Difference between revisions of "Testing Procedures"
(→13.5.2 Special Types of Corrosion) |
Doduco Admin (talk | contribs) (→13.5.4 Corrosion Testing) |
||
| (52 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | ==13.1 Terms and Definitions== | + | The procedures and standards for testing electrical contacts described below are mostly concentrated on contact applications in electromechanical devices. Since the range of applications for electrical contacts is very broad, a complete description of all relevant test procedures would extend the scope of this chapter of the Data Book. Therefore we limited the content here to contact coatings and switching contacts for information and power engineering. Because of the ongoing miniaturization of electromechanical devices the testing for effects of corrosive influences by the environment play an important role. Special testing procedures, such as these for brazed, soldered and welded contact joints are covered already in chapter 3 [[Manufacturing Technologies for Contact Parts|Manufacturing Technologies for Contact Parts ]]. |
| + | |||
| + | ==<!--13.1-->Terms and Definitions== | ||
Every technical device has to fulfill a series of requirements. Some of those which are important for agreement between contact manufacturer and user are part of DIN 40042 standard and described here in a summarized version: | Every technical device has to fulfill a series of requirements. Some of those which are important for agreement between contact manufacturer and user are part of DIN 40042 standard and described here in a summarized version: | ||
| − | + | '''Availability (Ready-for-Use) and Reliabilty''' | |
Availability (for use) defines the probability of a system or switching device to be in a functional stage at a given time | Availability (for use) defines the probability of a system or switching device to be in a functional stage at a given time | ||
| Line 13: | Line 14: | ||
Both, availability and reliability, are guaranteed for a pre-determined time span and/or a specific number of switching operations. This means they warrant the life expectancy of a switching device. At the end of the live span the failure rate exceeds pre-defined limit values. | Both, availability and reliability, are guaranteed for a pre-determined time span and/or a specific number of switching operations. This means they warrant the life expectancy of a switching device. At the end of the live span the failure rate exceeds pre-defined limit values. | ||
| − | + | '''Electrical Life''' | |
Electrical life is the number of operations reached under a given electrical load under specified operating conditions. | Electrical life is the number of operations reached under a given electrical load under specified operating conditions. | ||
| − | Since the criteria which determine the electrical life of switching contacts | + | Since the criteria which determine the electrical life of switching contacts depends on the type of switching devices they are used in, they are described in more detail under the testing procedures in information and power engineering. |
| + | ==<!--13.2-->Testing of Contact Surface Layers== | ||
| − | + | For applications at low switching loads contact layers with thicknesses in the range of just a few micrometers are widely used. For testing such thin layers, the actual coating properties must be distinguished from the functional properties. Coating properties include, besides others, porosity, hardness and ductility. | |
| − | + | Depending on the application, the most important function properties are for example frictional wear, contact resistance, material transfer or contact welding behavior. Besides these other technological properties such as adhesion strength, and solderability, maybe of importance for special applications like those for electronic components. | |
| − | For applications at low switching loads contact layers with thicknesses in the range of just a few micrometers are widely used. For testing such thin layers the actual coating properties must be distinguished from the functional properties. Coating properties include, besides others, porosity, hardness | ||
| − | Depending on the application, the most important function properties are for example frictional wear, contact resistance, material transfer | ||
The following descriptions are mainly applicable to electroplated contact coatings which are of the most economical importance in contact applications. They also apply however in similar form to surface layers which have been created by mechanical cladding or by sputtering. | The following descriptions are mainly applicable to electroplated contact coatings which are of the most economical importance in contact applications. They also apply however in similar form to surface layers which have been created by mechanical cladding or by sputtering. | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
| − | ==13.3 Test Procedures for the Communications Technology== | + | ==<!--13.3-->Test Procedures for the Communications Technology== |
