Difference between revisions of "Silver Based Materials"
(→Hard-Silver Alloys) |
Doduco Admin (talk | contribs) |
||
| (460 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
Pure silver (also called fine silver) exhibits the highest electrical and thermal conductivity of all metals. It is also resistant against oxidation. Major disadvantages are its low mechanical wear resistance, the low softening temperature, and especially its strong affinity to sulfur and sulfur compounds. In the presence of sulfur and sulfur containing compounds brownish to black silver sulfide layer are formed on its surface. These can cause increased contact resistance or even total failure of a switching device if they are not mechanically, electrically, or thermally destroyed. Other weaknesses of silver contacts are the tendency to weld under the influence of over-currents and the low resistance against material transfer when switching DC loads. In humid environments and under the influence of an electrical field silver can creep (silver migration) and cause electrical shorting between adjacent current paths. | Pure silver (also called fine silver) exhibits the highest electrical and thermal conductivity of all metals. It is also resistant against oxidation. Major disadvantages are its low mechanical wear resistance, the low softening temperature, and especially its strong affinity to sulfur and sulfur compounds. In the presence of sulfur and sulfur containing compounds brownish to black silver sulfide layer are formed on its surface. These can cause increased contact resistance or even total failure of a switching device if they are not mechanically, electrically, or thermally destroyed. Other weaknesses of silver contacts are the tendency to weld under the influence of over-currents and the low resistance against material transfer when switching DC loads. In humid environments and under the influence of an electrical field silver can creep (silver migration) and cause electrical shorting between adjacent current paths. | ||
| − | Table 2.11 shows the typically available quality grades of silver. In certain economic areas, i.e. China, there are additional grades with varying amounts of impurities available on the market. In powder form silver is used for a wide variety of silver based composite contact materials. Different manufacturing processes result in different grades of Ag powder as shown in Table 2.12. | + | <xr id="tab:Overview_of_the_Most_Widely_Used_Silver_Grades"/><!--(Table 2.11)--> shows the typically available quality grades of silver. In certain economic areas, i.e. China, there are additional grades with varying amounts of impurities available on the market. In powder form silver is used for a wide variety of silver based composite contact materials. Different manufacturing processes result in different grades of Ag powder as shown in <xr id="tab:Quality_Criteria_of_Differently_Manufactured_Silver_Powders"/><!--Table 2.12-->. Additional properties of silver powders and their usage are described in [[ Precious Metal Powders and Preparations#Precious_Metal_Powders|Precious Metal Powders ]] und [[Precious_Metal_Powders_and_Preparations|Table Different Types of Silver Powders.]]<!--(Tab. 8.1.)--> |
| − | Semi-finished silver materials can easily be warm or cold formed and can be clad to the usual base materials. For attachment of silver to contact carrier | + | |
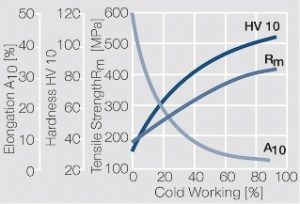
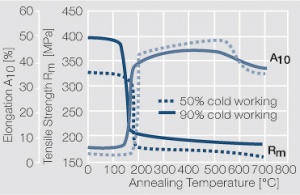
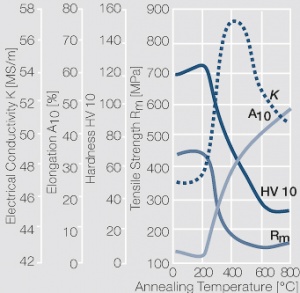
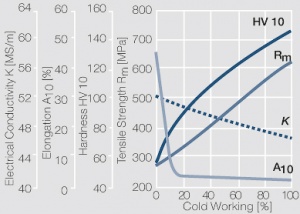
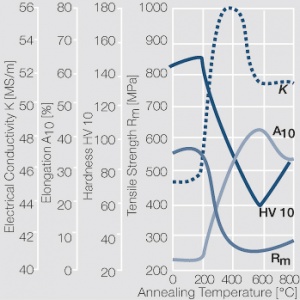
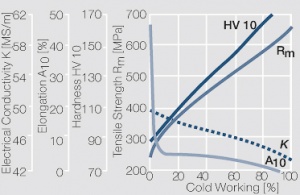
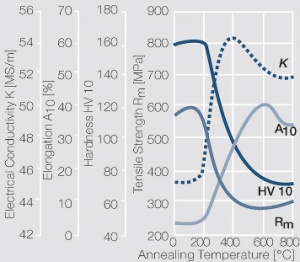
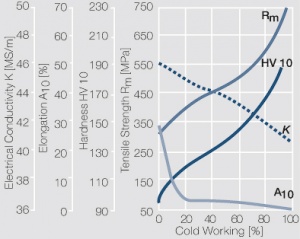
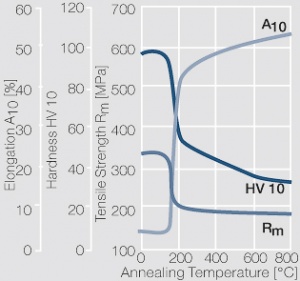
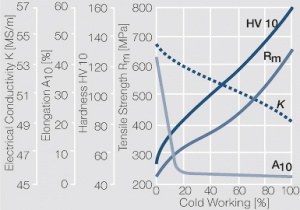
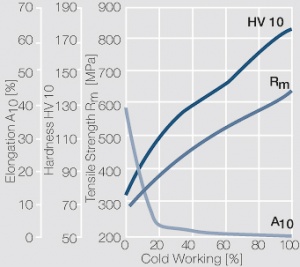
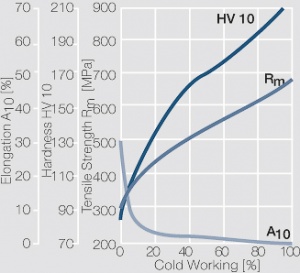
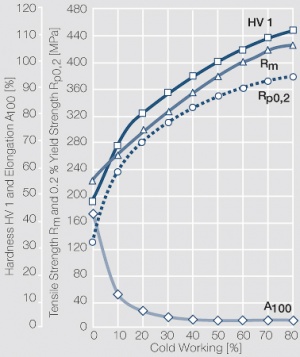
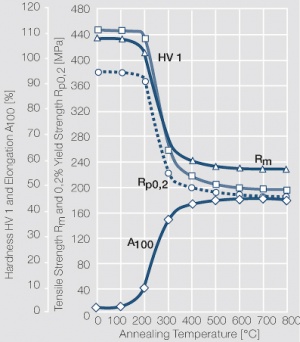
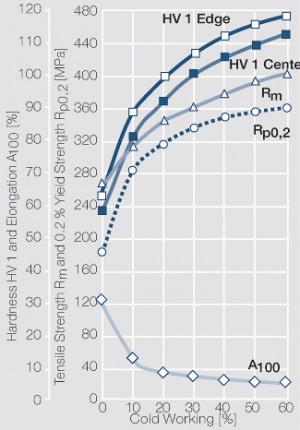
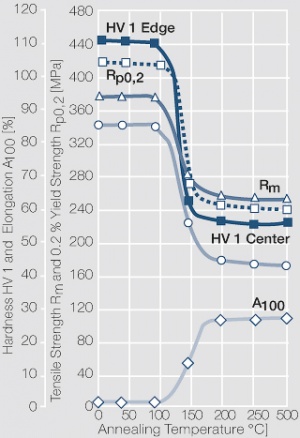
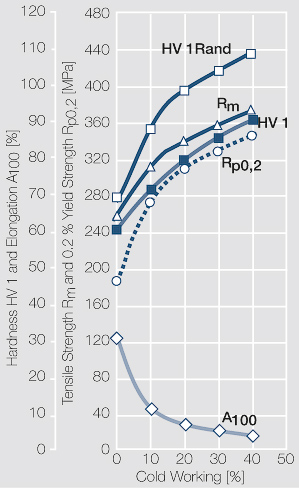
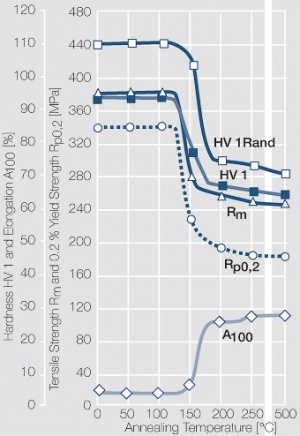
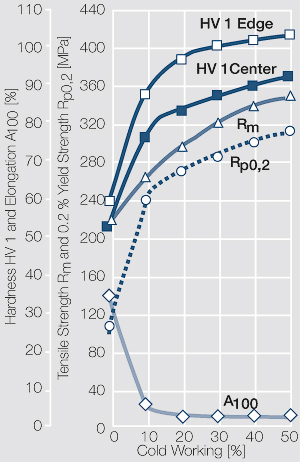
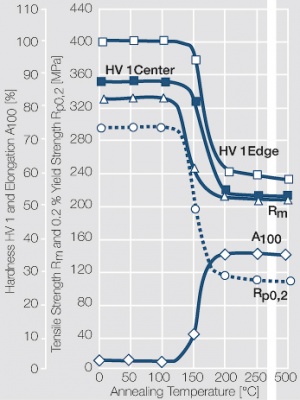
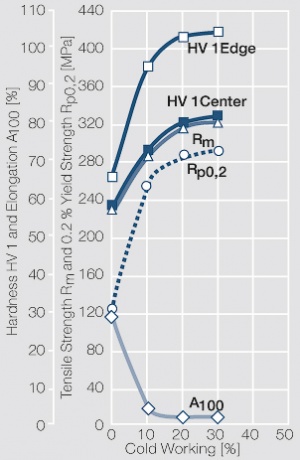
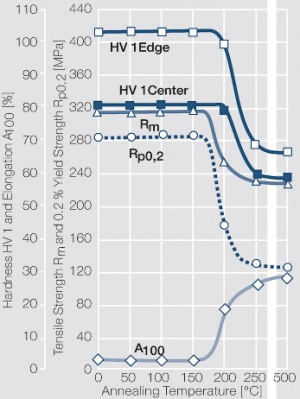
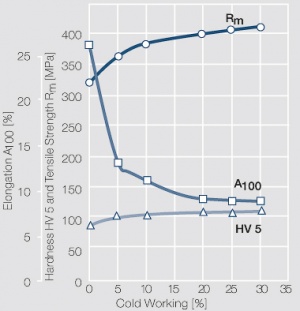
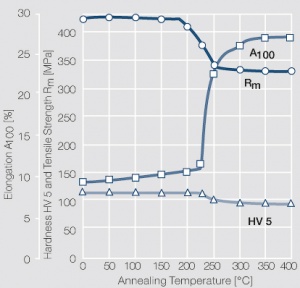
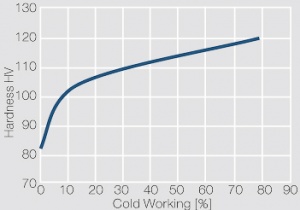
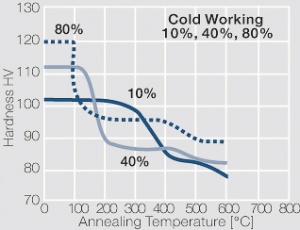
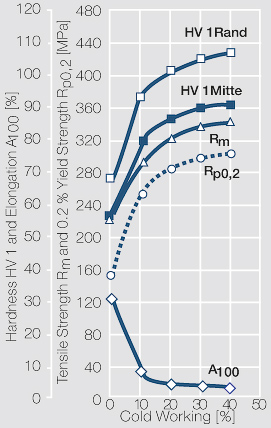
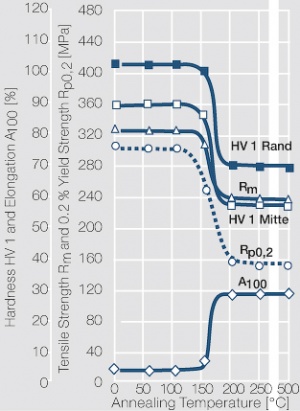
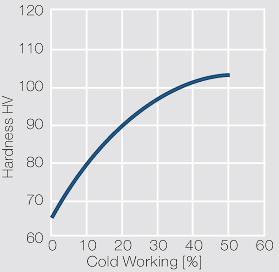
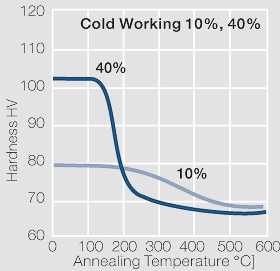
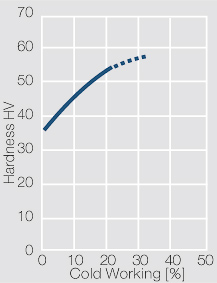
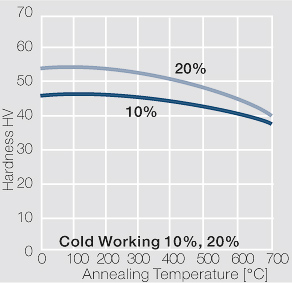
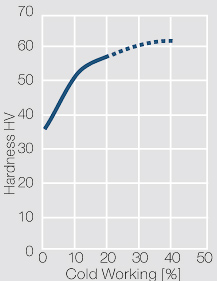
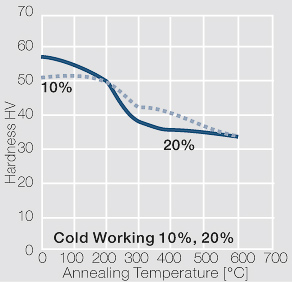
| − | materials welding of wire or profile cut-offs and brazing are most widely applied. Besides these mechanical processes such as wire insertion (wire staking) and the riveting (staking) of solid or composite contact rivets are used in the manufacture of contact components. | + | Semi-finished silver materials can easily be warm or cold formed and can be clad to the usual base materials (<xr id="fig:Strain hardening of Ag bei cold working"/> and <xr id="fig:Softening of Ag after annealing after different degrees"/>). For attachment of silver to contact carrier materials welding of wire or profile cut-offs and brazing are most widely applied. Besides these mechanical processes such as wire insertion (wire staking) and the riveting (staking) of solid or composite contact rivets are used in the manufacture of contact components. |
Contacts made from fine silver are applied in various electrical switching devices such as relays, pushbuttons, appliance and control switches for | Contacts made from fine silver are applied in various electrical switching devices such as relays, pushbuttons, appliance and control switches for | ||
| − | currents < 2 A | + | currents < 2 A (<xr id="tab:Application Examples and Forms of Supply for Silver and Silver Alloys"/>)<!--(Table 2.16)-->. Electroplated silver coatings are widely used to reduce the contact resistance and improve the brazing behavior of other contact materials and components. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | '''Table 2. | + | <figtable id="tab:Overview_of_the_Most_Widely_Used_Silver_Grades"> |
| + | <caption>'''<!--Table 2.11:-->Overview of the Most Widely Used Silver Grades'''</caption> | ||
| + | <table class="twocolortable"> | ||
| + | <tr><th><p class="s12">Designation</p></th><th><p class="s12">Composition minimum Ag [wt%]</p></th><th><p class="s12">Impurities</p><p class="s12">[ppm]</p></th><th><p class="s12">Notes on Usage</p></th></tr><tr><td><p class="s12">Spectroscopically</p><p class="s12">Pure Ag</p></td><td><p class="s11">99.999</p></td><td><p class="s11">Cu < 3</p><p class="s11">Zn < 1</p><p class="s11">Si < 1</p><p class="s11">Ca < 2</p><p class="s11">Fe < 1</p><p class="s11">Mg < 1</p><p class="s11">Cd < 1</p></td><td><p class="s12">Sheets, strips, rods, wires for electronic applications</p></td></tr><tr><td><p class="s12">High Purity Ag, oxygen-free</p></td><td><p class="s11">99.995</p></td><td><p class="s11">Cu < 30</p><p class="s11">Zn < 2</p><p class="s11">Si < 5</p><p class="s11">Ca < 10</p><p class="s11">Fe < 3</p><p class="s11">Mg < 5</p><p class="s11">Cd < 3</p></td><td><p class="s12">Ingots, bars, granulate for alloying purposes</p><p class="s12"></p></td></tr></table> | ||
| + | </figtable> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <figtable id="tab:Quality_Criteria_of_Differently_Manufactured_Silver_Powders"> | |
| − | [[File:Softening of Ag after annealing after different degrees.jpg| | + | <caption>'''<!--Table 2.12:-->Quality Criteria of Differently Manufactured Silver Powders'''</caption> |
| + | |||
| + | {| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !colspan="2" |Impurities | ||
| + | !Ag-Chem.* | ||
| + | !Ag-ES** | ||
| + | !Ag-V*** | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Cu | ||
| + | |ppm | ||
| + | |< 100 | ||
| + | |< 300 | ||
| + | |< 300 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Fe | ||
| + | |ppm | ||
| + | |< 50 | ||
| + | |< 100 | ||
| + | |< 100 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ni | ||
| + | |ppm | ||
| + | |< 50 | ||
| + | |< 50 | ||
| + | |< 50 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Cd | ||
| + | |ppm | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |< 50 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Zn | ||
| + | |ppm | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |< 10 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Na + K + Mg + Ca | ||
| + | |ppm | ||
| + | |< 80 | ||
| + | |< 50 | ||
| + | |< 50 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag CI | ||
| + | |ppm | ||
| + | |< 500 | ||
| + | |< 500 | ||
| + | |< 500 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |NO<sub>3</sub> | ||
| + | |ppm | ||
| + | |< 40 | ||
| + | |< 40 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Nh<sub>4</sub>CI | ||
| + | |ppm | ||
| + | |< 30 | ||
| + | |< 30 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !colspan="5" |Particle Size Distribution (screen analysis) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |> 100 μm | ||
| + | |% | ||
| + | |0 | ||
| + | |0 | ||
| + | |0 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |< 100 bis > 63 μm | ||
| + | |% | ||
| + | |< 5 | ||
| + | |< 5 | ||
| + | |< 15 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |< 36 μm | ||
| + | |% | ||
| + | |< 80 | ||
| + | |< 90 | ||
| + | |< 75 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Apparent Density | ||
| + | |g/cm<sup>3</sup> | ||
| + | |1.0 - 1.6 | ||
| + | |1.0 - 1.5 | ||
| + | |3 - 4 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Tap Density | ||
| + | |ml/100g | ||
| + | |40 - 50 | ||
| + | |40 - 50 | ||
| + | |15 - 25 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !colspan="5" |Press/Sintering Behavior | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Press Density | ||
| + | |g/cm<sup>3</sup> | ||
| + | |5.6 - 6.5 | ||
| + | |5.6 - 6.3 | ||
| + | |6.5 - 8.5 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Sinter Density | ||
| + | |g/cm<sup>3</sup> | ||
| + | |> 9 | ||
| + | |> 9.3 | ||
| + | |> 8 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Volume Shrinkage | ||
| + | |% | ||
| + | |> 34 | ||
| + | |> 35 | ||
| + | |> 0 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Annealing Loss | ||
| + | |% | ||
| + | |< 2 | ||
| + | |< 0.1 | ||
| + | |< 0.1 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </figtable> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <nowiki>*</nowiki> Manufactured by chemical precipitation <br /> | ||
| + | <nowiki>**</nowiki> Manufactured by electrolytic deposition <br /> | ||
| + | <nowiki>***</nowiki> Manufactured by atomizing of a melt | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="multiple-images"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <figure id="fig:Strain hardening of Ag bei cold working"> | ||
| + | [[File:Strain hardening of Ag bei cold working.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Strain hardening of Ag 99.95 - cold working</caption>]] | ||
| + | </figure> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <figure id="fig:Softening of Ag after annealing after different degrees"> | ||
| + | [[File:Softening of Ag after annealing after different degrees.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Softening of Ag 99.95 after annealing for 1 hr after different degrees of strain hardening</caption>]] | ||
| + | </figure> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div class="clear"></div> | ||
===Silver Alloys=== | ===Silver Alloys=== | ||
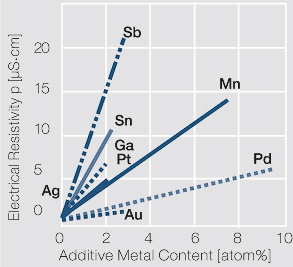
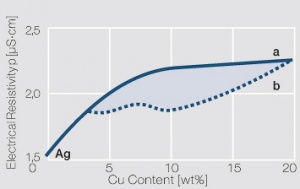
| − | To improve the physical and contact properties of fine silver melt-metallurgical produced silver alloys are used | + | To improve the physical and contact properties of fine silver, melt-metallurgical produced silver alloys are used (<xr id="tab:Physical Properties of Silver and Silver Alloys"/>)<!--(Table 2.13)-->. By adding metal components, the mechanical properties such as hardness and tensile strength as well as typical contact properties such as erosion resistance and resistance against material transfer in DC circuits are increased (<xr id="tab:Mechanical Properties of Silver and Silver Alloys"/>)<!--(Table 2.14)-->. On the other hand however, other properties such as electrical conductivity and chemical corrosion resistance can be negatively impacted by alloying (<xr id="fig:Influence of 1 10 atom of different alloying metals"/><!--(Fig. 2.47)--> and <xr id="fig:Electrical resistivity p of AgCu alloys"/>)<!--(Fig. 2.48)-->. |
| + | |||
| + | <figtable id="tab:Physical Properties of Silver and Silver Alloys"> | ||
| + | <caption>'''<!--Table 2.13:-->Physical Properties of Silver and Silver Alloys'''</caption> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !Material | ||
| + | !Silver Content<br />[wt%] | ||
| + | !Density<br />[g/cm<sup>3</sup>] | ||
| + | !Melting Point<br />or Range<br />[°C] | ||
| + | !Electrical<br />Resistivity<br />[μΩ·cm] | ||
| + | !Electrical<br />Conductivity<br />[MS/m] | ||
| + | !Thermal<br />Conductivity<br />[W/mK] | ||
| + | !Temp. Coefficient of<br />the Electr.Resistance<br />[10<sup>-3</sup>/K] | ||
| + | !Modulus of<br />Elasticity<br />[GPa] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag | ||
| + | |99.95 | ||
| + | |10.5 | ||
| + | |961 | ||
| + | |1.67 | ||
| + | |60 | ||
| + | |419 | ||
| + | |4.1 | ||
| + | |80 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |AgNi0.15 | ||
| + | |99.85 | ||
| + | |10.5 | ||
| + | |960 | ||
| + | |1.72 | ||
| + | |58 | ||
| + | |414 | ||
| + | |4.0 | ||
| + | |82 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |AgCu3 | ||
| + | |97 | ||
| + | |10.4 | ||
| + | |900 - 938 | ||
| + | |1.92 | ||
| + | |52 | ||
| + | |385 | ||
| + | |3.2 | ||
| + | |85 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |AgCu5 | ||
| + | |95 | ||
| + | |10.4 | ||
| + | |910 | ||
| + | |1.96 | ||
| + | |51 | ||
| + | |380 | ||
| + | |3.0 | ||
| + | |85 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |AgCu10 | ||
| + | |90 | ||
| + | |10.3 | ||
| + | |870 | ||
| + | |2.0 | ||
| + | |50 | ||
| + | |335 | ||
| + | |2.8 | ||
| + | |85 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |AgCu28 | ||
| + | |72 | ||
| + | |10.0 | ||
| + | |779 | ||
| + | |2.08 | ||
| + | |48 | ||
| + | |325 | ||
| + | |2.7 | ||
| + | |92 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag98CuNi<br />ARGODUR 27 | ||
| + | |98 | ||
| + | |10.4 | ||
| + | |940 | ||
| + | |1.92 | ||
| + | |52 | ||
| + | |385 | ||
| + | |3.5 | ||
| + | |85 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |AgCu24.5Ni0.5 | ||
| + | |75 | ||
| + | |10.0 | ||
| + | |805 | ||
| + | |2.20 | ||
| + | |45 | ||
| + | |330 | ||
| + | |2.7 | ||
| + | |92 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag99.5NiMg<br />ARGODUR 32<br />Not heat treated | ||
| + | |99.5 | ||
| + | |10.5 | ||
| + | |960 | ||
| + | |2.32 | ||
| + | |43 | ||
| + | |293 | ||
| + | |2.3 | ||
| + | |80 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |ARGODUR 32<br />Heat treated | ||
| + | |99.5 | ||
| + | |10.5 | ||
| + | |960 | ||
| + | |2.32 | ||
| + | |43 | ||
| + | |293 | ||
| + | |2.1 | ||
| + | |80 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </figtable> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="multiple-images"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <figure id="fig:Influence of 1 10 atom of different alloying metals"> | ||
| + | [[File:Influence of 1 10 atom of different alloying metals.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Influence of 1-10 atom% of different alloying metals on the electrical resistivity of silver</caption>]] | ||
| + | </figure> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <figure id="fig:Electrical resistivity p of AgCu alloys"> | ||
| + | [[File:Electrical resistivity p of AgCu alloys.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Electrical resistivity p of AgCu alloys with 0-20 weight% Cu in the soft annealed and tempered stage a) Annealed and quenched b) Tempered at 280°C</caption>]] | ||
| + | </figure> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div class="clear"></div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <figtable id="tab:Mechanical Properties of Silver and Silver Alloys"> | ||
| + | <caption>'''<!--Table 2.14:-->Mechanical Properties of Silver and Silver Alloys'''</caption> | ||
| + | <table class="twocolortable"> | ||
| + | <tr><th><p class="s12">Material</p></th><th><p class="s12">Hardness</p><p class="s12">Condition</p></th><th><p class="s12">Tensile Strength</p><p class="s12">R<span class="s31">m </span>[MPa]</p></th><th><p class="s12">Elongation A [%] min.</p></th><th><p class="s12">Vickers Hardness</p><p class="s12">HV 10</p></th></tr><tr><td><p class="s12">Ag</p></td><td><p class="s12">R 200</p><p class="s12">R 250</p><p class="s12">R 300</p><p class="s12">R 360</p></td><td><p class="s12">200 - 250</p><p class="s12">250 - 300</p><p class="s12">300 - 360</p><p class="s12">> 360</p></td><td><p class="s12">30</p><p class="s12">8</p><p class="s12">3</p><p class="s12">2</p></td><td><p class="s12">30</p><p class="s12">60</p><p class="s12">80</p><p class="s12">90</p></td></tr><tr><td><p class="s12">AgNi0.15</p><p class="s12"></p></td><td><p class="s12">R 220</p><p class="s12">R 270</p><p class="s12">R 320</p><p class="s12">R 360</p></td><td><p class="s12">220 - 270</p><p class="s12">270 - 320</p><p class="s12">320 - 360</p><p class="s12">> 360</p></td><td><p class="s12">25</p><p class="s12">6</p><p class="s12">2</p><p class="s12">1</p></td><td><p class="s12">40</p><p class="s12">70</p><p class="s12">85</p><p class="s12">100</p></td></tr><tr><td><p class="s12">AgCu3</p></td><td><p class="s12">R 250</p><p class="s12">R 330</p><p class="s12">R 400</p><p class="s12">R 470</p></td><td><p class="s12">250 - 330</p><p class="s12">330 - 400</p><p class="s12">400 - 470</p><p class="s12">> 470</p></td><td><p class="s12">25</p><p class="s12">4</p><p class="s12">2</p><p class="s12">1</p></td><td><p class="s12">45</p><p class="s12">90</p><p class="s12">115</p><p class="s12">120</p></td></tr><tr><td><p class="s12">AgCu5</p></td><td><p class="s12">R 270</p><p class="s12">R 350</p><p class="s12">R 460</p><p class="s12">R 550</p></td><td><p class="s12">270 - 350</p><p class="s12">350 - 460</p><p class="s12">460 - 550</p><p class="s12">> 550</p></td><td><p class="s12">20</p><p class="s12">4</p><p class="s12">2</p><p class="s12">1</p></td><td><p class="s12">55</p><p class="s12">90</p><p class="s12">115</p><p class="s12">135</p></td></tr><tr><td><p class="s12">AgCu10</p></td><td><p class="s12">R 280</p><p class="s12">R 370</p><p class="s12">R 470</p><p class="s12">R 570</p></td><td><p class="s12">280 - 370</p><p class="s12">370 - 470</p><p class="s12">470 - 570</p><p class="s12">> 570</p></td><td><p class="s12">15</p><p class="s12">3</p><p class="s12">2</p><p class="s12">1</p></td><td><p class="s12">60</p><p class="s12">95</p><p class="s12">130</p><p class="s12">150</p></td></tr><tr><td><p class="s12">AgCu28</p></td><td><p class="s12">R 300</p><p class="s12">R 380</p><p class="s12">R 500</p><p class="s12">R 650</p></td><td><p class="s12">300 - 380</p><p class="s12">380 - 500</p><p class="s12">500 - 650</p><p class="s12">> 650</p></td><td><p class="s12">10</p><p class="s12">3</p><p class="s12">2</p><p class="s12">1</p></td><td><p class="s12">90</p><p class="s12">120</p><p class="s12">140</p><p class="s12">160</p></td></tr><tr><td><p class="s12">Ag98CuNi</p><p class="s12">ARGODUR 27</p></td><td><p class="s12">R 250</p><p class="s12">R 310</p><p class="s12">R 400</p><p class="s12">R 450</p></td><td><p class="s12">250 - 310</p><p class="s12">310 - 400</p><p class="s12">400 - 450</p><p class="s12">> 450</p></td><td><p class="s12">20</p><p class="s12">5</p><p class="s12">2</p><p class="s12">1</p></td><td><p class="s12">50</p><p class="s12">85</p><p class="s12">110</p><p class="s12">120</p></td></tr><tr><td><p class="s12">AgCu24,5Ni0,5</p></td><td><p class="s12">R 300</p><p class="s12">R 600</p></td><td><p class="s12">300 - 380</p><p class="s12">> 600</p></td><td><p class="s12">10</p><p class="s12">1</p></td><td><p class="s12">105</p><p class="s12">180</p></td></tr><tr><td><p class="s12">Ag99,5NiMg</p><p class="s12">ARGODUR 32</p><p class="s12">Not heat treated</p></td><td><p class="s12">R 220</p><p class="s12">R 260</p><p class="s12">R 310</p><p class="s12">R 360</p></td><td><p class="s12">220</p><p class="s12">260</p><p class="s12">310</p><p class="s12">360</p></td><td><p class="s12">25</p><p class="s12">5</p><p class="s12">2</p><p class="s12">1</p></td><td><p class="s12">40</p><p class="s12">70</p><p class="s12">85</p><p class="s12">100</p></td></tr><tr><td><p class="s12">ARGODUR 32 Heat treated</p></td><td><p class="s12">R 400</p></td><td><p class="s12">400</p></td><td><p class="s12">2</p></td><td><p class="s12">130-170</p></td></tr></table> | ||
