector Contacts=== | ||
| − | + | '''Mechanical wear of sliding contacts''' | |
<table class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size:12px;width:40%"> | <table class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size:12px;width:40%"> | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
| − | + | '''Contact behavior of connectors''' | |
<div class="multiple-images"> | <div class="multiple-images"> | ||
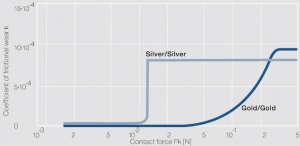
| + | [[File:Coefficient of frictional wear for the wear loss of sliding contacts Silver Silver.jpg|left|thumb|Figure 1: Coefficient of frictional wear for the wear loss of sliding contacts Silver/Silver and hard gold/hard gold as a function of the contact force]] | ||
| + | |||
<figure id="fig:Contact resistance Rk as a function of the contact force Fk"> | <figure id="fig:Contact resistance Rk as a function of the contact force Fk"> | ||
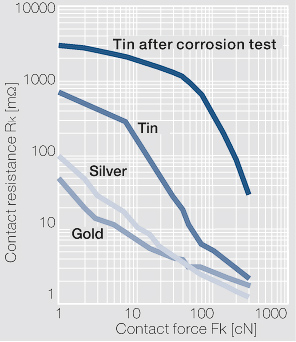
| − | [[File:Contact resistance Rk as a function of the contact force Fk.jpg|left|thumb|Figure | + | [[File:Contact resistance Rk as a function of the contact force Fk.jpg|left|thumb|Figure 2: Contact resistance R<sub>k</sub> as a function of the contact force F<sub>k</sub> for different surface coating materials. Measured against a spherical gold probe; I = 10 mA, U < 20 mV]] |
</figure> | </figure> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<figure id="fig:Contact resistance Rk as a function of the fretting wear cycles"> | <figure id="fig:Contact resistance Rk as a function of the fretting wear cycles"> | ||
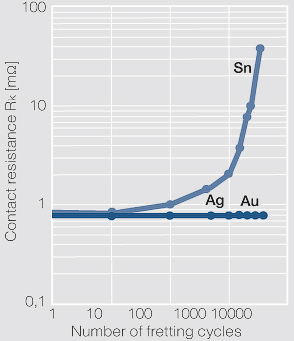
[[File:Contact resistance Rk as a function of the fretting wear cycles.jpg|left|thumb|Figure 3: Contact resistance R<sub>k</sub> as a function of the fretting wear cycles for different surface coating materials]] | [[File:Contact resistance Rk as a function of the fretting wear cycles.jpg|left|thumb|Figure 3: Contact resistance R<sub>k</sub> as a function of the fretting wear cycles for different surface coating materials]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:45, 11 January 2023
Physical Effects in Sliding and Connector Contacts
Mechanical wear of sliding contacts
| dV/dx = k x FK /3 HW |
| dV/dx Wear volume in mm3 per slide path length in mm |
| k Coefficient of frictional wear |
| HW Hardness of the softer material (Brinell or Vickers units) |
| FK Contact force in cN |
| Wear coefficient k during material transfer |
| Silver – Silver 120 x 10-4 |
| Platinum – Platinum 400 x 10-4 |
| Silver – Platinum 1.3 x 10-4 |
| Coefficient of fractional wear k during wear loss |
| Silver – silver 8 x 10-4 |
| Gold – gold 9 x 10-4 |
| Platinum – platinum 40 x 10-4 |
| Silver – gold 9 x 10-4 |
| Silver – platinum 5 x 10-4 |
Contact behavior of connectors
Table 1: Surface Coating Materials for Connectors
| Manufacturing method | Coating materials | Intermediate layer | Hardness HV | Frictional factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electroplating | Tin Nickel Nickel-phosphorus (NiP 6 - 15) Silver Hard gold (< 0.3 wt% Ni or Co) Palladium with Au- flash (<0,2μm) Palladium-nickel with Au-flash (<0.2μm) |
For brass: Copper or Nickel Nickel, Nickel-phosphorus Nickel Nickel |
50 - 90 300 - 600 500 - 1100 70 - 100 100 - 200 250 - 300 300 - 400 |
0.5 - 1 0.5 - 0.8 0.2 - 0.5 0.2 - 0.5 0.2 - 0.5 |
| Cladding | Gold-nickel (AuNi 5 -10) Silber-palladium (AgPd 10 - 30) |
Nickel Nickel |
160 - 200 120 - 170 |
0.2 - 0.5 0.2 - 0.5 |
| Hot-dipped tinning | Tin | Inter-metallic compound(1) Tin–copper | 400 - 500 |
(1) is formed during hot tinning process