| − | Testing of the contact behavior in the communications technology is usually performed on the actual devices such as for example in relays. Experience has shown that the interaction between all design and functional parameters such as contact forces, relative movement | + | Testing of the contact behavior in the communications technology is usually performed on the actual devices such as ,for example, in relays. Experience has shown, that the interaction between all design and functional parameters such as contact forces, relative movement and electrical loads, are determining the failure mode. Therefore only statistical performance tests on a larger number of switching devices lead to meaningful results. |
One must differentiate between static tests (for ex. contact resistance) and dynamic ones (for ex. electrical life). In certain electromechanical components and switching devices the contacts can be exposed to both, static and dynamic stresses (for ex. connectors, relays, switches, pushbuttons, circuit breakers). For statically stressed components the life expectancy is usually expressed as a time period, i.e. hours, while for dynamically stressed ones the expected functional life is defined as numbers of operations or switching cycles. | One must differentiate between static tests (for ex. contact resistance) and dynamic ones (for ex. electrical life). In certain electromechanical components and switching devices the contacts can be exposed to both, static and dynamic stresses (for ex. connectors, relays, switches, pushbuttons, circuit breakers). For statically stressed components the life expectancy is usually expressed as a time period, i.e. hours, while for dynamically stressed ones the expected functional life is defined as numbers of operations or switching cycles. | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
| + | ==<!--13.4-->Testing Procedures for Power Engineering== | ||
| − | + | The testing of electrical contacts for power engineering applications, serves on the one hand the continuous quality assurance, on the other one the new and improvement development efforts for contact materials. To optimize the contact and switching performance, contact materials and device designs have to complement each other. The success of such optimizing is proven by switching tests. | |
| − | The | + | The assessment of contact materials is performed using metallurgical test methods as well as switching tests in model test set-ups and in commercial switching devices. While physical properties, such as melting and boiling point, electrical conductivity etc. are fundamental for the selection of the base metals and the additional components of the materials, they cannot provide a clear indication of the contact and switching behavior. Metallurgical evaluations and tests are used primarily for determining material and working defects. The actual contact and switching behavior can however only be determined through switching tests in a model switch or preferably in the final electromechanical device. |
| − | + | Model testing devices offer the possibility of quick ratings of the make and break behavior and give a preliminary classification of potential contact materials. Since such tests are performed under ideal conditions, they cannot replace switching tests in actual devices. | |
| − | + | The electrical testing of commercially produced switching devices should follow DIN EN or IEC standards and rules. Special test standards exist for each type of switching device, which are differentiated by: | |
| − | |||
| − | The electrical testing of commercially produced switching devices should follow DIN EN or IEC standards and rules. Special test standards exist for each type of switching device which are differentiated by: | ||
*Make capacity | *Make capacity | ||
| Line 55: | Line 54: | ||
*Temperature rise | *Temperature rise | ||
| − | The following chapters are limited to metallurgical analysis and the testing of the most important properties of switching devices such as electrical life, temperature rise | + | The following chapters are limited to metallurgical analysis and the testing of the most important properties of switching devices such as electrical life, temperature rise and switching capacity. |
Main Articel: [[Testing Procedures for Power Engineering| Testing Procedures for Power Engineering]] | Main Articel: [[Testing Procedures for Power Engineering| Testing Procedures for Power Engineering]] | ||
| − | ==13.5 Corrosion Testing== | + | ==<!--13.5-->Corrosion Testing== |
| − | ===13.5.1 Definition of “Corrosion”=== | + | ===<!--13.5.1-->Definition of “Corrosion”=== |
The definition of corrosion can be found in DIN 500900 Part 1 as follows: Reaction of a metallic material with its environment, which produces a | The definition of corrosion can be found in DIN 500900 Part 1 as follows: Reaction of a metallic material with its environment, which produces a | ||