| + | </figtable> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
====Fine-Grain Silver==== | ====Fine-Grain Silver==== | ||
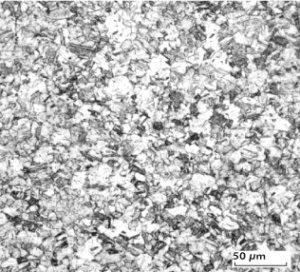
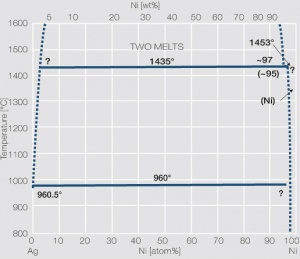
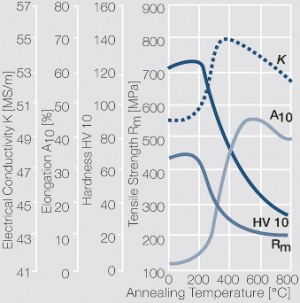
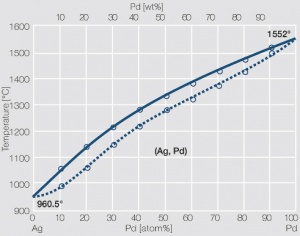
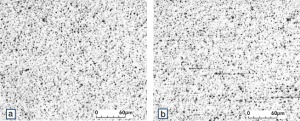
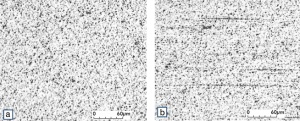
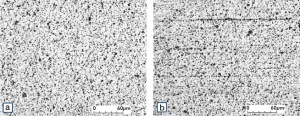
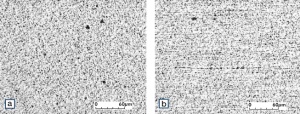
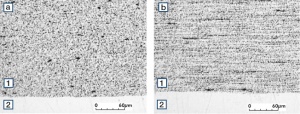
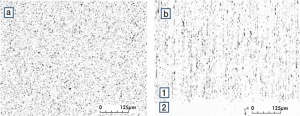
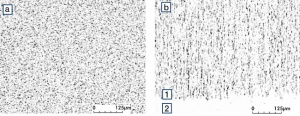
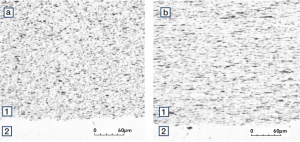
| − | Fine-Grain | + | Fine-Grain silver is defined as a silver alloy with an addition of 0.15 wt% of nickel. Silver and nickel are not soluble in each other in solid form. In liquid silver, only a small amount of nickel is soluble as the phase diagram illustrates (<xr id="fig:Phase diagram of silver nickel"/><!--(Fig. 2.51)-->). During solidification of the melt, this nickel addition gets finely dispersed in the silver matrix and eliminates the pronounce coarse grain growth after prolonged influence of elevated temperatures (<xr id="fig:Coarse grain micro structure of Ag"/><!--(Fig. 2.49)--> and <xr id="fig:Fine grain microstructure of AgNiO"/><!--(Fig. 2.50)-->). |
| − | [[File:Coarse grain micro structure of Ag.jpg| | + | |
| − | Fine- | + | <div class="multiple-images"> |
| − | tensile strength | + | |
| + | <figure id="fig:Coarse grain micro structure of Ag"> | ||
| + | [[File:Coarse grain micro structure of Ag.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Coarse grain micro structure of Ag 99.97 after 80% cold working and 1 hr annealing at 600°C</caption>]] | ||
| + | </figure> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <figure id="fig:Fine grain microstructure of AgNiO"> | ||
| + | [[File:Fine grain microstructure of AgNiO.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Fine grain microstructure of AgNi0.15 after 80% cold working and 1 hr annealing at 600°C</caption>]] | ||
| + | </figure> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <figure id="fig:Phase diagram of silver nickel"> | ||
| + | [[File:Phase diagram of silver nickel.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Phase diagram of silver nickel</caption>]] | ||
| + | </figure> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div class="clear"></div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Fine-Grain silver has almost the same chemical corrosion resistance as fine silver. Compared to pure silver, it exhibits a slightly increased hardness and tensile strength (<xr id="tab:Mechanical Properties of Silver and Silver Alloys"/><!--(Table 2.14)-->). The electrical conductivity is just slightly decreased by this low nickel addition. Because of its significantly improved contact properties, fine grain silver has replaced pure silver in many applications. | ||
====Hard-Silver Alloys==== | ====Hard-Silver Alloys==== | ||
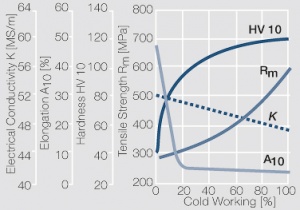
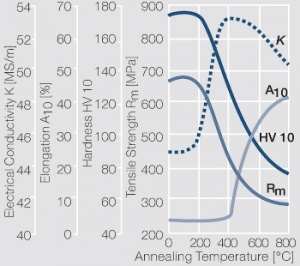
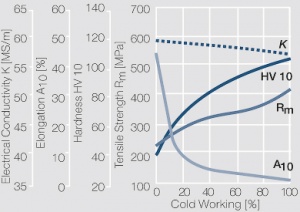
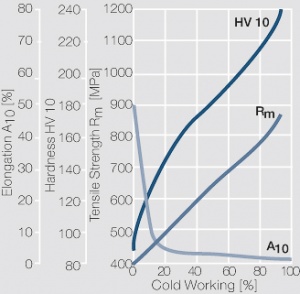
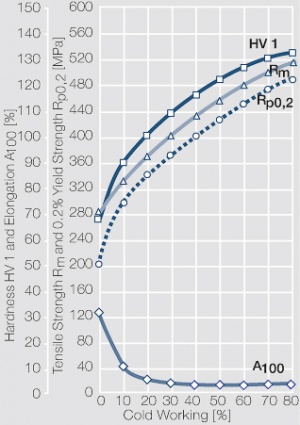
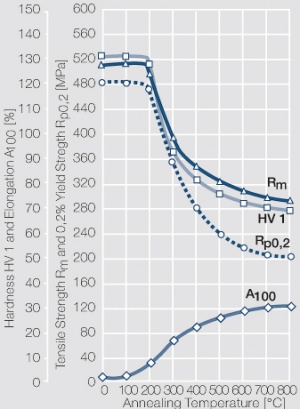
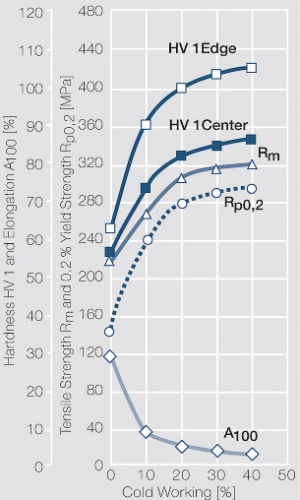
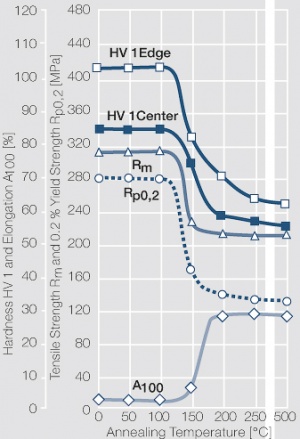
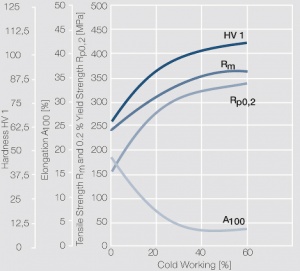
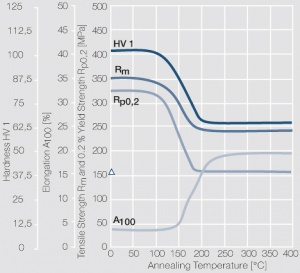
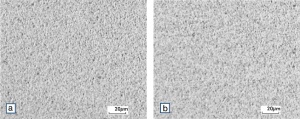
| − | Using copper as an alloying component increases the mechanical stability of silver significantly. The most important among the binary AgCu alloys is that of AgCu3, | + | Using copper as an alloying component increases the mechanical stability of silver significantly (<xr id="fig:Strain hardening of AgCu3 by cold working"/>, <xr id="fig:Softening of AgCu3 after annealing"/> and <xr id="fig:Strain hardening of AgCu5 by cold working"/>). The most important among the binary AgCu alloys is that of AgCu3, in europe also known as hard-silver. This material still has a chemical corrosion resistance close to that of fine silver. In comparison to pure silver and fine-grain silver, AgCu3 exhibits increased mechanical strength as well as higher arc erosion resistance and mechanical wear resistance. |
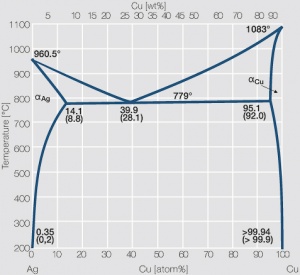
| − | Increasing the Cu content further also increases the mechanical strength of AgCu alloys and improves arc erosion resistance and resistance against material transfer while | + | Increasing the Cu content further also increases the mechanical strength of AgCu alloys and improves arc erosion resistance and resistance against material transfer while simultaneously the tendency to oxide formation becomes detrimental. This causes - during switching under arcing conditions - an increase in contact resistance with rising numbers of operation. In special applications, where highest mechanical strength is recommended and a reduced chemical resistance can be tolerated, the eutectic AgCu alloy with 28 wt% of copper is used (<xr id="fig:Phase diagram of silver copper"/>)<!--(Fig. 2.52)-->. AgCu10, also known as coin silver, has been replaced in many applications by composite silver-based materials while sterling silver (AgCu7.5) has never extended its important usage from decorative table wear and jewelry to industrial applications in electrical contacts. |
| − | Besides these binary alloys, ternary AgCuNi alloys are used in electrical contact applications. From this group the material ARGODUR 27, an alloy of 98 wt% Ag with a 2 wt% Cu and nickel addition has found practical importance close to that of AgCu3. This material is characterized by high resistance to oxidation and low tendency to re-crystallization during exposure to high temperatures. Besides high mechanical stability this AgCuNi alloy also exhibits a strong resistance against arc erosion. Because of its high resistance against material transfer the alloy AgCu24.5Ni0.5 has been used in the automotive industry for an extended time in the North American market. Caused by miniaturization and the related reduction in available contact forces in relays and switches this material has been replaced widely because of its tendency to oxide formation. | + | Besides these binary alloys, ternary AgCuNi alloys are used in electrical contact applications. From this group, the material ARGODUR 27, an alloy of 98 wt% Ag with a 2 wt% Cu and nickel addition has found practical importance close to that of AgCu3. This material is characterized by high resistance to oxidation and low tendency to re-crystallization during exposure to high temperatures. Besides high mechanical stability this AgCuNi alloy also exhibits a strong resistance against arc erosion. Because of its high resistance against material transfer, the alloy AgCu24.5Ni0.5 has been used in the automotive industry for an extended time in the North American market. Caused by miniaturization and the related reduction in available contact forces in relays and switches, this material has been replaced widely because of its tendency to oxide formation. |
The attachment methods used for the hard silver materials are mostly close to those applied for fine silver and fine grain silver. | The attachment methods used for the hard silver materials are mostly close to those applied for fine silver and fine grain silver. | ||
| − | Hard-silver alloys are widely used for switching applications in the information and energy technology for currents up to 10 A, in special cases also for higher current ranges | + | Hard-silver alloys are widely used for switching applications in the information and energy technology for currents up to 10 A, in special cases also for higher current ranges (<xr id="tab:Application Examples and Forms of Supply for Silver and Silver Alloys"/>)<!--(Table 2.16)-->. |
| + | |||
| + | Dispersion hardened alloys of silver with 0.5 wt% MgO and NiO (ARGODUR 32) are produced by internal oxidation. While the melt-metallurgical alloy is easy to cold-work and form, the material becomes very hard and brittle after dispersion hardening. Compared to fine silver and hard-silver, this material has a greatly improved temperature stability and can be exposed to brazing temperatures up to 800°C without decreasing its hardness and tensile strength. | ||
| + | Because of these mechanical properties and its high electrical conductivity ARGODUR 32 is mainly used in the form of contact springs that are exposed to high thermal and mechanical stresses in relays and contactors for aeronautic applications. | ||
| − | + | <div class="multiple-images"> | |
| − | |||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Phase diagram of silver copper"> | |
| + | [[File:Phase diagram of silver copper.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Phase diagram of silver-copper</caption>]] | ||
| + | </figure> | ||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Strain hardening of AgCu3 by cold working"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Strain hardening of AgCu3 by cold working.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Strain hardening of AgCu3 by cold working</caption>]] | |
| − | + | </figure> | |
| + | <figure id="fig:Softening of AgCu3 after annealing"> | ||
| + | [[File:Softening of AgCu3 after annealing.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Softening of AgCu3 after annealing for 1 hr after 80% cold working</caption>]] | ||
| + | </figure> | ||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Strain hardening of AgCu5 by cold working"> | |
| − | of | + | [[File:Strain hardening of AgCu5 by cold working.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Strain hardening of AgCu5 by cold working</caption>]] |
| − | + | </figure> | |
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Softening of AgCu5 after annealing"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Softening of AgCu5 after annealing.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Softening of AgCu5 after annealing for 1 hr after 80% cold working</caption>]] | |
| − | + | </figure> | |
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Strain hardening of AgCu 10 by cold working"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Strain hardening of AgCu 10 by cold working.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Strain hardening of AgCu 10 by cold working</caption>]] | |
| − | + | </figure> | |
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Softening of AgCu10 after annealing"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Softening of AgCu10 after annealing.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Softening of AgCu10 after annealing for 1 hr after 80% cold working</caption>]] | |
| − | + | </figure> | |
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Strain hardening of AgCu28 by cold working"> | |
| + | [[File:Strain hardening of AgCu28 by cold working.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Strain hardening of AgCu28 by cold working</caption>]] | ||
| + | </figure> | ||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Softening of AgCu28 after annealing"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Softening of AgCu28 after annealing.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Softening of AgCu28 after annealing for 1 hr after 80% cold working</caption>]] | |
| − | of | + | </figure> |
| − | |||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Strain hardening of AgNi0.15 by cold working"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Strain hardening of AgNiO15 by cold working.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Strain hardening of AgNiO15 by cold working</caption>]] | |
| − | + | </figure> | |
| − | |||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Softening of AgNi0.15 after annealing"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Softening of AgNiO15 after annealing.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Softening of AgNiO15 after annealing</caption>]] | |
| − | + | </figure> | |
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Strain hardening of ARGODUR 27"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Strain hardening of ARGODUR 27.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Strain hardening of AgCu1.8Ni0.2 (ARGODUR 27) by cold working</caption>]] | |
| − | + | </figure> | |
| − | |||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Softening of ARGODUR 27 after annealing"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Softening of ARGODUR 27 after annealing.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Softening of AgCu1.8Ni0.2 (ARGODUR 27) after annealing for 1 hr after 80% cold working</caption>]] | |
| − | + | </figure> | |
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div class="clear"></div> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <figtable id="tab:Contact and Switching Properties of Silver and Silver Alloys"> | |
| − | + | <caption>'''<!--Table 2.15:-->Contact and Switching Properties of Silver and Silver Alloys'''</caption> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px" | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | !Material | |
| + | !colspan="2" | Properties | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag<br />AgNi0.15 | ||
| + | |Highest electrical and thermal conductivity, high affinity to sulfur (sulfide formation), low welding resistance, low contact resistance, very good formability | ||
| + | |Oxidation resistant at higher make currents, limited arc erosion resistance, tendency to material transfer in DC circuits, easy to braze and weld to carrier materials | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag Alloys | ||
| + | |Increasing contact resistance with increasing | ||
| + | Cu content, compared to fine Ag higher arc erosion resistance and mechanical strength, lower tendency to material transfer | ||
| + | |Good formability, good brazing and welding properties | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </figtable> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <figtable id="tab:Application Examples and Forms of Supply for Silver and Silver Alloys"> | |
| − | + | <caption>'''<!--Table 2.16:-->Application Examples and Forms of Supply for Silver and Silver Alloys'''</caption> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px" | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | of ARGODUR 27 | + | !Material |
| − | for | + | !Application Examples |
| + | !Form of Supply | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag<br />AgNi0.15<br />AgCu3<br />AgNi98NiCu2<br />ARGODUR 27<br />AgCu24,5Ni0,5 | ||
| + | |Relays,<br />Micro switches,<br />Auxiliary current switches,<br />Control circuit devices,<br />Appliance switches,<br />Wiring devices (≤ 20A),<br />Main switches | ||
| + | |'''Semi-finished Materials:''' <br />Strips, wires, contact profiles, clad contact strips, toplay profiles, seam- welded strips<br />'''Contact Parts:'''<br />Contact tips, solid and composite rivets, weld buttons; clad, welded and riveted contact parts | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |AgCu5<br />AgCu10<br />AgCu28 | ||
| + | |Special applications | ||
| + | |'''Semi-finished Materials:'''<br />Strips, wires, contact profiles, clad contact strips, seam-welded strips<br />'''Contact parts:'''<br />Contact tips, solid contact rivets, weld buttons; clad, welded and riveted contact parts | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag99.5NiOMgO<br />ARGODUR 32 | ||
| + | |Miniature relays, aerospace relays and contactors, erosion wire for injection nozzles | ||
| + | |Contact springs, contact carrier parts | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </figtable> | ||
| − | + | ====Silver-Palladium Alloys==== | |
| + | The addition of 30 wt% Pd increases the mechanical properties as well as the resistance of silver against the influence of sulfur and sulfur containing compounds significantly (<xr id="tab:Physical Properties of Silver-Palladium Alloys"/><!--(Tab 2.17)--> and <xr id="tab:Mechanical Properties of Silver-Palladium Alloys"/>)<!--(Tab.2.18)-->. Alloys with 40-60 wt% Pd have an even higher resistance against silver sulfide formation. At these percentage ranges however, the catalytic properties of palladium can influence the contact resistance behavior negatively. The formability also decreases with increasing Pd contents. | ||
| − | + | AgPd alloys are hard, arc erosion resistant, and have a lower tendency towards material transfer under DC loads (<xr id="tab:Contact and Switching Properties of Silver-Palladium Alloys"/>)<!--(Table 2.19)-->. On the other hand, the electrical conductivity is decreased at higher Pd contents. The ternary alloy AgPd30Cu5 has an even higher hardness, which makes it suitable for use in sliding contact systems. | |
| − | = | + | AgPd alloys are mostly used in relays for the switching of medium to higher loads (> 60V, > 2A) as shown in <xr id="tab:Application Examples and Forms of Suppl for Silver-Palladium Alloys"/><!--(Table 2.20)-->. Because of the high palladium price, these formerly solid contacts have been widely replaced by multi-layer designs such as AgNi0.15 or AgNi10 with a thin Au surface layer. A broader field of application for AgPd alloys remains in the wear resistant sliding contact systems. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | <div class="multiple-images"> | |
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Phase diagram of silver palladium"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Phase diagram of silver palladium.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Phase diagram of silver-palladium</caption>]] | |
| − | + | </figure> | |
| − | + | ||
| + | <figure id="fig:Strain hardening of AgPd30 by cold working"> | ||
| + | [[File:Strain hardening of AgPd30 by cold working.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Strain hardening of AgPd30 by cold working</caption>]] | ||
| + | </figure> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <figure id="fig:Strain hardening of AgPd50 by cold working"> | ||
| + | [[File:Strain hardening of AgPd50 by cold working.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Strain hardening of AgPd50 by cold working</caption>]] | ||
| + | </figure> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <figure id="fig:Strain hardening of AgPd30Cu5 by cold working"> | ||