| Line 69: | Line 68: | ||
During corrosive influences metal is dissolved. This metal loss can be uniformly spread out over a certain area or be limited to locally smaller spots. This process usually proceeds with constant speed up to the total material loss, or after certain reaction times a natural corrosion limiting surface layer can be formed (i.e. on aluminum). | During corrosive influences metal is dissolved. This metal loss can be uniformly spread out over a certain area or be limited to locally smaller spots. This process usually proceeds with constant speed up to the total material loss, or after certain reaction times a natural corrosion limiting surface layer can be formed (i.e. on aluminum). | ||
| − | ===13.5.2 Special Types of Corrosion=== | + | ===<!--13.5.2-->Special Types of Corrosion=== |
*Contact corrosion: <br />Corrosion of a metal object after coming into physical contact with another metallic body. This can occur also on metallic impurities in alloys, on chemically and physically heterogeneous surfaces and on heterogeneous solutions on homogeneous surfaces, as well as through contacting a metal object by non-metallic materials through formation of corrosion compounds.<br /> | *Contact corrosion: <br />Corrosion of a metal object after coming into physical contact with another metallic body. This can occur also on metallic impurities in alloys, on chemically and physically heterogeneous surfaces and on heterogeneous solutions on homogeneous surfaces, as well as through contacting a metal object by non-metallic materials through formation of corrosion compounds.<br /> | ||
| Line 79: | Line 78: | ||
*Selective corrosion: <br />Preferred corrosion in specific microstructure areas (for example: loss of zinc in brasses with formation of copper enrichments).<br /> | *Selective corrosion: <br />Preferred corrosion in specific microstructure areas (for example: loss of zinc in brasses with formation of copper enrichments).<br /> | ||
| − | *Air access corrosion: <br />Through differences in the amount of exposure to air or oxygen surface areas of a metal are becoming cathodes at the more exposed spots and therefore corrode less than those protected (for example: gap corrosion in screw or press connections).<br /> | + | *Air access corrosion: <br />Through differences in the amount of exposure to air or oxygen, surface areas of a metal are becoming cathodes at the more exposed spots and therefore corrode less than those protected (for example: gap corrosion in screw or press connections).<br /> |
*Tension stress corrosion: <br />Crack formation of stress corrosion sensitive materials which are under mechanical pull stresses while exposed to corrosive media. Especially affected are zinc containing copper alloys (brasses) under the influence of ammonia or nitrates.<br /> | *Tension stress corrosion: <br />Crack formation of stress corrosion sensitive materials which are under mechanical pull stresses while exposed to corrosive media. Especially affected are zinc containing copper alloys (brasses) under the influence of ammonia or nitrates.<br /> | ||
| Line 87: | Line 86: | ||
*Hydrogen corrosion: <br />Cathodic reduction of H to H<sub>2</sub> (in acidic solutions) under conditions where the potential of the metal is less precious.<br /> | *Hydrogen corrosion: <br />Cathodic reduction of H to H<sub>2</sub> (in acidic solutions) under conditions where the potential of the metal is less precious.<br /> | ||
| − | *Fretting (frictional) corrosion: <br />Enrichment of oxide particles of non-precious metal (especially tinned) surfaces during relative movements at small | + | *Fretting (frictional) corrosion: <br />Enrichment of oxide particles of non-precious metal (especially tinned) surfaces during relative movements at small amplitudes (< 100 μm). They occur through transfer of oscillation of thermal displacement energy because of the difference in thermal expansion of the two contacting metals. This effect can be especially detrimental in connectors with tin plated surfaces, such as for example in automotive applications.<br /> |
| + | |||
| + | *Fatigue corrosion: <br />Fatigue fracture during repeated mechanical stresses in corrosive environments. This effect is often observed in brittle electroplated surface coatings exposed to repeated alternations between mechanical stress and corrosive chemicals. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===<!--13.5.3-->Electrochemical Potentials=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Corrosion effects are mainly governed by the electrode potential of the respective metals. The electrochemical potential table gives a measure of the corrosion resistance. Non-precious (corrosion prone) metals are characterized by a negative, precious (corrosion resistant) metals by a positive normal potential against hydrogen. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <figtable id="tab:Electrode Potential of Metals"> | ||