| + | [[File:Strain hardening of AgPd30Cu5 by cold working.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Strain hardening of AgPd30Cu5 by cold working</caption>]] | ||
| + | </figure> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <figure id="fig:Softening of AgPd30 AgPd50 AgPd30Cu5"> | ||
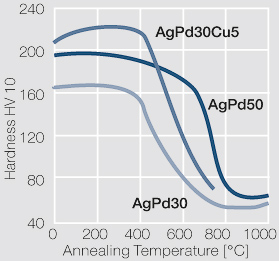
| + | [[File:Softening of AgPd30 AgPd50 AgPd30Cu5.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Softening of AgPd30, AgPd50, and AgPd30Cu5 after annealing of 1 hr after 80% cold working</caption>]] | ||
| + | </figure> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div class="clear"></div> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <figtable id="tab:Physical Properties of Silver-Palladium Alloys"> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <caption>'''<!--Table 2.17:--> Physical Properties of Silver-Palladium Alloys'''</caption> | |
| − | + | {| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px" | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | !Material | |
| + | !Palladium Content<br />[wt%] | ||
| + | !Density<br />[g/cm<sup>3</sup>] | ||
| + | !Melting Point<br />or Range<br />[°C] | ||
| + | !Electrical<br />Resistivity<br />[μΩ·cm] | ||
| + | !Electrical<br />Conductivity<br />[MS/m] | ||
| + | !Thermal<br />Conductivity<br />[W/m·K] | ||
| + | !Temp. Coefficient of<br />the Electr. Resistance<br />[10<sup>-3</sup>/K] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |AgPd30 | ||
| + | |30 | ||
| + | |10.9 | ||
| + | |1155 - 1220 | ||
| + | |14.7 | ||
| + | |6.8 | ||
| + | |60 | ||
| + | |0.4 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |AgPd40 | ||
| + | |40 | ||
| + | |11.1 | ||
| + | |1225 - 1285 | ||
| + | |20.8 | ||
| + | |4.8 | ||
| + | |46 | ||
| + | |0.36 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |AgPd50 | ||
| + | |50 | ||
| + | |11.2 | ||
| + | |1290 - 1340 | ||
| + | |32.3 | ||
| + | |3.1 | ||
| + | |34 | ||
| + | |0.23 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |AgPd60 | ||
| + | |60 | ||
| + | |11.4 | ||
| + | |1330 - 1385 | ||
| + | |41.7 | ||
| + | |2.4 | ||
| + | |29 | ||
| + | |0.12 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |AgPd30Cu5 | ||
| + | |30 | ||
| + | |10.8 | ||
| + | |1120 - 1165 | ||
| + | |15.6 | ||
| + | |6.4 | ||
| + | |28 | ||
| + | |0.37 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </figtable> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <figtable id="tab:Mechanical Properties of Silver-Palladium Alloys"> | |
| − | + | <caption>'''<!--Table 2.18:-->Mechanical Properties of Silver-Palladium Alloys'''</caption> | |
| − | + | <table class="twocolortable"> | |
| − | + | <tr><th><p class="s12">Material</p></th><th><p class="s12">Hardness</p><p class="s12">Condition</p></th><th><p class="s12">Tensile Strength</p><p class="s12">R<span class="s31"><sub>m</sub></span>[MPa]</p></th><th><p class="s12">Elongation A</p><p class="s12">[%]min.</p></th><th><p class="s12">Vickers Hardness</p><p class="s12">HV</p></th></tr><tr><td><p class="s12">AgPd30</p></td><td><p class="s12">R 320</p><p class="s12">R 570</p></td><td><p class="s12">320</p><p class="s12">570</p></td><td><p class="s12">38</p><p class="s12">3</p></td><td><p class="s12">65</p><p class="s12">145</p></td></tr><tr><td><p class="s12">AgPd40</p></td><td><p class="s12">R 350</p><p class="s12">R 630</p></td><td><p class="s12">350</p><p class="s12">630</p></td><td><p class="s12">38</p><p class="s12">2</p></td><td><p class="s12">72</p><p class="s12">165</p></td></tr><tr><td><p class="s12">AgPd50</p></td><td><p class="s12">R 340</p><p class="s12">R 630</p></td><td><p class="s12">340</p><p class="s12">630</p></td><td><p class="s12">35</p><p class="s12">2</p></td><td><p class="s12">78</p><p class="s12">185</p></td></tr><tr><td><p class="s12">AgPd60</p></td><td><p class="s12">R 430</p><p class="s12">R 700</p></td><td><p class="s12">430</p><p class="s12">700</p></td><td><p class="s12">30</p><p class="s12">2</p></td><td><p class="s12">85</p><p class="s12">195</p></td></tr><tr><td><p class="s12">AgPd30Cu5</p></td><td><p class="s12">R 410</p><p class="s12">R 620</p></td><td><p class="s12">410</p><p class="s12">620</p></td><td><p class="s12">40</p><p class="s12">2</p></td><td><p class="s12">90</p><p class="s12">190</p></td></tr></table> | |
| + | </figtable> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Table 2. | + | <figtable id="tab:Contact and Switching Properties of Silver-Palladium Alloys"> |
| + | <caption>'''<!--Table 2.19:-->Contact and Switching Properties of Silver-Palladium Alloys''</caption>' | ||
| − | + | {| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px" | |
| + | |- | ||
| + | !Material | ||
| + | !colspan="2" | Properties | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |AgPd30-60 | ||
| + | |Corrosion resistant, tendency to Brown Powder formation increases with Pd content, low tendency to material transfer in DC circuits, high ductility | ||
| + | |Resistant against Ag<sub>2</sub>S formation, low contact resistance, increasing hardness with higher Pd content, AgPd30 has highest arc erosion resistance, easy to weld and clad | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |AgPd30Cu5 | ||
| + | |High mechanical wear resistance | ||
| + | |High Hardness | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </figtable> | ||
| − | |||
| − | Table 2.20: Application Examples and Forms of Suppl for Silver-Palladium Alloys | + | <figtable id="tab:Application Examples and Forms of Suppl for Silver-Palladium Alloys"> |
| + | <caption>'''<!--Table 2.20:-->Application Examples and Forms of Suppl for Silver-Palladium Alloys'''</caption> | ||
| + | <table class="twocolortable"> | ||
| + | <tr><th><p class="s12">Material</p></th><th><p class="s12">Application Examples</p></th><th><p class="s12">Form of Supply</p></th></tr><tr><td><p class="s12">AgPd 30-60</p></td><td><p class="s12">Switches, relays, push-buttons,</p><p class="s12">connectors, sliding contacts</p></td><td><p class="s12">'''Semi-finished Materials:'''</p><p class="s12">Wires, micro profiles (weld tapes), clad</p><p class="s12">contact strips, seam-welded strips</p><p class="s12">'''Contact Parts:'''</p><p class="s12">Solid and composite rivets, weld buttons;</p><p class="s12">clad and welded contact parts, stamped parts</p></td></tr><tr><td><p class="s12">AgPd30Cu5</p></td><td><p class="s12">Sliding contacts, slider tracks</p></td><td><p class="s12">Wire-formed parts, contact springs, solid</p><p class="s12">and clad stamped parts</p></td></tr></table> | ||
| + | </figtable> | ||
===Silver Composite Materials=== | ===Silver Composite Materials=== | ||
| − | ====Silver-Nickel | + | ====Silver-Nickel Materials==== |
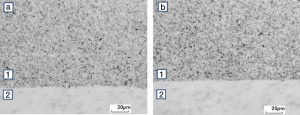
| − | Since silver and nickel are not soluble in each other in solid form and in the liquid | + | Since silver and nickel are not soluble in each other in solid form and also show very limited solubility in the liquid phase, silver nickel composite materials with higher Ni contents can only be produced by powder metallurgy. During extrusion of sintered Ag/Ni billets into wires, strips and rods, the Ni particles embedded in the Ag matrix are stretched and oriented in the microstructure into a pronounced fiber structure (<xr id="fig:Micro structure of AgNi9010"/><!--(Fig. 2.75)--> and <xr id="fig:Micro structure of AgNi 8020"/>)<!--(Fig. 2.76)--> |
| − | phase | + | |
| − | higher Ni contents can only be produced by powder metallurgy. During extrusion | + | The high density produced during hot extrusion, aids the arc erosion resistance of these materials (<xr id="tab:Physical Properties of Silver-Nickel (SINIDUR) Materials"/>)<!--(Tab 2.21)-->. The typical application of Ag/Ni contact materials is in devices for switching currents of up to 100A (<xr id="tab:Application Examples and Forms of Supply for Silver-Nickel (SINIDUR) Materials"/>)<!--(Table 2.24)-->. In this range, they are significantly more erosion resistant than silver or silver alloys. In addition, they exhibit with nickel contents < 20 wt% a low and over their operational lifetime consistent contact resistance and good arc moving properties. In DC applications Ag/Ni materials exhibit a relatively low tendency of material transfer distributed evenly over the contact surfaces (<xr id="tab:Contact and Switching Properties of Silver-Nickel (SINIDUR) Materials"/>)<!--(Table 2.23)-->. |
| − | of sintered Ag/Ni billets into wires, strips and rods the Ni particles embedded in | + | |
| − | the Ag matrix are stretched and oriented in the microstructure into a pronounced | + | Typically Ag/Ni materials are usually produced with contents of 10-40 wt% Ni. The most common used materials Ag/Ni 10 and Ag/Ni 20- and also Ag/Ni 15, mostly used in north america-, are easily formable and applied by cladding (<xr id="fig:Strain hardening of AgNi9010 by cold working"/>,<!--(Fig. 2.71)--> <xr id="fig:Softening of AgNi9010 after annealing"/>,<!--(Fig. 2.72)--> <xr id="fig:Strain hardening of AgNi8020"/>, <!--(Fig. 2.73)--> <xr id="fig:Softening of AgNi8020 after annealing"/>)<!--(Fig. 2.74)-->. They can be, without any additional welding aids, economically welded and brazed to the commonly used contact carrier materials. |
| − | fiber structure | + | The Ag/Ni materials with nickel contents of 30 and 40 wt% are used in switching devices, requiring a higher arc erosion resistance and where increases in contact resistance can be compensated through higher contact forces. |
| + | |||
| + | The most important applications for Ag/Ni contact materials are typically in relays, wiring devices, appliance switches, thermostatic controls, auxiliary switches and small contactors with nominal currents > 20A (<xr id="tab:Application Examples and Forms of Supply for Silver-Nickel (SINIDUR) Materials"/>)<!--(Table 2.24)-->. | ||
| − | + | <figtable id="tab:Physical Properties of Silver-Nickel (SINIDUR) Materials"> | |
| − | + | <caption>'''<!--Table 2.21:-->Physical Properties of Silver-Nickel Materials'''</caption> | |
| − | + | <table class="twocolortable"> | |
| − | + | <tr><th>Material</th><th>Silver Content</th><th>Density</th><th>Melting Point</th><th>ElectricalResistivity<i>p</i></th><th colspan="2">Electrical Resistivity (soft)</th></tr> | |
| − | + | <tr> | |
| − | + | <th></th><th>[wt%]</th><th>[g/cm<sup>3</sup>]</th><th>[°C]</th><th>[µΩ·cm]</th> | |
| − | + | <th>[% IACS]</th><th>[MS/m]</th></tr> | |
| − | + | <tr><td><p class="s11">Ag/Ni 90/10</p><p class="s11"></p></td><td><p class="s11">89 - 91</p></td><td><p class="s11">10.2 - 10.3</p></td><td><p class="s11">960</p></td><td><p class="s11">1.82 - 1.92</p></td><td><p class="s12">90 - 95</p></td><td><p class="s12">52 - 55</p></td></tr><tr><td><p class="s11">Ag/Ni 85/15</p><p class="s11"></p></td><td><p class="s11">84 - 86</p></td><td><p class="s11">10.1 - 10.2</p></td><td><p class="s11">960</p></td><td><p class="s11">1.89 - 2.0</p></td><td><p class="s12">86 - 91</p></td><td><p class="s12">50 - 53</p></td></tr><tr><td><p class="s11">Ag/Ni 80/20</p><p class="s11"></p></td><td><p class="s11">79 - 81</p></td><td><p class="s11">10.0 - 10.1</p></td><td><p class="s11">960</p></td><td><p class="s11">1.92 - 2.08</p></td><td><p class="s12">83 - 90</p></td><td><p class="s12">48 - 52</p></td></tr><tr><td><p class="s11">Ag/Ni 70/30</p><p class="s11"></p></td><td><p class="s11">69 - 71</p></td><td><p class="s11">9.8</p></td><td><p class="s11">960</p></td><td><p class="s11">2.44</p></td><td><p class="s12">71</p></td><td><p class="s12">41</p></td></tr><tr><td><p class="s11">Ag/Ni 60/40</p><p class="s11"></p></td><td><p class="s11">59 - 61</p></td><td><p class="s11">9.7</p></td><td><p class="s11">960</p></td><td><p class="s11">2.70</p></td><td><p class="s12">64</p></td><td><p class="s12">37</p></td></tr> | |
| + | </table> | ||
| + | </figtable> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <figtable id="tab:tab2.22"> | |
| − | + | <caption>'''<!-- Table 2.22:-->Mechanical Properties of Silver-Nickel Materials'''</caption> | |
| − | |||
| − | + | {| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px" | |
| + | |- | ||
| + | !Material | ||
| + | !Hardness Condition | ||
| + | !Tensile Strength R<sub>m</sub> [Mpa] | ||
| + | !Elongation A (soft annealed) [%] min. | ||
| + | !Vickers Hardness HV 10 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/Ni 90/10<br /> | ||
| + | |soft<br />R 220<br />R 280<br />R 340<br />R 400 | ||
| + | |< 250<br />220 - 280<br />280 - 340<br />340 - 400<br />> 400 | ||
| + | |25<br />20<br />3<br />2<br />1 | ||
| + | |< 50<br />50 - 70<br />65 - 90<br />85 - 105<br />> 100 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/Ni 85/15<br /> | ||
| + | |soft<br />R 300<br />R 350<br />R 380<br />R 400 | ||
| + | |< 275<br />250 - 300<br />300 - 350<br />350 - 400<br />> 400 | ||
| + | |20<br />4<br />2<br />2<br />1 | ||
| + | |< 70<br />70 - 90<br />85 - 105<br />100 - 120<br />> 115 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/Ni 80/20<br /> | ||
| + | |soft<br />R 300<br />R 350<br />R 400<br />R 450 | ||
| + | |< 300<br />300 - 350<br />350 - 400<br />400 - 450<br />> 450 | ||
| + | |20<br />4<br />2<br />2<br />1 | ||
| + | |< 80<br />80 - 95<br />90 - 110<br />100 - 125<br />> 120 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/Ni 70/30<br /> | ||
| + | |R 330<br />R 420<br />R 470<br />R 530 | ||
| + | |330 - 420<br />420 - 470<br />470 - 530<br />> 530 | ||
| + | |8<br />2<br />1<br />1 | ||
| + | |80<br />100<br />115<br />135 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/Ni 60/40<br /> | ||
| + | |R 370<br />R 440<br />R 500<br />R 580 | ||
| + | |370 - 440<br />440 - 500<br />500 - 580<br />> 580 | ||
| + | |6<br />2<br />1<br />1 | ||
| + | |90<br />110<br />130<br />150 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </figtable> | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | <div class="multiple-images"> | |
| − | Strain hardening | + | <figure id="fig:Strain hardening of AgNi9010 by cold working"> |
| − | of Ag/Ni 90/10 by cold working | + | [[File:Strain hardening of AgNi9010 by cold working.jpg|right|thumb|<caption>Strain hardening of Ag/Ni 90/10 by cold working</caption>]] |
| + | </figure> | ||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Softening of AgNi9010 after annealing"> | |
| − | Softening of Ag/Ni 90/10 | + | [[File:Softening of AgNi9010 after annealing.jpg|right|thumb|<caption>Softening of Ag/Ni 90/10 after annealing for 1 hr after 80% cold working</caption>]] |
| − | after annealing | + | </figure> |
| − | for 1 hr after 80% cold working | ||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Strain hardening of AgNi8020"> | |
| − | Strain hardening | + | [[File:Strain hardening of AgNi8020.jpg|right|thumb|<caption>Strain hardening of Ag/Ni 80/20 by cold working</caption>]] |
| − | of Ag/Ni 80/20 by cold working | + | </figure> |
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Softening of AgNi8020 after annealing"> | |
| − | Softening of Ag/Ni 80/20 | + | [[File:Softening of AgNi8020 after annealing.jpg|right|thumb|<caption>Softening of Ag/Ni 80/20 after annealing for 1 hr after 80% cold working</caption>]] |
| − | after annealing | + | </figure> |
| − | for 1 hr after 80% cold working | ||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Micro structure of AgNi9010"> | |
| − | b) parallel to the extrusion direction | + | [[File:Micro structure of AgNi9010.jpg|right|thumb|<caption>Micro structure of Ag/Ni 90/10 a) perpendicular to the extrusion direction b) parallel to the extrusion direction</caption>]] |
| + | </figure> | ||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Micro structure of AgNi 8020"> | |
| − | b) parallel | + | [[File:Micro structure of AgNi 8020.jpg|right|thumb|<caption>Micro structure of Ag/Ni 80/20 a) perpendicular to the extrusion direction b) parallel to the extrusion direction</caption>]] |
| + | </figure> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div class="clear"></div> | ||
| − | |||
| − | Table 2. | + | <figtable id="tab:Contact and Switching Properties of Silver-Nickel (SINIDUR) Materials"> |
| − | for Silver-Nickel (SINIDUR) Materials | + | <caption>'''<!-- Table 2.23:-->Contact and Switching Properties of Silver-Nickel Materials'''</caption> |
| + | |||
| + | {| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !Material | ||
| + | !Properties | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/Ni <br /> | ||
| + | |High arc erosion resistance at switching currents up to 100A,<br />Resistance against welding for starting current up to 100A,<br />low and over the electrical contact life nearly constant contact resistance for Ag/Ni 90/10 and Ag/Ni 80/20,<br />ow and spread-out material transfer under DC load,<br />non-conductive erosion residue on isolating components resulting in only minor change of the dielectric strength of switching devices,<br />good arc moving properties,<br />good arc extinguishing properties,<br />good or sufficient ductility depending on the Ni content,<br />easy to weld and braze | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </figtable> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <figtable id="tab:Application Examples and Forms of Supply for Silver-Nickel (SINIDUR) Materials"> | ||
| + | <caption>'''<!--Table 2.24:-->Application Examples and Forms of Supply for Silver-Nickel Materials'''</caption> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !Material | ||
| + | !Application Examples | ||
| + | !Switching or Nominal Current | ||
| + | !Form of Supply | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/Ni 90/10-80/20 | ||
| + | |Relays<br /> Automotive Relays - Resistive load - Motor load | ||
| + | |> 10A<br />> 10A | ||
| + | |rowspan="9" | '''Semi-finisched Materials:'''<br />Wires, profiles,<br />clad strips,<br />Seam-welded strips,<br />Toplay strips <br />'''Contact Parts:'''<br />Contact tips, solid<br />and composite<br />rivets, Weld buttons,<br />clad, welded,<br />brazed, and riveted<br />contact parts | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/Ni 90/10, Ag/Ni 85/15-80/20 | ||
| + | |Auxiliary current switches | ||
| + | |≤ 100A | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/Ni 90/10-80/20 | ||
| + | |Appliance switches | ||
| + | |≤ 50A | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/Ni 90/10 | ||
| + | |Wiring devices | ||
| + | |≤ 20A | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/Ni 90/10 | ||
| + | |Main switches, Automatic staircase illumination switches | ||
| + | |≤ 100A | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/Ni 90/10-80/20 | ||
| + | |Control<br />Thermostats | ||
| + | |> 10A<br />≤ 50A | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/Ni 90/10-80/20 | ||
| + | |Load switches | ||
| + | |≤ 20A | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/Ni 90/10-80/20 | ||
| + | |Contactors circuit breakers | ||
| + | |≤ 100A | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/Ni 90/10-80/20<br />paired with Ag/C 97/3-96/4 | ||
| + | |Motor protective circuit breakers | ||
| + | |≤ 40A | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/Ni 80/20-60/40<br />paired with Ag/C 96/4-95/5 | ||
| + | |Fault current circuit breakers | ||
| + | |≤ 100A | ||
| + | |rowspan="2" | Rods, Profiles,<br />Contact tips, Formed parts,<br />brazed and welded<br />contact parts | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/Ni 80/20-60/40<br />paired with Ag/C 96/4-95/5 | ||
| + | |Power switches | ||
| + | |> 100A | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </figtable> | ||
==== Silver-Metal Oxide Materials Ag/CdO, Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub>, Ag/ZnO==== | ==== Silver-Metal Oxide Materials Ag/CdO, Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub>, Ag/ZnO==== | ||