| + | <caption>'''<!--Table 13.3:-->Electrode Potential of Metals'''</caption> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !Metal | ||
| + | !Reaction | ||
| + | !Potential [V] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Aluminum | ||
| + | |AI → AI<sup>+++</sup> +3e | ||
| + | | - 1.71 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Zinc | ||
| + | |Zn → Zn<sup>++</sup> +2e | ||
| + | | - 0.76 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Chromium | ||
| + | |Cr → Cr<sup>++</sup> +2e | ||
| + | | - 0.71 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Iron | ||
| + | |Fe → Fe<sup>++</sup> +2e | ||
| + | | - 0.41 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Cadmium | ||
| + | |Cd → Cd<sup>++</sup> +2e | ||
| + | | - 0.40 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Indium | ||
| + | |In → In<sup>+++</sup> +3e | ||
| + | | - 0.34 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Cobalt | ||
| + | |Co → Co<sup>++</sup> +2e | ||
| + | | - 0.27 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Nickel | ||
| + | |Ni → Ni<sup>++</sup> +2e | ||
| + | | - 0.25 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Tin | ||
| + | |Sn → Sn<sup>++</sup> +2e | ||
| + | | - 0.13 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Lead | ||
| + | |Pd → Pd<sup>++</sup> +2e | ||
| + | | - 0.12 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Hydrogen | ||
| + | |H2 → H2<sup>++</sup> +2e | ||
| + | | - 0.00 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Copper | ||
| + | |Cu → Cu<sup>++</sup> +2e<br />Cu → Cu<sup>+</sup> +e | ||
| + | | + 0.34<br /> + 0.52 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Silver | ||
| + | |Ag → Ag<sup>+</sup> +e | ||
| + | | + 0.80 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Palladium | ||
| + | |Pd → Pd<sup>++</sup> +2e | ||
| + | | + 0.83 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Platinum | ||
| + | |Pt → Pt<sup>++</sup> +2e | ||
| + | | + 1.20 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Gold | ||
| + | |Au → Au<sup>+++</sup> +3e<br />Au → Au<sup>+</sup> +e | ||
| + | | + 1.42<br /> + 1.68 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </figtable> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===13.5.4 Corrosion Testing=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The following pages describe test methods and procedures which are mainly related to the effects of environmental exposure of electrical contacts which are used in contact components for the telecommunication and information technology. | ||
| + | Corrosion products on the surface of electrical contacts can reduce the reliability of contact making significantly by, for example, higher contact | ||
| + | resistance, which will negatively affect the transmission of current and data signals. This can cause major problems in electromechanical contact | ||
| + | components used in the information processing technology. Causes for the formation of tarnish film on electrical contacts include for example the presence of corrosive gases such as H<sub>2</sub>S, SO<sub>2</sub>, NO<sub>x</sub>, O<sub>3</sub>, Cl<sub>2</sub> and NH<sub>3</sub> (<xr id="tab:Typical Corrosive Gas Concentrations (ppm) Near Industrial Facilities"/><!--(Tab. 13.4)-->) in industrial environments. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <figtable id="tab:Typical Corrosive Gas Concentrations (ppm) Near Industrial Facilities"> | ||
| + | <caption>'''<!--Table 13.4:-->Typical Corrosive Gas Concentrations (ppm) Near Industrial Facilities'''</caption> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !Industrial Atmosphere | ||
| + | !SO<sub>2</sub> | ||
| + | !H<sub>2</sub>S | ||
| + | !NO<sub>2</sub> | ||
| + | !CI<sub>2</sub> | ||
| + | !O<sub>3</sub> | ||
| + | !NH<sub>3</sub> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Median value<br />Extreme value | ||
| + | |0.04<br />0.22 | ||
| + | |0.01<br />0.4 | ||
| + | |0.1<br />1.0 | ||
| + | |0.005<br /> | ||
| + | |0.02<br />0.2-0.6 | ||
| + | |0.2<br />0.2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Smell threshold<br />MAK-value[[#text-reference|<sup>1)</sup>]]<br />Life threatening | ||
| + | |0.18<br />2.0<br />400 | ||
| + | |0.02<br />10.0<br />700 | ||
| + | |0.1<br />5.0<br />200 | ||
| + | |0.005<br />0.5<br />3 | ||
| + | |0.02<br />0.1<br /> | ||
| + | |5<br />50<br />5000 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </figtable> | ||
| + | <div id="text-reference">1)MAK-Value: maximum allowable concentration in the workplace</div> | ||
| + | Corrosion tests – also called environmental – on electrical contacts in natural environments must be critically evaluated because they are the rather time consuming. | ||
| + | |||
| + | During different times of the year, temperature and relative humidity changes as well as changes in the concentration of corrosive gases can have significant influences on the formation of corrosion products. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Therefore, research and quality assurance efforts have centered for many years on developing test methods for electrical contacts which can predict in an accelerated time frame the corrosion behavior of electrical contacts in different corrosive atmospheres with reasonable accuracy. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Single components corrosive test atmospheres and testing with two gas exposures following each other, provide only limited validity. Flowing gas test | ||
| + | atmospheres with four components have proven to be the most likely ones to realistically simulate long term natural corrosive gas exposure (<xr id="tab:Some Standardized Corrosion Tests for Electrical Contacts"/><!--(Tab. 13.5)-->). | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <figtable id="tab:Some Standardized Corrosion Tests for Electrical Contacts"> | ||
| + | <caption>'''<!--Table 13.5:-->Some Standardized Corrosion Tests for Electrical Contacts'''</caption> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !Test Method | ||
| + | !Corrosive Gas | ||
| + | !Degree of <br />Severity 1 [ppb] | ||
| + | !Degree of <br />Severity 2 [ppb] | ||
| + | !Temperature [°C] | ||
| + | !Relative Humidity [%] | ||
| + | !Duration [d] | ||
| + | !Standard | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |1-component corrosive gas | ||
| + | |SO<sub>2</sub><br />H<sub>2</sub>S | ||
| + | |500<br />100 | ||
| + | |10000<br />10000 | ||
| + | |25 ± 1<br />25 ± 1 | ||
| + | |75 ± 3<br />75 ± 3 | ||
| + | |1, 4, 10 oder 21<br />1, 4, 10 oder 21 | ||
| + | |DIN 40046 Part 36<br />DIN 40046 Part 37 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |2-component corrosive gas<br />(used sequential) | ||
| + | |SO<sub>2</sub><br />+ H<sub>2</sub>S | ||
| + | |500<br />100 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |25 ± 1<br /> | ||
| + | |75 ± 3<br /> | ||
| + | |1, 4, 10 oder 21<br /> | ||
| + | |EC 68-2-60 TTD | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |4-component mixed corrosive gas | ||
| + | |H<sub>2</sub>S<br />CI<sub>2</sub><br />NO<sub>2</sub><br />SO<sub>2</sub> | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |10 ± 5<br />10 ± 5<br />200 ± 20<br />200 ± 20 | ||
| + | |25 ± 1 | ||
| + | |70 ± 3 | ||
| + | |10 | ||
| + | |IEC 68-2-60 Part 2,<br />Method 4 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |4-component mixed corrosive gas | ||
| + | |H<sub>2</sub>S<br />CI<sub>2</sub><br />NO<sub>2</sub><br />SO<sub>2</sub> | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |10 ± 1,5<br />10 ± 1,5<br />200 ± 30<br />100 ± 15 | ||
| + | |30 ± 1 | ||
| + | |70 ± 2 | ||
| + | |10 | ||
| + | |Telcordia GR-63-Core Section 5.5<br />Indoor | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |4-component mixed corrosive gas | ||
| + | |H<sub>2</sub>S<br />CI<sub>2</sub><br />NO<sub>2</sub><br />SO<sub>2</sub> | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |100 ± 15<br />20 ± 3<br />200 ± 30<br />200 ± 30 | ||
| + | |30 ± 1 | ||
| + | |70 ± 2 | ||
| + | |4 | ||
| + | |Telcordia GR-63-Core Section 5.5<br />Outdoor | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </figtable> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The differences in the corrosive gas concentrations and the test durations are dependent on the end application of the contact components and the | ||
| + | assessment of the exposure parameters. | ||
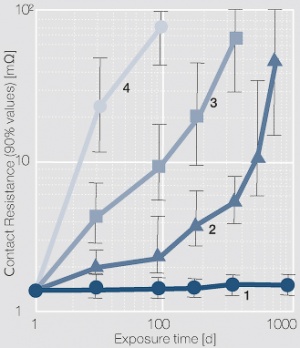
| + | Battelle (the Battelle Institute) has, for different applications, defined four climate classes which reflect the corrosion behavior of porous electroplated gold surfaces. Such gold layers are often used in connectors for the telecommunications and information technology (<xr id="tab:Classification of Corrosion Effects According to Battelle"/><!--(Tab. 13.5)--> and <xr id="fig:Influence of the corrosive gas concentration for four classes"/><!--(Fig. 13.14)-->). | ||
| + | |||
| + | <figure id="fig:Influence of the corrosive gas concentration for four classes"> | ||
| + | [[File:Influence of the corrosive gas concentration for four classes.jpg|left|thumb|Figure 1: Influence of the corrosive gas concentration for four classes (I–IV) on the contact resistance of a porous gold layer as a function of the exposure time (Battelle)]] | ||
| + | </figure> | ||
| + | <br style="clear:both;"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <figtable id="tab:Classification of Corrosion Effects According to Battelle"> | ||
| + | <caption>'''<!--Table 13.5:-->Classification of Corrosion Effects According to Battelle'''</caption> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !Class | ||
| + | !Application | ||
| + | !Corrosion Effects | ||
| + | !H<sub>2</sub>S [ppb] | ||
| + | !CI<sub>2</sub> [ppb] | ||
| + | !NO<sub>2</sub> [ppb] | ||
| + | !Temporature [°C] | ||
| + | !Relative Humidity [%] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |'''Ⅰ''' | ||
| + | |Controlled office climate | ||
| + | |None | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |'''Ⅱ''' | ||
| + | |Office climate | ||
| + | |Pore corrosion | ||