| − | The family of silver-metal oxide contact materials includes the material groups: | + | The family of silver-metal oxide contact materials includes the material groups: silver-cadmium oxide, silver-tin oxide, and silverzinc oxide. Because of their very good contact and switching properties like high resistance against welding, low contact resistance, and high arc erosion resistance, silver-metal oxides have gained an outstanding position in a broad field of applications. They are mainly used in low voltage electrical switching devices like relays, installation and distribution switches, appliances, industrial controls, motor controls, and protective devices (<xr id="tab:Application Examples of Silver–Metal Oxide Materials"/>)<!--(Table 2.31)-->. |
| − | silver-cadmium oxide | ||
| − | oxide | ||
| − | properties like high resistance against welding, low contact resistance, and high | ||
| − | arc erosion resistance, silver-metal oxides have gained an outstanding position | ||
| − | in a broad field of applications. They mainly | ||
| − | switching devices like relays, installation and distribution switches, appliances, | ||
| − | industrial controls, motor controls, and protective devices | ||
| − | *Silver-cadmium oxide | + | *'''Silver-cadmium oxide materials''' |
| − | Silver-cadmium oxide | + | Silver-cadmium oxide materials with 10-15 wt% are produced by both, internal oxidation and powder metallurgical methods. |
| − | by both, internal oxidation and powder metallurgical methods | ||
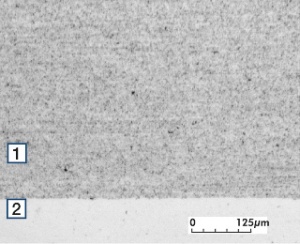
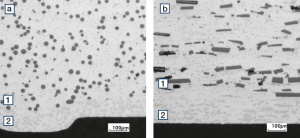
| − | The manufacturing of strips and wires by internal oxidation starts with a molten | + | The manufacturing of strips and wires by internal oxidation starts with a molten alloy of silver and cadmium. During a heat treatment below it's melting point in an oxygen rich atmosphere of such a homogeneous alloy, the oxygen diffuses from the surface into the bulk of the material and oxidizes the Cd to CdO in a more or less fine particle precipitation inside the Ag matrix. The CdO particles are rather fine in the surface area and getting larger towards the center of the material (<xr id="fig:Micro structure of AgCdO9010"/>)<!--(Fig. 2.83)-->. |
| − | alloy of silver and cadmium. During a heat treatment below it's melting point in | ||
| − | oxygen rich atmosphere | ||
| − | the surface into the bulk of the material and oxidizes the Cd to CdO in a more or | ||
| − | less fine particle precipitation inside the Ag matrix. The CdO particles are rather | ||
| − | fine in the surface area and | ||
| − | of the material | ||
| − | During the manufacturing of Ag/CdO contact material by internal oxidation the | + | During the manufacturing of Ag/CdO contact material by internal oxidation, the processes vary depending on the type of semi-finished material. For Ag/CdO wires, a complete oxidation of the AgCd wire is performed, followed by wire-drawing to the required diameter (<xr id="fig:Strain hardening of internally oxidized AgCdO9010"/><!--(Figs. 2.77)--> and <xr id="fig:Softening of internally oxidized AgCdO9010"/>)<!--(Fig. 2.78)-->. The resulting material is used for example, in the production of contact rivets. For Ag/CdO strip materials two processes are commonly used: Cladding of an AgCd alloy strip with fine silver, followed by complete oxidation, results in a strip material with a small depletion area in the center of it's thickness and an Ag backing suitable for easy attachment by brazing (sometimes called "Conventional Ag/CdO"). Using a technology that allows the partial oxidation of a dual-strip AgCd alloy material in a higher pressure pure oxygen atmosphere, yields a composite Ag/CdO strip material that has - besides a relatively fine CdO precipitation - also an easily brazable AgCd alloy backing. These materials are mainly used as the basis for contact profiles and contact tips. |
| − | processes vary depending on the type of semi-finished material. | ||
| − | For Ag/CdO wires a complete oxidation of the AgCd wire is performed, followed | ||
| − | by wire-drawing to the required diameter | ||
| − | material is used for example in the production of contact rivets. For Ag/CdO strip | ||
| − | materials two processes are commonly used: Cladding of an AgCd alloy strip | ||
| − | with fine silver followed by complete oxidation results in a strip material with a | ||
| − | small depletion area in the center of it's thickness and | ||
| − | easy attachment by brazing (sometimes called | ||
| − | a technology that allows the partial oxidation of a dual-strip AgCd alloy material | ||
| − | in a higher pressure pure oxygen atmosphere yields a composite Ag/CdO strip | ||
| − | material that has besides a relatively fine CdO precipitation also | ||
| − | AgCd alloy backing | ||
| − | used as the basis for contact profiles and contact tips. | ||
| − | During powder metallurgical production the powder mixed made by different | + | During powder metallurgical production, the powder mixed made by different processes are typically converted by pressing, sintering and extrusion to wires and strips. The high degree of deformation during hot extrusion, produces a uniform and fine dispersion of CdO particles in the Ag matrix while at the same time achieving a high density which is advantageous for good contact properties (<xr id="fig:Micro structure of AgCdO9010P"/>)<!--(Fig. 2.84)-->. To obtain a backing suitable for brazing, a fine silver layer is applied by either com-pound extrusion or hot cladding prior to or right after the extrusion. |
| − | processes are typically converted by pressing, sintering and extrusion to wires | ||
| − | and strips. The high degree of deformation during hot extrusion produces a | ||
| − | uniform and fine dispersion of CdO particles in the Ag matrix while at the same | ||
| − | time achieving a high density which is advantageous for good contact properties | ||
| − | |||
| − | by either com-pound extrusion or hot cladding prior to or right after the extrusion | ||
| − | |||
| − | For larger contact tips, and especially those with a rounded shape, the single tip | + | For larger contact tips, and especially those with a rounded shape, the single tip Press-Sinter-Repress process (PSR) offers economical advantages. The powder mix is pressed into a die close to the final desired shape, the "green" tips are sintered, and in most cases, the repress process forms the exact final shape while at the same time, increasing the contact density and hardness. |
| − | Press-Sinter-Repress process (PSR) offers economical advantages. The | ||
| − | powder mix is pressed | ||
| − | are sintered, and in most cases the repress process forms the final | ||
| − | while at the same time increasing the contact density and hardness. | ||
| − | Using different silver powders and minor additives for the basic Ag and CdO | + | Using different silver powders and minor additives for the basic Ag and CdO, starting materials can help influence certain contact properties for specialized applications. |
| − | starting materials can help influence certain contact properties for specialized | ||
| − | applications. | ||
| − | + | <div class="multiple-images"> | |
| − | Strain hardening of internally oxidized | + | <figure id="fig:Strain hardening of internally oxidized AgCdO9010"> |
| − | Ag/CdO 90/10 by cold working | + | [[File:Strain hardening of internally oxidized AgCdO9010.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Strain hardening of internally oxidized Ag/CdO 90/10 by cold working</caption>]] |
| + | </figure> | ||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Softening of internally oxidized AgCdO9010"> | |
| − | Softening of internally oxidized | + | [[File:Softening of internally oxidized AgCdO9010.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Softening of internally oxidized (i.o.) Ag/CdO 90/10 after annealing for 1 hr after 40% cold working</caption>]] |
| − | Ag/CdO 90/10 after annealing | + | </figure> |
| − | for 1 hr after 40% cold working | ||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Strain hardening of AgCdO9010P"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Strain hardening of AgCdO9010P.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Strain hardening of powder metallurgical (p.m.) Ag/CdO 90/10 by cold working</caption>]] | |
| − | ( | + | </figure> |
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Softening of AgCdO9010P after annealing"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Softening of AgCdO9010P after annealing.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Softening of powder metallurgical Ag/CdO 90/10 after annealing for 1 hr after 40% cold working</caption>]] | |
| − | Ag/CdO 90/10 | + | </figure> |
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Strain hardening of AgCdO8812"> | |
| − | of Ag/CdO | + | [[File:Strain hardening of AgCdO8812.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Strain hardening of powder metallurgical Ag/CdO 88/12</caption>]] |
| − | + | </figure> | |
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Softening of AgCdO8812WP after annealing"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Softening of AgCdO8812WP after annealing.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Softening of powder metallurgical Ag/CdO 88/12 after annealing for 1 hr after different degrees of cold working</caption>]] | |
| − | of Ag/CdO 88/12 | + | </figure> |
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Micro structure of AgCdO9010"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Micro structure of AgCdO9010.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Micro structure of Ag/CdO 90/10 i.o. a) close to surface b) in center area</caption>]] | |
| − | + | </figure> | |
| − | |||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Micro structure of AgCdO9010P"> | |
| − | b) | + | [[File:Micro structure of AgCdO9010P.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Micro structure of Ag/CdO 90/10 p.m.: a) perpendicular to extrusion direction b) parallel to extrusion direction</caption>]] |
| + | </figure> | ||
| − | + | </div> | |
| − | + | <div class="clear"></div> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *'''Silver–tin oxide materials''' | |
| − | + | Over the past years, many Ag/CdO contact materials have been replaced by Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> based materials with 2-14 wt% SnO<sub>2</sub> because of the toxicity of Cadmium. This changeover was further favored by the fact that Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> contacts quite often show improved contact and switching properties such as lower arc erosion, higher weld resistance and a significant lower tendency towards material transfer in DC switching circuits (<xr id="tab:Contact and Switching Properties of Silver–Metal Oxide Materials"/>)<!--(Table 2.30)-->. Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> materials have been optimized for a broad range of applications by other metal oxide additives and modification in the manufacturing processes that result in different metallurgical, physical and electrical properties (<xr id="tab:tab2.28"/><!--(Tab. 2.28)--> and <xr id="tab:tab2.29"/>)<!--(Table 2.29)-->. | |
| − | + | Manufacturing of Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> by ''internal oxidation'' is possible in principle, but during heat treatment of alloys containing > 5 wt% of tin in oxygen, dense oxide layers formed on the surface of the material prohibit the further diffusion of oxygen into the bulk of the material. By adding Indium or Bismuth to the alloy, the internal oxidation is possible and results in materials that typically are rather hard and brittle and may show somewhat elevated contact resistance and is limited to applications in relays. Adding a brazable fine silver layer to such materials results in a semifinished material, suitable for the manufacture as smaller weld profiles (<xr id="fig:Micro structure of Ag SnO2 92 8 WTOS F"/>)<!--(Fig. 2.116)-->. Because of their resistance to material transfer and low arc erosion, these materials find for example a broader application in automotive relays (<xr id="tab:Application Examples of Silver–Metal Oxide Materials"/>)<!--(Table 2.31)-->. | |
| − | |||
| − | Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | materials | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ''Powder metallurgy'' plays a significant role in the manufacturing of Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> contact materials. Besides SnO<sub>2</sub> a smaller amount (<1 wt%) of one or more other metal oxides such as WO<sub>3</sub>, MoO<sub>3</sub>, CuO and/or Bi<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub> are added. These | |
| − | + | additives improve the wettability of the oxide particles and increase the viscosity of the Ag melt. They also provide additional benefits to the mechanical and arcing contact properties of materials in this group (<xr id="tab:tab2.26"/>)<!--(Table 2.26)-->. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | ( | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <figtable id="tab:tab2.26"> | |
| − | + | <caption>'''<!--Table 2.26:--> Physical and Mechanical Properties as well as Manufacturing Processes and Forms of Supply of Extruded Silver-Tin Oxide Contact Materials'''</caption> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | of | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | {| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px" | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | !Material | |
| − | + | !Silver Content<br />[wt%] | |
| − | + | !Additives | |
| + | !Theoretical<br />Density<br />[g/cm<sup>3</sup>] | ||
| + | !Electrical<br />Conductivity<br />[MS/m] | ||
| + | !Vickers<br />Hardness<br />[HV0,1] | ||
| + | !Tensile<br />Strength<br />[MPa] | ||
| + | !Elongation (soft annealed)<br />A[%]min. | ||
| + | !Manufacturing<br />Process | ||
| + | !Form of Supply | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 98/2 SPW | ||
| + | |97 - 99 | ||
| + | |WO<sub>3</sub> | ||
| + | |10,4 | ||
| + | |59 ± 2 | ||
| + | |57 ± 15 | ||
| + | |215 | ||
| + | |35 | ||
| + | |Powder Metallurgy | ||
| + | |1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 92/8 SPW | ||
| + | |91 - 93 | ||
| + | |WO<sub>3</sub> | ||
| + | |10,1 | ||
| + | |51 ± 2 | ||
| + | |62 ± 15 | ||
| + | |255 | ||
| + | |25 | ||
| + | |Powder Metallurgy | ||
| + | |1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 90/10 SPW | ||
| + | |89 - 91 | ||
| + | |WO<sub>3</sub> | ||
| + | |10 | ||
| + | |47 ± 5 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |250 | ||
| + | |25 | ||
| + | |Powder Metallurgy | ||
| + | |1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 88/12 SPW | ||
| + | |87 - 89 | ||
| + | |WO<sub>3</sub> | ||
| + | |9.9 | ||
| + | |46 ± 5 | ||
| + | |67 ± 15 | ||
| + | |270 | ||
| + | |20 | ||
| + | |Powder Metallurgy | ||
| + | |1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 92/8 SPW4 | ||
| + | |91 - 93 | ||
| + | |WO<sub>3</sub> | ||
| + | |10,1 | ||
| + | |51 ± 2 | ||
| + | |62 ± 15 | ||
| + | |255 | ||
| + | |25 | ||
| + | |Powder Metallurgy | ||
| + | |1,2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 90/10 SPW4 | ||
| + | |89 - 91 | ||
| + | |WO<sub>3</sub> | ||
| + | |10 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |Powder Metallurgy | ||
| + | |1,2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 88/12 SPW4<br /> | ||
| + | |87 - 89 | ||
| + | |WO<sub>3</sub> | ||
| + | |9,8 | ||
| + | |46 ± 5 | ||
| + | |80 ± 10 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |Powder Metallurgy | ||
| + | |1,2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 88/12 SPW6 | ||
| + | |87 - 89 | ||
| + | |MoO<sub>3</sub> | ||
| + | |9.8 | ||
| + | |42 ± 5 | ||
| + | |70 ± 10 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |Powder Metallurgy | ||
| + | |2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 97/3 SPW7 | ||
| + | |96 - 98 | ||
| + | |Bi<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub> and WO<sub>3</sub> | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |Powder Metallurgy | ||
| + | |2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 90/10 SPW7 | ||
| + | |89 - 91 | ||
| + | |Bi<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub> and WO<sub>3</sub> | ||
| + | |9,9 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |Powder Metallurgy | ||
| + | |2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 88/12 SPW7 | ||
| + | |87 - 89 | ||
| + | |Bi<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub> and WO<sub>3</sub> | ||
| + | |9.8 | ||
| + | |42 ± 5 | ||
| + | |70 ± 10 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |Powder Metallurgy | ||
| + | |2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 98/2 PMT1 | ||
| + | |97 - 99 | ||
| + | |Bi<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub> and CuO | ||
| + | |10,4 | ||
| + | |57 ± 2 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |215 | ||
| + | |35 | ||
| + | |Powder Metallurgy | ||
| + | |1,2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 96/4 PMT1 | ||
| + | |95 - 97 | ||
| + | |Bi<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub> and CuO | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |Powder Metallurgy | ||
| + | |1,2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 94/6 PMT1 | ||
| + | |93 - 95 | ||
| + | |Bi<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub> and CuO | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |Powder Metallurgy | ||
| + | |1,2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 92/8 PMT1 | ||
| + | |91 - 93 | ||
| + | |Bi<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub> and CuO | ||
| + | |10 | ||
| + | |50 ± 2 | ||
| + | |62 ± 15 | ||
| + | |240 | ||
| + | |25 | ||
| + | |Powder Metallurgy | ||
| + | |1,2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 90/10 PMT1 | ||
| + | |89 - 91 | ||
| + | |Bi<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub> and CuO | ||
| + | |10 | ||
| + | |48 ± 2 | ||
| + | |65 ± 15 | ||
| + | |240 | ||
| + | |25 | ||
| + | |Powder Metallurgy | ||
| + | |1,2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 88/12 PMT1 | ||
| + | |87 - 89 | ||
| + | |Bi<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub> and CuO | ||
| + | |9,9 | ||
| + | |46 ± 5 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |260 | ||
| + | |20 | ||
| + | |Powder Metallurgy | ||
| + | |1,2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 90/10 PE | ||
| + | |89 - 91 | ||
| + | |Bi<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub> and CuO | ||
| + | |9,8 | ||
| + | |48 ± 2 | ||
| + | |55 - 100 | ||
| + | |230 - 330 | ||
| + | |28 | ||
| + | |Powder Metallurgy | ||
| + | |1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 88/12 PE | ||
| + | |87 - 89 | ||
| + | |Bi<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub> and CuO | ||
| + | |9,7 | ||
| + | |46 ± 5 | ||
| + | |60 - 106 | ||
| + | |235 - 330 | ||
| + | |25 | ||
| + | |Powder Metallurgy | ||
| + | |1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 88/12 PMT2 | ||
| + | |87 - 89 | ||
| + | |CuO | ||
| + | |9,9 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |90 ± 10 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |Powder Metallurgy | ||
| + | |1,2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 86/14 PMT3 | ||
| + | |85 - 87 | ||
| + | |Bi<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub> and CuO | ||
| + | |9,8 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |95 ± 10 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |Powder Metallurgy | ||
| + | |2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 94/6 LC1 | ||
| + | |93 - 95 | ||