| + | |10 + 0/-4 | ||
| + | |10 + 0/-2 | ||
| + | |200 ± 25 | ||
| + | |30 ± 2 | ||
| + | |70 ± 2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |'''Ⅲ''' | ||
| + | |Moderate industrial climate | ||
| + | |Pore and creep corrosion | ||
| + | |100 ± 10 | ||
| + | |20 ± 5 | ||
| + | |200 ± 25 | ||
| + | |30 ± 2 | ||
| + | |75 ± 2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |'''Ⅳ''' | ||
| + | |Corrosive industrial climate | ||
| + | |Surface creep corrosion | ||
| + | |200 ± 10 | ||
| + | |50 ± 5 | ||
| + | |200 ± 25 | ||
| + | |50 ± 2 | ||
| + | |75 ± 2 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </figtable> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The dominant corrosion effects for thin gold coatings are pore corrosion and at higher gas concentrations creep corrosion from the base materials onto the coating, starting at the boundary line between non-precious base metal and contact layer. | ||
| + | The measurement of contact resistance allows an indirect classification of corrosion product layers. While the analysis of thicker corrosive product layers in the range of 0.1 – 1 μm can be performed by classic methods such as SEM and X-ray microprobe, thinner layers of 10 – 100 nm require the use of ionoptical analysis equipment. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Vinaricky, E. (Hrsg.): Elektrische Kontakte, Werkstoffe und Anwendungen. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York 2002 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Nobel, F.J.; Ostrow, B.D.; Thomson, D.W.: Porosity Testing of Gold Deposits. Plating 52 (1965) 1001-1008 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Bedetti, F.V.; Chiarenzelli, R.V.: Porosity Testing of Electroplated Gold. Plating 53 (1966) 305-308 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Antler, M.: Gold-plated Contacts: Effect of Substrate Roughness on Reliability. Plating 56 (1969) 1139-1144 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Huck, M.; Mayer, U.: Korrosionsbeständigkeit und Werkstoffeigenschaften galvanischer Legierungsniederschläge für die Elektroindustrie. Metalloberfläche 10, (1984) 427-434 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Wund, K.; Schnabl, R.: Gold und seine Legierungen in der Galvanotechnik. Galvanotechnik 77(2) (1986) 312-324 | ||
| + | |||
| + | DIN EN ISO 6507: Metallic materials - Vickers hardness test - Part 1: Test method | ||
| + | |||
| + | DIN ISO 4516: Metallic and other inorganic coating - Vickers and Knoop hardness test | ||
| + | |||
| + | Dengel, D.: Wichtige Gesichtspunkte für die Härtemessung nach Vickers und nach Knoop im Bereich der Kleinlast und Mikrolast. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Z. Werkstofftechnik 4 (1973) 292-298 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Schnabl, R.: Herstellverfahren und Prüfungen für Kontaktschichten in der Nachrichtentechnik. Buchreihe „Kontakt & Studium“, Bd. 366: Werkstoffe für elektrische Kontakte und ihre Anwendungen, Expert-Verlag, Renningen,Bd | ||
| + | |||
| + | 366, (1997) 279-310 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Bogenschütz, A.F.; Jostan, J.L.; Mussinger, W.: Galvanische | ||
| + | |||
| + | Korrosionsschutzschichten für elektronische Anwendungen. Metalloberfläche | ||
| + | 34 (1980) 45-53, 93-136, 163-168, 187-194 (mit J. Ruf), 229-235, 261-269 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Huck, M.: Kontaktzuverlässigkeit von Steckverbindern. Metall 37 (1983) H.7, | ||
| + | |||
| + | 685-690 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Kaspar, F.: Drahtbonden zur Kontaktierung auf elektronischen Baugruppen, 13 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Werkstoffen und Beschichtungen. VDE-Fachbericht 55, (1999) 97-103 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Weiser,J.: Prüfverfahren in der Informationstechnik. In Vinaricky, E. (Hrsg.): Elektrische Kontakte, Werkstoffe und Anwendungen. Springer Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York (2002) 600 - 609 | ||
| + | |||
| + | I Data Book I Testing Procedures I | ||
| + | |||
| + | Schäfer, E.: Zuverlässigkeit, Verfügbarkeit und Sicherheit in der Elektronik, Vogel-Verlag, (1979) | ||
| + | |||
| + | Siepmann, R.: Elektronische Lastnachbildung, Siemens Comp., (1990) 28 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Johler, W.: Untere und obere Einsatzgrenzen von Signalrelais. VDE-Fachbericht 63 (2007) 31-40 | ||
| + | |||
| + | IEC/EN 61810-2: Electromechanical elementary relays - Part 2: Reliability | ||
| + | |||
| + | IEC/EN 61810-7: Electromechanical elementary relays - Part 7: Test and measurement procedures | ||
| + | |||
| + | Braumann, P.; Koffler, A.: Einfluss von Herstellungsverfahren, Metalloxidgehalt und Wirkzusätzen auf das Schaltverhalten von AgSnO2 in Relais (1). | ||
| + | VDE-Fachbericht 59 (2003) 133-142 | ||
| + | Braumann, P.; Koffler, A.: Einfluss von Herstellungsverfahren, Metalloxidgehalt und Wirkzusätzen auf das Schaltverhalten von AgSnO2 in Relais (2). | ||
| + | VDE-Fachbericht 61 (2005) 149-154 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Schöpf, Th.: Silber/Zinnoxid und andere Silber/Metalloxidwerkstoffe in | ||
| + | |||
| + | Netzrelais. VDE-Fachbericht 51 (1997) 41-50 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Behrens, V.; Honig, Th.; Kraus, A.; Michal, R.: Schalteigenschaften von verschiedenen Silber/Zinnoxid-Werkstoffen in Kfz-Relais. | ||
| + | |||
| + | VDE-Fachbericht 51 (1997) 51-57 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Braumann, P.: Prüfung der elektrischen Lebensdauer von Kfz-Relais. VDE-Fachbericht 55 (1999) 49-59 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Schröder, K.-H.: Prüfverfahren in der Energietechnik. In Vinaricky, E. (Hrsg.): Elektrische Kontakte, Werkstoffe und Anwendungen. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York (2002) 609-633 | ||
| + | |||
| + | IEC/EN 60947-4-1: Low-voltage switchgear and controlgear - Part 4-1: Contactors and motor-starters-Electromechanical contactors and motor starters | ||
| + | |||
| + | IEC/EN 60947-5-1: Low-voltage switchgear and controlgear - Part 5-1: Control circuit devices and switching elements- Electromechanical control circuit devices | ||
| + | |||
| + | IEC/EN 60947-2: Low-voltage switchgear and controlgear - Part 2: Circuitbreakers | ||
| + | |||
| + | UL 489: „Molded Case Circuit Breakers, Molded Case Switches and Circuit Breaker enclosures“ | ||
| + | |||
| + | Braumann, P.; Koffler, A.; Schröder, K.-H.: Analysis of Interrelation Between Mechanical and Eletrical Phenomena During Making Operations of Contacts: Proc. 17th Int. Conf. on Electrical Contacts, Nagoya, Japan, 1994 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Braumann, P.; Koffler, A.: The Importance of Characterizing the Make and Break Operations to Allow Effective Contact Material Development. 19. ITK Nürnberg, VDE-Verlag, Berlin, Offenbach, (1998) 325-333 | ||
| + | |||
| + | EN ISO 8044: Corrosion of metals and alloys - Basic terms and definitions. Berlin, Beuth-Verlag 1999 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Abbott, W.H.: Contact Corrosion. in Slade, P.: Electrical Contacts, Principles and Applications: Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, Basel, (1999) 113 - 154 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Slade, P.: Introduction to Contact Tarnishing and Corrosion. in Slade, P.: Electrical Contacts, Principles and Applications: Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, Basel, (1999) 89 - 112 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Cosack, U.: Survey of Corrosion Tests with Pollutant Gases and their Relevance for Contact Material. Proc. of the 13th Intern. Conf. on Electr. Contacts, Lausanne, Switzerland, (1986) 316-325 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Schnabl, R.; Paulsen, R.: Korrosionserscheinungen an Edelmetallen und | ||
| + | |||
| + | Trägerwerkstoffen. Metall 7 (1987) 696-701 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Abbott, W.H.: The Development and Performance Characteristics of Flowing Mixed Gas Test Environments. IEEE Transactions on Components, Hybrids, and Manufacturing Technology, Vol. 2, No. 1, (1988) 22-35 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Hienomen, R.; Rakkolainen, J.; Saarinen, T.; Aberg, M.: Nordic Project on Corrosion in Electronics. A Comparative Study on Field and Laboratory Test Results of Various Electronic Contacts. Proc. 14th Int. Conf. on Electric Contacts, Paris, (1988) 271-275 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Leygraf, Ch.: Indoor Athmosperic Corrosion. VDE-Fachbericht 63 (2007) 39-52 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ASTM Designation B 845-97: Standard Guide for Mixed Flowing Gas (MFG) Tests for Electrical Contacts, 1997 | ||
| + | |||
| + | IEC Standard 68-2-60, Environmental Testing Part 2: Tests Flowing-Mixed Gas | ||
| + | |||
| + | Corrosion Test, 1995 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Telcordia GR-63-CORE Issue 2, Section 5.5 : Airborne Contaminants Test | ||
| + | |||
| + | Methods, Nov. 2000 | ||
| − | + | [[de:Prüfverfahren]] | |
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 13:06, 4 January 2023
The procedures and standards for testing electrical contacts described below are mostly concentrated on contact applications in electromechanical devices. Since the range of applications for electrical contacts is very broad, a complete description of all relevant test procedures would extend the scope of this chapter of the Data Book. Therefore we limited the content here to contact coatings and switching contacts for information and power engineering. Because of the ongoing miniaturization of electromechanical devices the testing for effects of corrosive influences by the environment play an important role. Special testing procedures, such as these for brazed, soldered and welded contact joints are covered already in chapter 3 Manufacturing Technologies for Contact Parts .