| + | |Bi<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub> and In<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub> | ||
| + | |9,8 | ||
| + | |45 ± 5 | ||
| + | |55 ± 10 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |Powder Metallurgy | ||
| + | |2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 90/10 POX1 | ||
| + | |89 - 91 | ||
| + | |In<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub> | ||
| + | |9,9 | ||
| + | |50 ± 5 | ||
| + | |85 ± 15 | ||
| + | |310 | ||
| + | |25 | ||
| + | |Internal Oxidation | ||
| + | |1,2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 90/10 POX1 | ||
| + | |87 - 89 | ||
| + | |In<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub> | ||
| + | |9,8 | ||
| + | |48 ± 5 | ||
| + | |90 ± 15 | ||
| + | |325 | ||
| + | |25 | ||
| + | |Internal Oxidation | ||
| + | |1,2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 90/10 POX1 | ||
| + | |85 - 87 | ||
| + | |In<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub> | ||
| + | |9,6 | ||
| + | |45 ± 5 | ||
| + | |95 ± 15 | ||
| + | |330 | ||
| + | |20 | ||
| + | |Internal Oxidation | ||
| + | |1,2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </figtable> | ||
| − | + | 1 = Wires, Rods, Contact rivets, 2 = Strips, Profiles, Contact tips | |
| − | |||
| − | :''' | + | In the manufacture for the initial powder mixes, different processes are applied which provide specific advantages of the resulting materials in respect to their contact properties <!--[[#figures|(Figs. 43 – 75)]]-->. Some of them are described here as follows: |
| + | :'''a) Powder blending from single component powders''' <br> In this common process all components, including additives that are part of the powder mix, are blended as single powders. The blending is usually performed in the dry stage in blenders of different design. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :'''b) Powder blending on the basis of doped powders''' <br> For incorporation of additive oxides in the SnO<sub>2</sub> powder, the reactive spray process has shown advantages. This process starts with a waterbased solution of the tin and other metal compounds. This solution is nebulized under high pressure and temperature in a reactor chamber. Through the rapid evaporation of the water, each small droplet is converted into a salt crystal and from there gets transformed by oxidation into a tin oxide particle in which the additive metals are distributed evenly as oxides. The so created doped AgSnO<sub>2</sub> powder is then mechanically mixed with silver powder. | ||
| − | :''' | + | :'''c) Powder blending based on coated oxide powders''' <br> In this process, tin oxide powder is blended with lower melting additive oxides such as for example Ag<sub>2</sub> MoO<sub>4</sub> and then heat treated. The SnO<sub>2</sub> particles are coated in this step with a thin layer of the additive oxide. |
| − | + | :'''d) Powder blending based on internally oxidized alloy powders''' <br> A combination of powder metallurgy and internal oxidation this process starts with atomized Ag alloy powder which is subsequently oxidized in pure oxygen. During this process the Sn and other metal components are transformed to metal oxide and precipitated inside the silver matrix of each powder particle. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | :'''e) Powder blending based on chemically precipitated compound powders''' <br> A silver salt solution is added to a suspension of for example SnO<sub>2</sub> together with a precipitation agent. In a chemical reaction, silver and silver oxide respectively are precipitated around the additive metal oxide particles, who act as crystallization sites. Further chemical treatment then reduces the silver oxide with the resulting precipitated powder, being a mix of Ag and SnO<sub>2</sub>. | |
| − | |||
| − | Ag | ||
| − | + | Further processing of these differently produced powders follows the conventional processes of pressing, sintering and hot extrusion to wires and strips. From these contact parts, contact rivets and tips are manufactured. To obtain a brazable backing, the same processes as used for Ag/CdO are applied. As for Ag/CdO, larger contact tips can also be manufactured using the press-sinter-repress (PSR) process (<xr id="tab:Physical Properties of Powder Metallurgical Silver-Metal Oxide Materials with Fine Silver Backing Produced by the Press-Sinter-Repress Process"/>)<!--(Table 2.27)-->. | |
| − | + | <div id="figures"> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <div class="multiple-images"> | |
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Strain hardening of AgSNO2 92 8 PE"> | |
| + | [[File:Strain hardening of AgSNO2 92 8 PE.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Strain hardening of Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 92/8 PE by cold working</caption>]] | ||
| + | </figure> | ||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Softening of AgSnO2 92 8 PE"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Softening of AgSnO2 92 8 PE.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Softening of Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 92/8 PE after annealing for 1 hr after 40% cold working</caption>]] | |
| − | Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> | + | </figure> |
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Strain hardening of Ag SnO2 88 12 PE"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Strain hardening of Ag SnO2 88 12 PE.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Strain hardening of Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 88/12 PE by cold working</caption>]] | |
| − | + | </figure> | |
| − | |||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Softening of Ag SnO2 88 12 PE after annealing"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Softening of Ag SnO2 88 12 PE after annealing.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Softening of Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 88/12 PE after annealing for 1 hr after 40% cold working</caption>]] | |
| − | Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 88/12 | + | </figure> |
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Strain hardening of oxidized AgSnO2 88 12 PW4"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Strain hardening of oxidized AgSnO2 88 12 PW4.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Strain hardening of oxidized Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 88/12 PW4 by cold working</caption>]] | |
| − | + | </figure> | |
| − | |||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Softening of Ag SnO2 88 12 PW4 after annealing"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Softening of Ag SnO2 88 12 PW4 after annealing.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Softening of Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 88/12 PW4 after annealing for 1 hr after 30% cold working</caption>]] | |
| − | Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> | + | </figure> |
| − | |||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Strain hardening of internally oxidized Ag SnO2 88 12 TOS F"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Strain hardening of internally oxidized Ag SnO2 88 12 TOS F.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Strain hardening of internally oxidized Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 88/12 TOS F by cold working</caption>]] | |
| − | Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> | + | </figure> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | cold working | ||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Softening of Ag SnO2 88 12 TOS F after annealing"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Softening of Ag SnO2 88 12 TOS F after annealing.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Softening of Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 88/12 TOS F after annealing for 1 hr after 30% cold working</caption>]] | |
| − | of Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> | + | </figure> |
| − | |||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Strain hardening of internally oxidized Ag SnO2 88 12P"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Strain hardening of internally oxidized Ag SnO2 88 12P.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Strain hardening of internally oxidized Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 88/12P by cold working</caption>]] | |
| − | Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> | + | </figure> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Softening of Ag SnO2 88 12P after annealing"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Softening of Ag SnO2 88 12P after annealing.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Softening of Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 88/12 SP after annealing for 1 hr after 40% cold working</caption>]] | |
| − | + | </figure> | |
| − | Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 88/12 | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Strain hardening of Ag SnO2 88 12 WPD"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Strain hardening of Ag SnO2 88 12 WPD.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Strain hardening of Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 88/12 WPD by cold working</caption>]] | |
| − | Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 88/12 | + | </figure> |
| − | |||
| − | cold working | ||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Softening of Ag SnO2 88 12 WPD after annealing"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Softening of Ag SnO2 88 12 WPD after annealing.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Softening of Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 88/12 WPD after annealing for 1 hr after different degrees of cold working</caption>]] | |
| − | + | </figure> | |
| − | Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 88/ | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Micro structure of Ag SnO2 92 8 PE"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Micro structure of Ag SnO2 92 8 PE.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Micro structure of Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 92/8 PE: a) perpendicular to extrusion direction b) parallel to extrusion direction</caption>]] | |
| − | Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> | + | </figure> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Micro structure of Ag SnO2 88 12 PE"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Micro structure of Ag SnO2 88 12 PE.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Micro structure of Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 88/12 PE: a) perpendicular to extrusion direction b) parallel to extrusion direction</caption>]] | |
| − | Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 88/12 | + | </figure> |
| − | |||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Micro structure of Ag SnO2 88 12 PW"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Micro structure of Ag SnO2 88 12 PW.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Micro structure of Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 88/12 SPW: a) perpendicular to extrusion direction b) parallel to extrusion direction</caption>]] | |
| − | + | </figure> | |
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Micro structure of Ag SnO2 88 12 TOS F"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Micro structure of Ag SnO2 88 12 TOS F.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Micro structure of Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 88/12 TOS F: a) perpendicular to extrusion direction b) parallel to extrusion direction</caption>]] | |
| − | Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> | + | </figure> |
| − | |||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Micro structure of Ag SnO2 92 8 WTOS F"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Micro structure of Ag SnO2 92 8 WTOS F.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Micro structure of Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 92/8 WTOS F: a) perpendicular to extrusion direction b) parallel to extrusion direction,1) AgSnO2 contact layer, 2) Ag backing layer</caption>]] | |
| − | + | </figure> | |
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Micro structure of Ag SnO2 88 12 WPD"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Micro structure of Ag SnO2 88 12 WPD.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Micro structure of Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 88/12 WPD: parallel to extrusion direction 1) AgSnO2 contact layer, 2) Ag backing layer</caption>]] | |
| − | Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> 88/12 WPD | + | </figure> |
| − | |||
| − | + | <div class="clear"></div> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <figtable id="tab:Physical Properties of Powder Metallurgical Silver-Metal Oxide Materials with Fine Silver Backing Produced by the Press-Sinter-Repress Process"> | |
| − | + | <caption>'''<!--Table 2.27:-->Physical Properties of Powder Metallurgical Silver-Metal Oxide Materials with Fine Silver Backing Produced by the Press-Sinter-Repress Process'''</caption> | |
| − | + | <table class="twocolortable"> | |
| − | + | <tr><th rowspan="2"><p class="s11">Material</p><p class="s11"></p></th><th rowspan="2"><p class="s11">Additives</p></th><th rowspan="2"><p class="s11">Density</p><p class="s11">[ g/cm<sup>3</sup>]</p></th><th rowspan="2"><p class="s11">Electrical</p><p class="s11">Resistivity</p><p class="s11">[µ<span class="s14">S ·</span>cm]</p></th><th colspan="2"><p class="s11">Electrical</p><p class="s11">Conductivity</p></th><th rowspan="2"><p class="s11">Vickers</p><p class="s11">Hardness</p><p class="s11">HV 10.</p></th></tr> | |
| + | <tr><th><p class="s11">[%IACS]</p></th><th><p>[MS/m]</p></th></tr> | ||
| + | <tr><td><p class="s11">AgCdO 90/10</p><p class="s11"></p></td><td/><td><p class="s11">10.1</p></td><td><p class="s11">2.08</p></td><td><p class="s12">83</p></td><td><p class="s12">48</p></td><td><p class="s11">60</p></td></tr><tr><td><p class="s11">AgCdO 85/15 </p></td><td/><td><p class="s11">9.9</p></td><td><p class="s11">2.27</p></td><td><p class="s12">76</p></td><td><p class="s12">44</p></td><td><p class="s11">65</p></td></tr><tr><td><p class="s11">AgSnO<sub>2</sub> 90/10</p></td><td><p class="s11">CuO and</p><p class="s11">Bi<sub>2</sub> O<sub>3</sub></p></td><td><p class="s11">9.8</p></td><td><p class="s11">2.22</p></td><td><p class="s12">78</p></td><td><p class="s12">45</p></td><td><p class="s11">55</p></td></tr><tr><td><p class="s11">AgSnO<sub>2</sub> 88/12</p></td><td><p class="s11">CuO and</p><p class="s11">Bi<sub>2</sub> O<sub>3</sub></p></td><td><p class="s11">9.6</p></td><td><p class="s11">2.63</p></td><td><p class="s12">66</p></td><td><p class="s12">38</p></td><td><p class="s11">60</p></td></tr></table> | ||
| + | Form of Support: formed parts, stamped parts, contact tips | ||
| + | </figtable> | ||
| − | + | *'''Silver–zinc oxide materials''' | |
| − | + | Silver zinc oxide contact materials with mostly 6 - 10 wt% oxide content, including other small metal oxides, are produced exclusively by powder metallurgy [[#figures1|(Figs. 58 – 63)]]<!--(Table 2.28)-->. Adding WO<sub>3</sub> or Ag<sub>2</sub>WO<sub>4</sub> in the process - as described in the preceding chapter on Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> - has proven most effective for applications in AC relays, wiring devices, and appliance controls. Just like with the other Ag metal oxide materials, semi-finished materials in strip and wire form are used to manufacture contact tips and rivets. Because of their high resistance against welding and arc erosion Ag/ZnO materials present an economic alternative to Cd free Ag-tin oxide contact materials (<xr id="tab:Contact and Switching Properties of Silver–Metal Oxide Materials"/><!--(Tab. 2.30)--> and <xr id="tab:Application Examples of Silver–Metal Oxide Materials"/>)<!--(Tab. 2.31)-->. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <figtable id="tab:tab2.28"> | |
| − | + | <caption>'''<!--Table 2.28:--> Physical and Mechanical Properties as well as Manufacturing Processes and Forms of Supply of Extruded Silver-Zinc Oxide Contact'''</caption> | |
| − | + | {| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px" | |
| − | + | |- | |
| + | !Material | ||
| + | !Silver Content<br />[wt%] | ||
| + | !Additives | ||
| + | !Density<br />[g/cm<sup>3</sup>] | ||
| + | !Electrical<br />Resistivity<br />[μΩ·cm] | ||
| + | !colspan="2" style="text-align:center"|Electrical<br />Conductivity<br />[% IACS] [MS/m] | ||
| + | !Vickers<br />Hardness<br />Hv1 | ||
| + | !Tensile<br />Strength<br />[MPa] | ||
| + | !Elongation<br />(soft annealed)<br />A[%]min. | ||
| + | !Manufacturing<br />Process | ||
| + | !Form of<br />Supply | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/ZnO 92/8P<br /> | ||
| + | |91 - 93 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |9.8 | ||
| + | |2.22 | ||
| + | |78 | ||
| + | |45 | ||
| + | |60 - 95 | ||
| + | |220 - 350 | ||
| + | |25 | ||
| + | |Powder Metallurgy<br />a) indiv. powders | ||
| + | |1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/ZnO 92/8PW25<br /> | ||
| + | |91 - 93 | ||
| + | |Ag<sub>2</sub>WO<sub>4</sub> | ||
| + | |9.6 | ||
| + | |2.08 | ||
| + | |83 | ||
| + | |48 | ||
| + | |65 - 105 | ||
| + | |230 - 340 | ||
| + | |25 | ||
| + | |Powder Metallurgy<br />c) coated | ||
| + | |1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/ZnO 90/10PW25<br /> | ||
| + | |89 - 91 | ||
| + | |Ag<sub>2</sub>WO<sub>4</sub> | ||
| + | |9.6 | ||
| + | |2.17 | ||
| + | |79 | ||
| + | |46 | ||
| + | |65 - 100 | ||
| + | |230 - 350 | ||
| + | |20 | ||
| + | |Powder Metallurgy<br />c) coated | ||
| + | |1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/ZnO 92/8WP<br /> | ||
| + | |91 - 93 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |9.8 | ||
| + | |2.0 | ||
| + | |86 | ||
| + | |50 | ||
| + | |60 - 95 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |Powder Metallurgy<br />with Ag backing a) individ. | ||
| + | |2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/ZnO 92/8WPW25<br /> | ||
| + | |91 - 93 | ||
| + | |Ag<sub>2</sub>WO<sub>4</sub> | ||
| + | |9.6 | ||
| + | |2.08 | ||
| + | |83 | ||
| + | |48 | ||
| + | |65 - 105 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |Powder Metallurgy<br />c) coated | ||
| + | |2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/ZnO 90/10WPW25<br /> | ||
| + | |89 - 91 | ||
| + | |Ag<sub>2</sub>WO<sub>4</sub> | ||
| + | |9.6 | ||
| + | |2.7 | ||
| + | |79 | ||
| + | |46 | ||
| + | |65 - 110 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |Powder Metallurgy<br />c) coated | ||
| + | |2 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </figtable> | ||
| − | + | 1 = Wires, Rods, Contact rivets, 2 = Strips, Profiles, Contact tips | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <div class="multiple-images"> | |
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Strain hardening of Ag ZnO 92 8 PW25"> | |
| + | [[File:Strain hardening of Ag ZnO 92 8 PW25.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Strain hardening of Ag/ZnO 92/8 PW25 by cold working</caption>]] | ||
| + | </figure> | ||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Softening of Ag ZnO 92 8 PW25"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Softening of Ag ZnO 92 8 PW25.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Softening of Ag/ZnO 92/8 PW25 after annealing for 1 hr after 30% cold working</caption>]] | |
| + | </figure> | ||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Strain hardening of Ag ZnO 92 8 WPW25"> | |
| − | Ag | + | [[File:Strain hardening of Ag ZnO 92 8 WPW25.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Strain hardening of Ag/ZnO 92/8 WPW25 by cold working</caption>]] |
| − | + | </figure> | |
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Softening of Ag ZnO 92 8 WPW25"> | |
| − | Ag | + | [[File:Softening of Ag ZnO 92 8 WPW25.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Softening of Ag/ZnO 92/8 WPW25 after annealing for 1hr after different degrees of cold working</caption>]] |
| − | + | </figure> | |
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Micro structure of Ag ZnO 92 8 PW25"> | |
| − | b) parallel to extrusion direction | + | [[File:Micro structure of Ag ZnO 92 8 Pw25.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Micro structure of Ag/ZnO 92/8 PW25: a) perpendicular to extrusion direction b) parallel to extrusion direction</caption>]] |
| + | </figure> | ||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Micro structure of Ag ZnO 92 8 WPW25"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Micro structure of Ag ZnO 92 8 WPW25.jpg|right|thumb|<caption>Micro structure of Ag/ZnO 92/8 WPW25:a) perpendicular to extrusion direction b) parallel to extrusion direction, 1) Ag/ZnO contact layer, 2) Ag backing layer</caption>]] | |
| + | </figure> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div class="clear"></div> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Table 2. | + | <figtable id="tab:tab2.29"> |
| − | + | <caption>'''<!--Table 2.29:-->Optimizing of Silver–Tin Oxide Materials Regarding their Switching Properties and Forming Behavior'''</caption> | |
| + | <table class="twocolortable"> | ||
| + | <tr><th><p class="s12">Material/</p><p class="s12">Material Group</p></th><th><p class="s12">Special Properties<th colspan="2"></p></th></tr><tr><td><p class="s12">Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> PE</p></td><td><p class="s12">Especially suitable for automotive relays</p><p class="s12">(lamp loads)</p></td><td><p class="s12">Good formability (contact rivets)</p></td></tr><tr><td><p class="s12">Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> TOS F</p></td><td><p class="s12">Especially suited for high inductive</p><p class="s12">DC loads</p></td><td><p class="s12">Very good formability (contact rivets)</p></td></tr><tr><td><p class="s12">Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> WPD</p></td><td><p class="s12">Especially suited for severe loads (AC-4)</p><p class="s12">and high switching currents</p></td><td/></tr><tr><td><p class="s12">Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> W TOS F</p></td><td><p class="s12">Especially suitable for high inductive DC</p><p class="s12">loads</p></td><td/></tr></table> | ||
| + | </figtable> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <figtable id="tab:Contact and Switching Properties of Silver–Metal Oxide Materials"> | |
| − | + | <caption>'''<!--Table 2.30:-->Contact and Switching Properties of Silver–Metal Oxide Materials'''</caption> | |
| − | + | {| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px" | |
| − | Ag/ZnO | + | |- |
| − | + | !Material | |
| + | !Properties | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub><br /> | ||
| + | |Environmentally friendly materials,<br /> | ||
| + | Very high resistance against welding during current-on-switching,<br />Weld resistance increases with higher oxide contents,<br /> | ||
| + | Low and stable contact resistance over the life of the device and good<br />temperature rise properties through use of special additives,<br /> | ||
| + | High arc erosion resistance and contact life,<br /> | ||
| + | Very low and flat material transfer during DC load switching,<br /> | ||
| + | Good arc moving and very good arc extinguishing properties | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/ZnO<br /> | ||
| + | |Environmentally friendly materials,<br /> | ||
| + | High resistance against welding during current-on-switching<br />(capacitor contactors),<br /> | ||
| + | Low and stable contact resistance through special oxide additives,<br />Very high arc erosion resistance at high switching currents,<br /> | ||
| + | Less favorable than Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub> for electrical life and material transfer,<br /> | ||
| + | With Ag<sub>2</sub>WO<sub>4</sub> additive especially suitable for AC relays | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </figtable> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <figtable id="tab:Application Examples of Silver–Metal Oxide Materials"> | |
| − | + | <caption>'''<!--Table 2.31:-->Application Examples of Silver–Metal Oxide Materials'''</caption> | |
| + | <table class="twocolortable"> | ||
| + | <tr><th><p class="s12">Material</p></th><th><p class="s12">Application Examples</p></th></tr><tr><td><p class="s12">Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub><span class="s48"></span></p></td><td><p class="s12">Micro switches, Network relays, Automotive relays, Appliance switches,</p><p class="s12">Main switches, contactors, Fault current protection relays (paired against</p><p class="s12">Ag/C), (Main) Power switches</p></td></tr><tr><td><p class="s12">Ag/ZnO</p></td><td><p class="s12">Wiring devices, AC relays, Appliance switches, Motor-protective circuit</p><p class="s12">breakers (paired with Ag/Ni or Ag/C), Fault current circuit breakers paired againct Ag/C, (Main) Power switches</p></td></tr></table> | ||
| + | </figtable> | ||
| − | + | ====Silver–Graphite Materials==== | |
| − | + | Ag/C contact materials are usually produced by powder metallurgy with graphite contents of 2 – 6 wt% (<xr id="tab:tab2.32"/>)<!--(Table 2.32)-->. The earlier typical manufacturing process of single pressed tips by pressing - sintering - repressing (PSR) has been replaced in Europe for quite some time by extrusion. In North America and some other regions however the PSR process is still used to some extend mainly for cost reasons. | |
| − | + | The extrusion of sintered billets is now the dominant manufacturing method for semi-finished AgC materials<!--[[#figures3|(Figs. 64 – 67)]]<!--(Figs. 2.126 – 2.129)-->. The hot extrusion process results in a high density material with graphite particles stretched and oriented in the extrusion direction [[#figures4|(Figs. 68 – 71)]]<!--(Figs. 2.130 – 2.133)-->. Depending on the extrusion method in either rod or strip form, the graphite particles can be oriented in the finished contact tips perpendicular or parallel to the switching contact surface (<xr id="fig:Micro structure of Ag C 95 5"/><!--(Fig. 2.131)--> and <xr id="fig:Micro structure of Ag C 96 4 D"/>)<!--(Fig. 2.132)-->. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Since the graphite particles in the Ag matrix of Ag/C materials prevent contact tips from directly being welded or brazed, a graphite free bottom layer is required. This is achieved by burning out (de-graphitizing) the graphite selectively on one side of the tips. | |
| − | + | Ag/C contact materials exhibit on the one hand an extremely high resistance to contact welding but on the other have a low arc erosion resistance. This is caused by the reaction of graphite with the oxygen in the surrounding atmosphere at the high temperatures created by the arcing. The weld resistance is especially high for materials with the graphite particle orientation parallel to the arcing contact surface. Since the contact surface after arcing consists of pure silver, the contact resistance stays consistantly low during the electrical life of the contact parts. | |
| − | + | A disadvantage of the Ag/C materials is their rather high erosion rate. In materials with parallel graphite orientation this can be improved, if a part of the graphite is incorporated into the material (Ag/C DF) in the form of fibers (<xr id="fig:Micro structure of Ag C DF"/>)<!--(Fig. 2.133)-->. The weld resistance is determined by the total content of graphite particles. | |
| − | Ag/C | ||
| − | with graphite | ||
| − | |||
| − | ( | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Ag/C tips with vertical graphite particle orientation are produced in a specific sequence: Extrusion to rods, cutting of double thickness tips, burning out of graphite to a controlled layer thickness, and a second cutting to single tips. Such contact tips are especially well suited for applications which require both, a high weld resistance and a sufficiently high arc erosion resistance (<xr id="tab:tab2.33"/>)<!--(Table 2.33)-->. For attachment of Ag/C tips welding and brazing techniques are applied. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Welding the actual process depends on the material's graphite orientation. For Ag/C tips with vertical graphite orientation the contacts are assembled with single tips. For parallel orientation a more economical attachment starting with contact material in strip or profile tape form is used in integrated stamping and welding operations with the tape fed into the weld station, cut off to tip form and then welded to the carrier material before forming the final contact assembly part. For special low energy welding, the Ag/C profile tapes can be pre-coated with a thin layer of high temperature brazing alloys such as CuAgP. | |
| − | tips | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Ag/C | + | In a rather limited way, Ag/C with 2 – 3 wt% graphite can be produced in wire form and headed into contact rivet shape with low head deformation ratios. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | The main applications for Ag/C materials are protective switching devices such as miniature molded case circuit breakers, motor-protective circuit breakers, and fault current circuit breakers, where during short circuit failures, highest resistance against welding is required (<xr id="tab:tab2.34"/>)<!--(Table 2.34)-->. For higher currents the low arc erosion resistance of Ag/C is compensated by asymmetrical pairing with more erosion resistant materials such as Ag/Ni, Ag/W and Ag/WC. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Ag | + | <div class="multiple-images"> |
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Strain hardening of Ag C 96 4 D"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Strain hardening of Ag C 96 4 D.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Strain hardening of Ag/C 96/4 by cold working</caption>]] | |
| − | + | </figure> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Softening of Ag C 96 4 D"> | |
| − | Ag | + | [[File:Softening of Ag C 96 4 D.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Softening of Ag/C 96/4 after annealing</caption>]] |
| − | + | </figure> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Strain hardening of Ag C DF"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Strain hardening of Ag C DF.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Strain hardening of Ag/C DF by cold working</caption>]] | |
| + | </figure> | ||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Softening of Ag C DF after annealing"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Softening of Ag C DF after annealing.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Softening of Ag/C DF after annealing</caption>]] | |
| − | + | </figure> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Micro structure of Ag C 97 3"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Micro structure of Ag C 97 3.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Micro structure of Ag/C 97/3: a) perpendicular to extrusion direction b) parallel to extrusion direction, 1) Ag/C contact layer, 2) Ag backing layer</caption>]] | |
| − | of Ag/C | + | </figure> |
| − | |||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Micro structure of Ag C 95 5"> | |
| − | + | [[File:Micro structure of Ag C 95 5.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Micro structure of Ag/C 95/5: a) perpendicular to extrusion direction b) parallel to extrusion direction, 1) Ag/C contact layer, 2) Ag backing layer</caption>]] | |
| − | + | </figure> | |
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Micro structure of Ag C 96 4 D"> | |
| − | of Ag/C | + | [[File:Micro structure of Ag C 96 4 D.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Micro structure of Ag/C 96/4: a) perpendicular to extrusion direction b) parallel to extrusion direction, 1) Ag/C contact layer, 2) Ag backing layer</caption>]] |
| + | </figure> | ||
| − | + | <figure id="fig:Micro structure of Ag C DF"> | |
| − | of Ag/C DF | + | [[File:Micro structure of Ag C DF.jpg|left|thumb|<caption>Micro structure of Ag/C DF: a) perpendicular to extrusion direction b) parallel to extrusion direction, 1) Ag/C contact layer, 2) Ag/Ni 90/10 backing layer</caption>]] |
| + | </figure> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div class="clear"></div> | ||
| − | + | <figtable id="tab:tab2.32"> | |
| − | + | <caption>'''<!--Table 2.32:-->Physical Properties of Silver–Graphite Contact Materials'''</caption> | |
| − | + | {| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px" | |
| − | + | |- | |
| + | !Material | ||
| + | !Silver Content<br />[wt%] | ||
| + | !Density<br />[g/cm<sup>3</sup>] | ||
| + | !Melting Point<br />[°C] | ||
| + | !Electrical Resistivity<br />[μΩ·cm] | ||
| + | !colspan="2" style="text-align:center"|Electrical<br />Conductivity<br />[% IACS] [MS/m] | ||
| + | !Vickers-Hardnes<br />HV10<br />42 - 45 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/C 98/2 | ||
| + | |97.5 - 98.5 | ||
| + | |9.5 | ||
| + | |960 | ||
| + | |1.85 - 1.92 | ||
| + | |90 - 93 | ||
| + | |48 - 50 | ||
| + | |42 - 44 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/C 97/3 | ||
| + | |96.5 - 97.5 | ||
| + | |9.1 | ||
| + | |960 | ||
| + | |1.92 - 2.0 | ||
| + | |86 - 90 | ||
| + | |45 - 48 | ||
| + | |41 - 43 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/C 96/4 | ||
| + | |95.5 - 96.5 | ||
| + | |8.7 | ||
| + | |960 | ||
| + | |2.04 - 2.13 | ||
| + | |81 - 84 | ||
| + | |42 - 46 | ||
| + | |40 - 42 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Ag/C 95/5 | ||
| + | |94.5 - 95.5 | ||
| + | |8.5 | ||
| + | |960 | ||
| + | |2.12 - 2.22 | ||
| + | |78 - 81 | ||
| + | |40 - 44 | ||
| + | |40 - 60 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |AgC DF<br />GRAPHOR DF[[#text-reference1|<sup>1</sup>]] | ||
| + | |95.7 - 96.7 | ||
| + | |8.7 - 8.9 | ||
| + | |960 | ||
| + | |2.27 - 2.50 | ||
| + | |69 - 76 | ||
| + | |40 - 44 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <div id="text-reference1"><sub>1</sub> Graphite content 3.8 wt%, Graphite particles and fibers parallel to switching surface</div> | ||
| + | </figtable> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Table 2.33: Contact and Switching properties of Silver–Graphite | + | <figtable id="tab:tab2.33"> |
| + | <caption>'''<!--Table 2.33:-->Contact and Switching properties of Silver–Graphite Contact Materials'''</caption> | ||
| + | <table class="twocolortable"> | ||
| + | <tr><th><p class="s12">Material</p></p></th><th><p class="s11">Properties</p></th></tr><tr><td><p class="s12">Ag/C</p></p></td><td><p class="s12">Highest resistance against welding during make operations at high currents,</p><p class="s12">High resistance against welding of closed contacts during short circuit,</p><p class="s12">Increase of weld resistance with higher graphite contents, Low contact resistance,</p><p class="s12">Low arc erosion resistance, especially during break operations, Higher arc erosion with increasing graphite contents, at the same time carbon build-up on switching chamber walls increases, silver-graphite with vertical orientation has better arc erosion resistance, parallel orientation has better weld resistance,</p><p class="s12">Limited arc moving properties, therefore paired with other materials,</p><p class="s12">Limited formability,</p><p class="s12">Can be welded and brazed with decarbonized backing, GRAPHOR DF is optimized for arc erosion resistance and weld resistance</p></td></tr></table> | ||
| + | </figtable> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <figtable id="tab:tab2.34"> | |
| − | ( | + | <caption>'''<!--Table 2.34:-->Application Examples and Forms of Supply of Silver– Graphite Contact Materials'''</caption> |
| + | <table class="twocolortable"> | ||
| + | <tr><th><p class="s12">Material</p><p class="s12"></p></th><th><p class="s12">Application Examples</p></th><th><p class="s12">Form of Supply</p></th></tr><td><p class="s12">Ag/C 98/2</p><p class="s12"></p></td><td><p class="s12">Motor circuit breakers, paired with Ag/Ni</p></td><td><p class="s12">Contact tips, brazed and welded contact parts, some contact rivets </p><p class="s12">Contact profiles (weld tapes), Contact tips, brazed and welded contact parts</p></td></tr><tr><td><p class="s12">Ag/C 97/3</p><p class="s12"></p><p class="s12">Ag/C 96/4</p><p class="s12"></p><p class="s12">Ag/C 95/5</p><p class="s12"></p><p class="s12">Ag/C DF</p></td><td><p class="s12">Circuit breakers, paired with Cu, Motor-protective circuit breakers, paired with Ag/Ni,</p><p class="s12">Fault current circuit breakers, paired with Ag/Ni, Ag/W, Ag/WC, Ag/SnO<sub>2</sub><span class="s45"></span>, Ag/ZnO,</p><p class="s12">(Main) Power switches, paired with Ag/Ni, Ag/W</p></td><td><p class="s12">Contact tips, brazed and welded contact</p><p class="s12">parts, some contact rivets with</p><p class="s12">Ag/C97/3</p></td></tr></table> | ||
| + | </figtable> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
[[Contact Materials for Electrical Engineering#References|References]] | [[Contact Materials for Electrical Engineering#References|References]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[de:Werkstoffe_auf_Silber-Basis]] | ||
Revision as of 12:35, 27 March 2023
Contents
Pure Silver
Pure silver (also called fine silver) exhibits the highest electrical and thermal conductivity of all metals. It is also resistant against oxidation. Major disadvantages are its low mechanical wear resistance, the low softening temperature, and especially its strong affinity to sulfur and sulfur compounds. In the presence of sulfur and sulfur containing compounds brownish to black silver sulfide layer are formed on its surface. These can cause increased contact resistance or even total failure of a switching device if they are not mechanically, electrically, or thermally destroyed. Other weaknesses of silver contacts are the tendency to weld under the influence of over-currents and the low resistance against material transfer when switching DC loads. In humid environments and under the influence of an electrical field silver can creep (silver migration) and cause electrical shorting between adjacent current paths.
Table 1 shows the typically available quality grades of silver. In certain economic areas, i.e. China, there are additional grades with varying amounts of impurities available on the market. In powder form silver is used for a wide variety of silver based composite contact materials. Different manufacturing processes result in different grades of Ag powder as shown in Table 2. Additional properties of silver powders and their usage are described in Precious Metal Powders und Table Different Types of Silver Powders.
Semi-finished silver materials can easily be warm or cold formed and can be clad to the usual base materials (Figure 1 and Figure 2). For attachment of silver to contact carrier materials welding of wire or profile cut-offs and brazing are most widely applied. Besides these mechanical processes such as wire insertion (wire staking) and the riveting (staking) of solid or composite contact rivets are used in the manufacture of contact components.
Contacts made from fine silver are applied in various electrical switching devices such as relays, pushbuttons, appliance and control switches for currents < 2 A (Table 6). Electroplated silver coatings are widely used to reduce the contact resistance and improve the brazing behavior of other contact materials and components.
Designation | Composition minimum Ag [wt%] | Impurities [ppm] | Notes on Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
Spectroscopically Pure Ag | 99.999 | Cu < 3 Zn < 1 Si < 1 Ca < 2 Fe < 1 Mg < 1 Cd < 1 | Sheets, strips, rods, wires for electronic applications |
High Purity Ag, oxygen-free | 99.995 | Cu < 30 Zn < 2 Si < 5 Ca < 10 Fe < 3 Mg < 5 Cd < 3 | Ingots, bars, granulate for alloying purposes |
| Impurities | Ag-Chem.* | Ag-ES** | Ag-V*** | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | ppm | < 100 | < 300 | < 300 |
| Fe | ppm | < 50 | < 100 | < 100 |
| Ni | ppm | < 50 | < 50 | < 50 |
| Cd | ppm | < 50 | ||
| Zn | ppm | < 10 | ||
| Na + K + Mg + Ca | ppm | < 80 | < 50 | < 50 |
| Ag CI | ppm | < 500 | < 500 | < 500 |
| NO3 | ppm | < 40 | < 40 | |
| Nh4CI | ppm | < 30 | < 30 | |
| Particle Size Distribution (screen analysis) | ||||
| > 100 μm | % | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| < 100 bis > 63 μm | % | < 5 | < 5 | < 15 |
| < 36 μm | % | < 80 | < 90 | < 75 |
| Apparent Density | g/cm3 | 1.0 - 1.6 | 1.0 - 1.5 | 3 - 4 |
| Tap Density | ml/100g | 40 - 50 | 40 - 50 | 15 - 25 |
| Press/Sintering Behavior | ||||
| Press Density | g/cm3 | 5.6 - 6.5 | 5.6 - 6.3 | 6.5 - 8.5 |
| Sinter Density | g/cm3 | > 9 | > 9.3 | > 8 |
| Volume Shrinkage | % | > 34 | > 35 | > 0 |
| Annealing Loss | % | < 2 | < 0.1 | < 0.1 |
* Manufactured by chemical precipitation
** Manufactured by electrolytic deposition
*** Manufactured by atomizing of a melt
Silver Alloys
To improve the physical and contact properties of fine silver, melt-metallurgical produced silver alloys are used (Table 3). By adding metal components, the mechanical properties such as hardness and tensile strength as well as typical contact properties such as erosion resistance and resistance against material transfer in DC circuits are increased (Table 4). On the other hand however, other properties such as electrical conductivity and chemical corrosion resistance can be negatively impacted by alloying (Figure 3 and Figure 4).
| Material | Silver Content [wt%] |
Density [g/cm3] |
Melting Point or Range [°C] |
Electrical Resistivity [μΩ·cm] |
Electrical Conductivity [MS/m] |
Thermal Conductivity [W/mK] |
Temp. Coefficient of the Electr.Resistance [10-3/K] |
Modulus of Elasticity [GPa] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag | 99.95 | 10.5 | 961 | 1.67 | 60 | 419 | 4.1 | 80 |
| AgNi0.15 | 99.85 | 10.5 | 960 | 1.72 | 58 | 414 | 4.0 | 82 |
| AgCu3 | 97 | 10.4 | 900 - 938 | 1.92 | 52 | 385 | 3.2 | 85 |
| AgCu5 | 95 | 10.4 | 910 | 1.96 | 51 | 380 | 3.0 | 85 |
| AgCu10 | 90 | 10.3 | 870 | 2.0 | 50 | 335 | 2.8 | 85 |
| AgCu28 | 72 | 10.0 | 779 | 2.08 | 48 | 325 | 2.7 | 92 |
| Ag98CuNi ARGODUR 27 |
98 | 10.4 | 940 | 1.92 | 52 | 385 | 3.5 | 85 |
| AgCu24.5Ni0.5 | 75 | 10.0 | 805 | 2.20 | 45 | 330 | 2.7 | 92 |
| Ag99.5NiMg ARGODUR 32 Not heat treated |
99.5 | 10.5 | 960 | 2.32 | 43 | 293 | 2.3 | 80 |
| ARGODUR 32 Heat treated |
99.5 | 10.5 | 960 | 2.32 | 43 | 293 | 2.1 | 80 |
Material | Hardness Condition | Tensile Strength Rm [MPa] | Elongation A [%] min. | Vickers Hardness HV 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Ag | R 200 R 250 R 300 R 360 | 200 - 250 250 - 300 300 - 360 > 360 | 30 8 3 2 | 30 60 80 90 |
AgNi0.15 | R 220 R 270 R 320 R 360 | 220 - 270 270 - 320 320 - 360 > 360 | 25 6 2 1 | 40 70 85 100 |
AgCu3 | R 250 R 330 R 400 R 470 | 250 - 330 330 - 400 400 - 470 > 470 | 25 4 2 1 | 45 90 115 120 |
AgCu5 | R 270 R 350 R 460 R 550 | 270 - 350 350 - 460 460 - 550 > 550 | 20 4 2 1 | 55 90 115 135 |
AgCu10 | R 280 R 370 R 470 R 570 | 280 - 370 370 - 470 470 - 570 > 570 | 15 3 2 1 | 60 95 130 150 |
AgCu28 | R 300 R 380 R 500 R 650 | 300 - 380 380 - 500 500 - 650 > 650 | 10 3 2 1 | 90 120 140 160 |
Ag98CuNi ARGODUR 27 | R 250 R 310 R 400 R 450 | 250 - 310 310 - 400 400 - 450 > 450 | 20 5 2 1 | 50 85 110 120 |
AgCu24,5Ni0,5 | R 300 R 600 | 300 - 380 > 600 | 10 1 | 105 180 |
Ag99,5NiMg ARGODUR 32 Not heat treated | R 220 R 260 R 310 R 360 | 220 260 310 360 | 25 5 2 1 | 40 70 85 100 |
ARGODUR 32 Heat treated | R 400 | 400 | 2 | 130-170 |
Fine-Grain Silver
Fine-Grain silver is defined as a silver alloy with an addition of 0.15 wt% of nickel. Silver and nickel are not soluble in each other in solid form. In liquid silver, only a small amount of nickel is soluble as the phase diagram illustrates (Figure 7). During solidification of the melt, this nickel addition gets finely dispersed in the silver matrix and eliminates the pronounce coarse grain growth after prolonged influence of elevated temperatures (Figure 5 and Figure 6).
Fine-Grain silver has almost the same chemical corrosion resistance as fine silver. Compared to pure silver, it exhibits a slightly increased hardness and tensile strength (Table 4). The electrical conductivity is just slightly decreased by this low nickel addition. Because of its significantly improved contact properties, fine grain silver has replaced pure silver in many applications.
Hard-Silver Alloys
Using copper as an alloying component increases the mechanical stability of silver significantly (Figure 9, Figure 10 and Figure 11). The most important among the binary AgCu alloys is that of AgCu3, in europe also known as hard-silver. This material still has a chemical corrosion resistance close to that of fine silver. In comparison to pure silver and fine-grain silver, AgCu3 exhibits increased mechanical strength as well as higher arc erosion resistance and mechanical wear resistance.
Increasing the Cu content further also increases the mechanical strength of AgCu alloys and improves arc erosion resistance and resistance against material transfer while simultaneously the tendency to oxide formation becomes detrimental. This causes - during switching under arcing conditions - an increase in contact resistance with rising numbers of operation. In special applications, where highest mechanical strength is recommended and a reduced chemical resistance can be tolerated, the eutectic AgCu alloy with 28 wt% of copper is used (Figure 8). AgCu10, also known as coin silver, has been replaced in many applications by composite silver-based materials while sterling silver (AgCu7.5) has never extended its important usage from decorative table wear and jewelry to industrial applications in electrical contacts.
Besides these binary alloys, ternary AgCuNi alloys are used in electrical contact applications. From this group, the material ARGODUR 27, an alloy of 98 wt% Ag with a 2 wt% Cu and nickel addition has found practical importance close to that of AgCu3. This material is characterized by high resistance to oxidation and low tendency to re-crystallization during exposure to high temperatures. Besides high mechanical stability this AgCuNi alloy also exhibits a strong resistance against arc erosion. Because of its high resistance against material transfer, the alloy AgCu24.5Ni0.5 has been used in the automotive industry for an extended time in the North American market. Caused by miniaturization and the related reduction in available contact forces in relays and switches, this material has been replaced widely because of its tendency to oxide formation.
The attachment methods used for the hard silver materials are mostly close to those applied for fine silver and fine grain silver.
Hard-silver alloys are widely used for switching applications in the information and energy technology for currents up to 10 A, in special cases also for higher current ranges (Table 6).
Dispersion hardened alloys of silver with 0.5 wt% MgO and NiO (ARGODUR 32) are produced by internal oxidation. While the melt-metallurgical alloy is easy to cold-work and form, the material becomes very hard and brittle after dispersion hardening. Compared to fine silver and hard-silver, this material has a greatly improved temperature stability and can be exposed to brazing temperatures up to 800°C without decreasing its hardness and tensile strength. Because of these mechanical properties and its high electrical conductivity ARGODUR 32 is mainly used in the form of contact springs that are exposed to high thermal and mechanical stresses in relays and contactors for aeronautic applications.
| Material | Properties | |
|---|---|---|
| Ag AgNi0.15 |
Highest electrical and thermal conductivity, high affinity to sulfur (sulfide formation), low welding resistance, low contact resistance, very good formability | Oxidation resistant at higher make currents, limited arc erosion resistance, tendency to material transfer in DC circuits, easy to braze and weld to carrier materials |
| Ag Alloys | Increasing contact resistance with increasing
Cu content, compared to fine Ag higher arc erosion resistance and mechanical strength, lower tendency to material transfer |
Good formability, good brazing and welding properties |
| Material | Application Examples | Form of Supply |
|---|---|---|
| Ag AgNi0.15 AgCu3 AgNi98NiCu2 ARGODUR 27 AgCu24,5Ni0,5 |
Relays, Micro switches, Auxiliary current switches, Control circuit devices, Appliance switches, Wiring devices (≤ 20A), Main switches |
Semi-finished Materials: Strips, wires, contact profiles, clad contact strips, toplay profiles, seam- welded strips Contact Parts: Contact tips, solid and composite rivets, weld buttons; clad, welded and riveted contact parts |
| AgCu5 AgCu10 AgCu28 |
Special applications | Semi-finished Materials: Strips, wires, contact profiles, clad contact strips, seam-welded strips Contact parts: Contact tips, solid contact rivets, weld buttons; clad, welded and riveted contact parts |
| Ag99.5NiOMgO ARGODUR 32 |
Miniature relays, aerospace relays and contactors, erosion wire for injection nozzles | Contact springs, contact carrier parts |
Silver-Palladium Alloys
The addition of 30 wt% Pd increases the mechanical properties as well as the resistance of silver against the influence of sulfur and sulfur containing compounds significantly (Table 7 and Table 8). Alloys with 40-60 wt% Pd have an even higher resistance against silver sulfide formation. At these percentage ranges however, the catalytic properties of palladium can influence the contact resistance behavior negatively. The formability also decreases with increasing Pd contents.
AgPd alloys are hard, arc erosion resistant, and have a lower tendency towards material transfer under DC loads (Table 9). On the other hand, the electrical conductivity is decreased at higher Pd contents. The ternary alloy AgPd30Cu5 has an even higher hardness, which makes it suitable for use in sliding contact systems.
AgPd alloys are mostly used in relays for the switching of medium to higher loads (> 60V, > 2A) as shown in Table 10. Because of the high palladium price, these formerly solid contacts have been widely replaced by multi-layer designs such as AgNi0.15 or AgNi10 with a thin Au surface layer. A broader field of application for AgPd alloys remains in the wear resistant sliding contact systems.
| Material | Palladium Content [wt%] |
Density [g/cm3] |
Melting Point or Range [°C] |
Electrical Resistivity [μΩ·cm] |
Electrical Conductivity [MS/m] |
Thermal Conductivity [W/m·K] |
Temp. Coefficient of the Electr. Resistance [10-3/K] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AgPd30 | 30 | 10.9 | 1155 - 1220 | 14.7 | 6.8 | 60 | 0.4 |
| AgPd40 | 40 | 11.1 | 1225 - 1285 | 20.8 | 4.8 | 46 | 0.36 |
| AgPd50 | 50 | 11.2 | 1290 - 1340 | 32.3 | 3.1 | 34 | 0.23 |
| AgPd60 | 60 | 11.4 | 1330 - 1385 | 41.7 | 2.4 | 29 | 0.12 |
| AgPd30Cu5 | 30 | 10.8 | 1120 - 1165 | 15.6 | 6.4 | 28 | 0.37 |
Material | Hardness Condition | Tensile Strength Rm[MPa] | Elongation A [%]min. | Vickers Hardness HV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
AgPd30 | R 320 R 570 | 320 570 | 38 3 | 65 145 |
AgPd40 | R 350 R 630 | 350 630 | 38 2 | 72 165 |
AgPd50 | R 340 R 630 | 340 630 | 35 2 | 78 185 |
AgPd60 | R 430 R 700 | 430 700 | 30 2 | 85 195 |
AgPd30Cu5 | R 410 R 620 | 410 620 | 40 2 | 90 190 |
| Material | Properties | |
|---|---|---|
| AgPd30-60 | Corrosion resistant, tendency to Brown Powder formation increases with Pd content, low tendency to material transfer in DC circuits, high ductility | Resistant against Ag2S formation, low contact resistance, increasing hardness with higher Pd content, AgPd30 has highest arc erosion resistance, easy to weld and clad |
| AgPd30Cu5 | High mechanical wear resistance | High Hardness |
Material | Application Examples | Form of Supply |
|---|---|---|
AgPd 30-60 | Switches, relays, push-buttons, connectors, sliding contacts | Semi-finished Materials: Wires, micro profiles (weld tapes), clad contact strips, seam-welded strips Contact Parts: Solid and composite rivets, weld buttons; clad and welded contact parts, stamped parts |
AgPd30Cu5 | Sliding contacts, slider tracks | Wire-formed parts, contact springs, solid and clad stamped parts |
Silver Composite Materials
Silver-Nickel Materials
Since silver and nickel are not soluble in each other in solid form and also show very limited solubility in the liquid phase, silver nickel composite materials with higher Ni contents can only be produced by powder metallurgy. During extrusion of sintered Ag/Ni billets into wires, strips and rods, the Ni particles embedded in the Ag matrix are stretched and oriented in the microstructure into a pronounced fiber structure (Figure 30 and Figure 31)
The high density produced during hot extrusion, aids the arc erosion resistance of these materials (Table 11). The typical application of Ag/Ni contact materials is in devices for switching currents of up to 100A (Table 14). In this range, they are significantly more erosion resistant than silver or silver alloys. In addition, they exhibit with nickel contents < 20 wt% a low and over their operational lifetime consistent contact resistance and good arc moving properties. In DC applications Ag/Ni materials exhibit a relatively low tendency of material transfer distributed evenly over the contact surfaces (Table 13).
Typically Ag/Ni materials are usually produced with contents of 10-40 wt% Ni. The most common used materials Ag/Ni 10 and Ag/Ni 20- and also Ag/Ni 15, mostly used in north america-, are easily formable and applied by cladding (Figure 26, Figure 27, Figure 28, Figure 29). They can be, without any additional welding aids, economically welded and brazed to the commonly used contact carrier materials. The Ag/Ni materials with nickel contents of 30 and 40 wt% are used in switching devices, requiring a higher arc erosion resistance and where increases in contact resistance can be compensated through higher contact forces.
The most important applications for Ag/Ni contact materials are typically in relays, wiring devices, appliance switches, thermostatic controls, auxiliary switches and small contactors with nominal currents > 20A (Table 14).
| Material | Silver Content | Density | Melting Point | ElectricalResistivityp | Electrical Resistivity (soft) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [wt%] | [g/cm3] | [°C] | [µΩ·cm] | [% IACS] | [MS/m] | |
Ag/Ni 90/10 | 89 - 91 | 10.2 - 10.3 | 960 | 1.82 - 1.92 | 90 - 95 | 52 - 55 |
Ag/Ni 85/15 | 84 - 86 | 10.1 - 10.2 | 960 | 1.89 - 2.0 | 86 - 91 | 50 - 53 |
Ag/Ni 80/20 | 79 - 81 | 10.0 - 10.1 | 960 | 1.92 - 2.08 | 83 - 90 | 48 - 52 |
Ag/Ni 70/30 | 69 - 71 | 9.8 | 960 | 2.44 | 71 | 41 |
Ag/Ni 60/40 | 59 - 61 | 9.7 | 960 | 2.70 | 64 | 37 |
| Material | Hardness Condition | Tensile Strength Rm [Mpa] | Elongation A (soft annealed) [%] min. | Vickers Hardness HV 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag/Ni 90/10 |
soft R 220 R 280 R 340 R 400 |
< 250 220 - 280 280 - 340 340 - 400 > 400 |
25 20 3 2 1 |
< 50 50 - 70 65 - 90 85 - 105 > 100 |
| Ag/Ni 85/15 |
soft R 300 R 350 R 380 R 400 |
< 275 250 - 300 300 - 350 350 - 400 > 400 |
20 4 2 2 1 |
< 70 70 - 90 85 - 105 100 - 120 > 115 |
| Ag/Ni 80/20 |
soft R 300 R 350 R 400 R 450 |
< 300 300 - 350 350 - 400 400 - 450 > 450 |
20 4 2 2 1 |
< 80 80 - 95 90 - 110 100 - 125 > 120 |
| Ag/Ni 70/30 |
R 330 R 420 R 470 R 530 |
330 - 420 420 - 470 470 - 530 > 530 |
8 2 1 1 |
80 100 115 135 |
| Ag/Ni 60/40 |
R 370 R 440 R 500 R 580 |
370 - 440 440 - 500 500 - 580 > 580 |
6 2 1 1 |
90 110 130 150 |
| Material | Properties |
|---|---|
| Ag/Ni |
High arc erosion resistance at switching currents up to 100A, Resistance against welding for starting current up to 100A, low and over the electrical contact life nearly constant contact resistance for Ag/Ni 90/10 and Ag/Ni 80/20, ow and spread-out material transfer under DC load, non-conductive erosion residue on isolating components resulting in only minor change of the dielectric strength of switching devices, good arc moving properties, good arc extinguishing properties, good or sufficient ductility depending on the Ni content, easy to weld and braze |
| Material | Application Examples | Switching or Nominal Current | Form of Supply |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ag/Ni 90/10-80/20 | Relays Automotive Relays - Resistive load - Motor load |
> 10A > 10A |
Semi-finisched Materials: Wires, profiles, clad strips, Seam-welded strips, Toplay strips Contact Parts: Contact tips, solid and composite rivets, Weld buttons, clad, welded, brazed, and riveted contact parts |
| Ag/Ni 90/10, Ag/Ni 85/15-80/20 | Auxiliary current switches | ≤ 100A | |
| Ag/Ni 90/10-80/20 | Appliance switches | ≤ 50A | |
| Ag/Ni 90/10 | Wiring devices | ≤ 20A | |
| Ag/Ni 90/10 | Main switches, Automatic staircase illumination switches | ≤ 100A | |
| Ag/Ni 90/10-80/20 | Control Thermostats |
> 10A ≤ 50A | |
| Ag/Ni 90/10-80/20 | Load switches | ≤ 20A | |
| Ag/Ni 90/10-80/20 | Contactors circuit breakers | ≤ 100A | |
| Ag/Ni 90/10-80/20 paired with Ag/C 97/3-96/4 |
Motor protective circuit breakers | ≤ 40A | |
| Ag/Ni 80/20-60/40 paired with Ag/C 96/4-95/5 |
Fault current circuit breakers | ≤ 100A | Rods, Profiles, Contact tips, Formed parts, brazed and welded contact parts |
| Ag/Ni 80/20-60/40 paired with Ag/C 96/4-95/5 |
Power switches | > 100A |
Silver-Metal Oxide Materials Ag/CdO, Ag/SnO2, Ag/ZnO
The family of silver-metal oxide contact materials includes the material groups: silver-cadmium oxide, silver-tin oxide, and silverzinc oxide. Because of their very good contact and switching properties like high resistance against welding, low contact resistance, and high arc erosion resistance, silver-metal oxides have gained an outstanding position in a broad field of applications. They are mainly used in low voltage electrical switching devices like relays, installation and distribution switches, appliances, industrial controls, motor controls, and protective devices (Table 20).
- Silver-cadmium oxide materials
Silver-cadmium oxide materials with 10-15 wt% are produced by both, internal oxidation and powder metallurgical methods.
The manufacturing of strips and wires by internal oxidation starts with a molten alloy of silver and cadmium. During a heat treatment below it's melting point in an oxygen rich atmosphere of such a homogeneous alloy, the oxygen diffuses from the surface into the bulk of the material and oxidizes the Cd to CdO in a more or less fine particle precipitation inside the Ag matrix. The CdO particles are rather fine in the surface area and getting larger towards the center of the material (Figure 38).
During the manufacturing of Ag/CdO contact material by internal oxidation, the processes vary depending on the type of semi-finished material. For Ag/CdO wires, a complete oxidation of the AgCd wire is performed, followed by wire-drawing to the required diameter (Figure 32 and Figure 33). The resulting material is used for example, in the production of contact rivets. For Ag/CdO strip materials two processes are commonly used: Cladding of an AgCd alloy strip with fine silver, followed by complete oxidation, results in a strip material with a small depletion area in the center of it's thickness and an Ag backing suitable for easy attachment by brazing (sometimes called "Conventional Ag/CdO"). Using a technology that allows the partial oxidation of a dual-strip AgCd alloy material in a higher pressure pure oxygen atmosphere, yields a composite Ag/CdO strip material that has - besides a relatively fine CdO precipitation - also an easily brazable AgCd alloy backing. These materials are mainly used as the basis for contact profiles and contact tips.
During powder metallurgical production, the powder mixed made by different processes are typically converted by pressing, sintering and extrusion to wires and strips. The high degree of deformation during hot extrusion, produces a uniform and fine dispersion of CdO particles in the Ag matrix while at the same time achieving a high density which is advantageous for good contact properties (Figure 39). To obtain a backing suitable for brazing, a fine silver layer is applied by either com-pound extrusion or hot cladding prior to or right after the extrusion.
For larger contact tips, and especially those with a rounded shape, the single tip Press-Sinter-Repress process (PSR) offers economical advantages. The powder mix is pressed into a die close to the final desired shape, the "green" tips are sintered, and in most cases, the repress process forms the exact final shape while at the same time, increasing the contact density and hardness.
Using different silver powders and minor additives for the basic Ag and CdO, starting materials can help influence certain contact properties for specialized applications.
- Silver–tin oxide materials
Over the past years, many Ag/CdO contact materials have been replaced by Ag/SnO2 based materials with 2-14 wt% SnO2 because of the toxicity of Cadmium. This changeover was further favored by the fact that Ag/SnO2 contacts quite often show improved contact and switching properties such as lower arc erosion, higher weld resistance and a significant lower tendency towards material transfer in DC switching circuits (Table 19). Ag/SnO2 materials have been optimized for a broad range of applications by other metal oxide additives and modification in the manufacturing processes that result in different metallurgical, physical and electrical properties (Table 17 and Table 18).
Manufacturing of Ag/SnO2 by internal oxidation is possible in principle, but during heat treatment of alloys containing > 5 wt% of tin in oxygen, dense oxide layers formed on the surface of the material prohibit the further diffusion of oxygen into the bulk of the material. By adding Indium or Bismuth to the alloy, the internal oxidation is possible and results in materials that typically are rather hard and brittle and may show somewhat elevated contact resistance and is limited to applications in relays. Adding a brazable fine silver layer to such materials results in a semifinished material, suitable for the manufacture as smaller weld profiles (Figure 56). Because of their resistance to material transfer and low arc erosion, these materials find for example a broader application in automotive relays (Table 20).
Powder metallurgy plays a significant role in the manufacturing of Ag/SnO2 contact materials. Besides SnO2 a smaller amount (<1 wt%) of one or more other metal oxides such as WO3, MoO3, CuO and/or Bi2O3 are added. These additives improve the wettability of the oxide particles and increase the viscosity of the Ag melt. They also provide additional benefits to the mechanical and arcing contact properties of materials in this group (Table 15).
| Material | Silver Content [wt%] |
Additives | Theoretical Density [g/cm3] |
Electrical Conductivity [MS/m] |
Vickers Hardness [HV0,1] |
Tensile Strength [MPa] |
Elongation (soft annealed) A[%]min. |
Manufacturing Process |
Form of Supply |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag/SnO2 98/2 SPW | 97 - 99 | WO3 | 10,4 | 59 ± 2 | 57 ± 15 | 215 | 35 | Powder Metallurgy | 1 |
| Ag/SnO2 92/8 SPW | 91 - 93 | WO3 | 10,1 | 51 ± 2 | 62 ± 15 | 255 | 25 | Powder Metallurgy | 1 |
| Ag/SnO2 90/10 SPW | 89 - 91 | WO3 | 10 | 47 ± 5 | 250 | 25 | Powder Metallurgy | 1 | |
| Ag/SnO2 88/12 SPW | 87 - 89 | WO3 | 9.9 | 46 ± 5 | 67 ± 15 | 270 | 20 | Powder Metallurgy | 1 |
| Ag/SnO2 92/8 SPW4 | 91 - 93 | WO3 | 10,1 | 51 ± 2 | 62 ± 15 | 255 | 25 | Powder Metallurgy | 1,2 |
| Ag/SnO2 90/10 SPW4 | 89 - 91 | WO3 | 10 | Powder Metallurgy | 1,2 | ||||
| Ag/SnO2 88/12 SPW4 |
87 - 89 | WO3 | 9,8 | 46 ± 5 | 80 ± 10 | Powder Metallurgy | 1,2 | ||
| Ag/SnO2 88/12 SPW6 | 87 - 89 | MoO3 | 9.8 | 42 ± 5 | 70 ± 10 | Powder Metallurgy | 2 | ||
| Ag/SnO2 97/3 SPW7 | 96 - 98 | Bi2O3 and WO3 | Powder Metallurgy | 2 | |||||
| Ag/SnO2 90/10 SPW7 | 89 - 91 | Bi2O3 and WO3 | 9,9 | Powder Metallurgy | 2 | ||||
| Ag/SnO2 88/12 SPW7 | 87 - 89 | Bi2O3 and WO3 | 9.8 | 42 ± 5 | 70 ± 10 | Powder Metallurgy | 2 | ||
| Ag/SnO2 98/2 PMT1 | 97 - 99 | Bi2O3 and CuO | 10,4 | 57 ± 2 | 215 | 35 | Powder Metallurgy | 1,2 | |
| Ag/SnO2 96/4 PMT1 | 95 - 97 | Bi2O3 and CuO | Powder Metallurgy | 1,2 | |||||
| Ag/SnO2 94/6 PMT1 | 93 - 95 | Bi2O3 and CuO | Powder Metallurgy | 1,2 | |||||
| Ag/SnO2 92/8 PMT1 | 91 - 93 | Bi2O3 and CuO | 10 | 50 ± 2 | 62 ± 15 | 240 | 25 | Powder Metallurgy | 1,2 |
| Ag/SnO2 90/10 PMT1 | 89 - 91 | Bi2O3 and CuO | 10 | 48 ± 2 | 65 ± 15 | 240 | 25 | Powder Metallurgy | 1,2 |
| Ag/SnO2 88/12 PMT1 | 87 - 89 | Bi2O3 and CuO | 9,9 | 46 ± 5 | 260 | 20 | Powder Metallurgy | 1,2 | |
| Ag/SnO2 90/10 PE | 89 - 91 | Bi2O3 and CuO | 9,8 | 48 ± 2 | 55 - 100 | 230 - 330 | 28 | Powder Metallurgy | 1 |
| Ag/SnO2 88/12 PE | 87 - 89 | Bi2O3 and CuO | 9,7 | 46 ± 5 | 60 - 106 | 235 - 330 | 25 | Powder Metallurgy | 1 |
| Ag/SnO2 88/12 PMT2 | 87 - 89 | CuO | 9,9 | 90 ± 10 | Powder Metallurgy | 1,2 | |||
| Ag/SnO2 86/14 PMT3 | 85 - 87 | Bi2O3 and CuO | 9,8 | 95 ± 10 | Powder Metallurgy | 2 | |||
| Ag/SnO2 94/6 LC1 | 93 - 95 | Bi2O3 and In2O3 | 9,8 | 45 ± 5 | 55 ± 10 | Powder Metallurgy | 2 | ||
| Ag/SnO2 90/10 POX1 | 89 - 91 | In2O3 | 9,9 | 50 ± 5 | 85 ± 15 | 310 | 25 | Internal Oxidation | 1,2 |
| Ag/SnO2 90/10 POX1 | 87 - 89 | In2O3 | 9,8 | 48 ± 5 | 90 ± 15 | 325 | 25 | Internal Oxidation | 1,2 |
| Ag/SnO2 90/10 POX1 | 85 - 87 | In2O3 | 9,6 | 45 ± 5 | 95 ± 15 | 330 | 20 | Internal Oxidation | 1,2 |
1 = Wires, Rods, Contact rivets, 2 = Strips, Profiles, Contact tips
In the manufacture for the initial powder mixes, different processes are applied which provide specific advantages of the resulting materials in respect to their contact properties . Some of them are described here as follows:
- a) Powder blending from single component powders
In this common process all components, including additives that are part of the powder mix, are blended as single powders. The blending is usually performed in the dry stage in blenders of different design.
- b) Powder blending on the basis of doped powders
For incorporation of additive oxides in the SnO2 powder, the reactive spray process has shown advantages. This process starts with a waterbased solution of the tin and other metal compounds. This solution is nebulized under high pressure and temperature in a reactor chamber. Through the rapid evaporation of the water, each small droplet is converted into a salt crystal and from there gets transformed by oxidation into a tin oxide particle in which the additive metals are distributed evenly as oxides. The so created doped AgSnO2 powder is then mechanically mixed with silver powder.
- c) Powder blending based on coated oxide powders
In this process, tin oxide powder is blended with lower melting additive oxides such as for example Ag2 MoO4 and then heat treated. The SnO2 particles are coated in this step with a thin layer of the additive oxide.
- d) Powder blending based on internally oxidized alloy powders
A combination of powder metallurgy and internal oxidation this process starts with atomized Ag alloy powder which is subsequently oxidized in pure oxygen. During this process the Sn and other metal components are transformed to metal oxide and precipitated inside the silver matrix of each powder particle.
- e) Powder blending based on chemically precipitated compound powders
A silver salt solution is added to a suspension of for example SnO2 together with a precipitation agent. In a chemical reaction, silver and silver oxide respectively are precipitated around the additive metal oxide particles, who act as crystallization sites. Further chemical treatment then reduces the silver oxide with the resulting precipitated powder, being a mix of Ag and SnO2.
Further processing of these differently produced powders follows the conventional processes of pressing, sintering and hot extrusion to wires and strips. From these contact parts, contact rivets and tips are manufactured. To obtain a brazable backing, the same processes as used for Ag/CdO are applied. As for Ag/CdO, larger contact tips can also be manufactured using the press-sinter-repress (PSR) process (Table 16).
Material | Additives | Density [ g/cm3] | Electrical Resistivity [µS ·cm] | Electrical Conductivity | Vickers Hardness HV 10. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
[%IACS] | [MS/m] | |||||
AgCdO 90/10 | 10.1 | 2.08 | 83 | 48 | 60 | |
AgCdO 85/15 | 9.9 | 2.27 | 76 | 44 | 65 | |
AgSnO2 90/10 | CuO and Bi2 O3 | 9.8 | 2.22 | 78 | 45 | 55 |
AgSnO2 88/12 | CuO and Bi2 O3 | 9.6 | 2.63 | 66 | 38 | 60 |
- Silver–zinc oxide materials
Silver zinc oxide contact materials with mostly 6 - 10 wt% oxide content, including other small metal oxides, are produced exclusively by powder metallurgy (Figs. 58 – 63). Adding WO3 or Ag2WO4 in the process - as described in the preceding chapter on Ag/SnO2 - has proven most effective for applications in AC relays, wiring devices, and appliance controls. Just like with the other Ag metal oxide materials, semi-finished materials in strip and wire form are used to manufacture contact tips and rivets. Because of their high resistance against welding and arc erosion Ag/ZnO materials present an economic alternative to Cd free Ag-tin oxide contact materials (Table 19 and Table 20).
| Material | Silver Content [wt%] |
Additives | Density [g/cm3] |
Electrical Resistivity [μΩ·cm] |
Electrical Conductivity [% IACS] [MS/m] |
Vickers Hardness Hv1 |
Tensile Strength [MPa] |
Elongation (soft annealed) A[%]min. |
Manufacturing Process |
Form of Supply | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag/ZnO 92/8P |
91 - 93 | 9.8 | 2.22 | 78 | 45 | 60 - 95 | 220 - 350 | 25 | Powder Metallurgy a) indiv. powders |
1 | |
| Ag/ZnO 92/8PW25 |
91 - 93 | Ag2WO4 | 9.6 | 2.08 | 83 | 48 | 65 - 105 | 230 - 340 | 25 | Powder Metallurgy c) coated |
1 |
| Ag/ZnO 90/10PW25 |
89 - 91 | Ag2WO4 | 9.6 | 2.17 | 79 | 46 | 65 - 100 | 230 - 350 | 20 | Powder Metallurgy c) coated |
1 |
| Ag/ZnO 92/8WP |
91 - 93 | 9.8 | 2.0 | 86 | 50 | 60 - 95 | Powder Metallurgy with Ag backing a) individ. |
2 | |||
| Ag/ZnO 92/8WPW25 |
91 - 93 | Ag2WO4 | 9.6 | 2.08 | 83 | 48 | 65 - 105 | Powder Metallurgy c) coated |
2 | ||
| Ag/ZnO 90/10WPW25 |
89 - 91 | Ag2WO4 | 9.6 | 2.7 | 79 | 46 | 65 - 110 | Powder Metallurgy c) coated |
2 | ||
1 = Wires, Rods, Contact rivets, 2 = Strips, Profiles, Contact tips
Material/ Material Group | Special Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|
Ag/SnO2 PE | Especially suitable for automotive relays (lamp loads) | Good formability (contact rivets) | |
Ag/SnO2 TOS F | Especially suited for high inductive DC loads | Very good formability (contact rivets) | |
Ag/SnO2 WPD | Especially suited for severe loads (AC-4) and high switching currents | ||
Ag/SnO2 W TOS F | Especially suitable for high inductive DC loads | ||
| Material | Properties |
|---|---|
| Ag/SnO2 |
Environmentally friendly materials, Very high resistance against welding during current-on-switching, |
| Ag/ZnO |
Environmentally friendly materials, High resistance against welding during current-on-switching |
Material | Application Examples |
|---|---|
Ag/SnO2 | Micro switches, Network relays, Automotive relays, Appliance switches, Main switches, contactors, Fault current protection relays (paired against Ag/C), (Main) Power switches |
Ag/ZnO | Wiring devices, AC relays, Appliance switches, Motor-protective circuit breakers (paired with Ag/Ni or Ag/C), Fault current circuit breakers paired againct Ag/C, (Main) Power switches |
Silver–Graphite Materials
Ag/C contact materials are usually produced by powder metallurgy with graphite contents of 2 – 6 wt% (Table 21). The earlier typical manufacturing process of single pressed tips by pressing - sintering - repressing (PSR) has been replaced in Europe for quite some time by extrusion. In North America and some other regions however the PSR process is still used to some extend mainly for cost reasons.
The extrusion of sintered billets is now the dominant manufacturing method for semi-finished AgC materials. The hot extrusion process results in a high density material with graphite particles stretched and oriented in the extrusion direction (Figs. 68 – 71). Depending on the extrusion method in either rod or strip form, the graphite particles can be oriented in the finished contact tips perpendicular or parallel to the switching contact surface (Figure 69 and Figure 70).
Since the graphite particles in the Ag matrix of Ag/C materials prevent contact tips from directly being welded or brazed, a graphite free bottom layer is required. This is achieved by burning out (de-graphitizing) the graphite selectively on one side of the tips.
Ag/C contact materials exhibit on the one hand an extremely high resistance to contact welding but on the other have a low arc erosion resistance. This is caused by the reaction of graphite with the oxygen in the surrounding atmosphere at the high temperatures created by the arcing. The weld resistance is especially high for materials with the graphite particle orientation parallel to the arcing contact surface. Since the contact surface after arcing consists of pure silver, the contact resistance stays consistantly low during the electrical life of the contact parts.
A disadvantage of the Ag/C materials is their rather high erosion rate. In materials with parallel graphite orientation this can be improved, if a part of the graphite is incorporated into the material (Ag/C DF) in the form of fibers (Figure 71). The weld resistance is determined by the total content of graphite particles.
Ag/C tips with vertical graphite particle orientation are produced in a specific sequence: Extrusion to rods, cutting of double thickness tips, burning out of graphite to a controlled layer thickness, and a second cutting to single tips. Such contact tips are especially well suited for applications which require both, a high weld resistance and a sufficiently high arc erosion resistance (Table 22). For attachment of Ag/C tips welding and brazing techniques are applied.
Welding the actual process depends on the material's graphite orientation. For Ag/C tips with vertical graphite orientation the contacts are assembled with single tips. For parallel orientation a more economical attachment starting with contact material in strip or profile tape form is used in integrated stamping and welding operations with the tape fed into the weld station, cut off to tip form and then welded to the carrier material before forming the final contact assembly part. For special low energy welding, the Ag/C profile tapes can be pre-coated with a thin layer of high temperature brazing alloys such as CuAgP.
In a rather limited way, Ag/C with 2 – 3 wt% graphite can be produced in wire form and headed into contact rivet shape with low head deformation ratios.
The main applications for Ag/C materials are protective switching devices such as miniature molded case circuit breakers, motor-protective circuit breakers, and fault current circuit breakers, where during short circuit failures, highest resistance against welding is required (Table 23). For higher currents the low arc erosion resistance of Ag/C is compensated by asymmetrical pairing with more erosion resistant materials such as Ag/Ni, Ag/W and Ag/WC.
| Material | Silver Content [wt%] |
Density [g/cm3] |
Melting Point [°C] |
Electrical Resistivity [μΩ·cm] |
Electrical Conductivity [% IACS] [MS/m] |
Vickers-Hardnes HV10 42 - 45 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag/C 98/2 | 97.5 - 98.5 | 9.5 | 960 | 1.85 - 1.92 | 90 - 93 | 48 - 50 | 42 - 44 |
| Ag/C 97/3 | 96.5 - 97.5 | 9.1 | 960 | 1.92 - 2.0 | 86 - 90 | 45 - 48 | 41 - 43 |
| Ag/C 96/4 | 95.5 - 96.5 | 8.7 | 960 | 2.04 - 2.13 | 81 - 84 | 42 - 46 | 40 - 42 |
| Ag/C 95/5 | 94.5 - 95.5 | 8.5 | 960 | 2.12 - 2.22 | 78 - 81 | 40 - 44 | 40 - 60 |
| AgC DF GRAPHOR DF1 |
95.7 - 96.7 | 8.7 - 8.9 | 960 | 2.27 - 2.50 | 69 - 76 | 40 - 44 | |
Material | Properties |
|---|---|
Ag/C | Highest resistance against welding during make operations at high currents, High resistance against welding of closed contacts during short circuit, Increase of weld resistance with higher graphite contents, Low contact resistance, Low arc erosion resistance, especially during break operations, Higher arc erosion with increasing graphite contents, at the same time carbon build-up on switching chamber walls increases, silver-graphite with vertical orientation has better arc erosion resistance, parallel orientation has better weld resistance, Limited arc moving properties, therefore paired with other materials, Limited formability, Can be welded and brazed with decarbonized backing, GRAPHOR DF is optimized for arc erosion resistance and weld resistance |
Material | Application Examples | Form of Supply |
|---|---|---|
Ag/C 98/2 | Motor circuit breakers, paired with Ag/Ni | Contact tips, brazed and welded contact parts, some contact rivets Contact profiles (weld tapes), Contact tips, brazed and welded contact parts |
Ag/C 97/3 Ag/C 96/4 Ag/C 95/5 Ag/C DF | Circuit breakers, paired with Cu, Motor-protective circuit breakers, paired with Ag/Ni, Fault current circuit breakers, paired with Ag/Ni, Ag/W, Ag/WC, Ag/SnO2, Ag/ZnO, (Main) Power switches, paired with Ag/Ni, Ag/W | Contact tips, brazed and welded contact parts, some contact rivets with Ag/C97/3 |