Contents
Terms and Definitions
Every technical device has to fulfill a series of requirements. Some of those which are important for agreement between contact manufacturer and user are part of DIN 40042 standard and described here in a summarized version:
Availability (Ready-for-Use) and Reliabilty
Availability (for use) defines the probability of a system or switching device to be in a functional stage at a given time
Reliability describes the system's ability to fulfill at any time the requirements of an application within pre-defined limitations.
Both, availability and reliability, are guaranteed for a pre-determined time span and/or a specific number of switching operations. This means they warrant the life expectancy of a switching device. At the end of the live span the failure rate exceeds pre-defined limit values.
Electrical Life
Electrical life is the number of operations reached under a given electrical load under specified operating conditions. Since the criteria which determine the electrical life of switching contacts depends on the type of switching devices they are used in, they are described in more detail under the testing procedures in information and power engineering.
Testing of Contact Surface Layers
For applications at low switching loads contact layers with thicknesses in the range of just a few micrometers are widely used. For testing such thin layers, the actual coating properties must be distinguished from the functional properties. Coating properties include, besides others, porosity, hardness and ductility. Depending on the application, the most important function properties are for example frictional wear, contact resistance, material transfer or contact welding behavior. Besides these other technological properties such as adhesion strength, and solderability, maybe of importance for special applications like those for electronic components.
The following descriptions are mainly applicable to electroplated contact coatings which are of the most economical importance in contact applications. They also apply however in similar form to surface layers which have been created by mechanical cladding or by sputtering.
Main Articel: Testing of Contact Surface Layers
Test Procedures for the Communications Technology
Testing of the contact behavior in the communications technology is usually performed on the actual devices such as ,for example, in relays. Experience has shown, that the interaction between all design and functional parameters such as contact forces, relative movement and electrical loads, are determining the failure mode. Therefore only statistical performance tests on a larger number of switching devices lead to meaningful results.
One must differentiate between static tests (for ex. contact resistance) and dynamic ones (for ex. electrical life). In certain electromechanical components and switching devices the contacts can be exposed to both, static and dynamic stresses (for ex. connectors, relays, switches, pushbuttons, circuit breakers). For statically stressed components the life expectancy is usually expressed as a time period, i.e. hours, while for dynamically stressed ones the expected functional life is defined as numbers of operations or switching cycles.
Main Articel: Test Procedures for the Communications Technology
Testing Procedures for Power Engineering
The testing of electrical contacts for power engineering applications, serves on the one hand the continuous quality assurance, on the other one the new and improvement development efforts for contact materials. To optimize the contact and switching performance, contact materials and device designs have to complement each other. The success of such optimizing is proven by switching tests.
The assessment of contact materials is performed using metallurgical test methods as well as switching tests in model test set-ups and in commercial switching devices. While physical properties, such as melting and boiling point, electrical conductivity etc. are fundamental for the selection of the base metals and the additional components of the materials, they cannot provide a clear indication of the contact and switching behavior. Metallurgical evaluations and tests are used primarily for determining material and working defects. The actual contact and switching behavior can however only be determined through switching tests in a model switch or preferably in the final electromechanical device.
Model testing devices offer the possibility of quick ratings of the make and break behavior and give a preliminary classification of potential contact materials. Since such tests are performed under ideal conditions, they cannot replace switching tests in actual devices.
The electrical testing of commercially produced switching devices should follow DIN EN or IEC standards and rules. Special test standards exist for each type of switching device, which are differentiated by:
- Make capacity
- Break capacity
- Electrical life
- Temperature rise
The following chapters are limited to metallurgical analysis and the testing of the most important properties of switching devices such as electrical life, temperature rise and switching capacity.
Main Articel: Testing Procedures for Power Engineering
Corrosion Testing
Definition of “Corrosion”
The definition of corrosion can be found in DIN 500900 Part 1 as follows: Reaction of a metallic material with its environment, which produces a measurable change in the material and can lead to corrosion damage. This reaction is in most cases an electrochemical one. It can however also be based on chemical and metal-physics effects.
During corrosive influences metal is dissolved. This metal loss can be uniformly spread out over a certain area or be limited to locally smaller spots. This process usually proceeds with constant speed up to the total material loss, or after certain reaction times a natural corrosion limiting surface layer can be formed (i.e. on aluminum).
Special Types of Corrosion
- Contact corrosion:
Corrosion of a metal object after coming into physical contact with another metallic body. This can occur also on metallic impurities in alloys, on chemically and physically heterogeneous surfaces and on heterogeneous solutions on homogeneous surfaces, as well as through contacting a metal object by non-metallic materials through formation of corrosion compounds.
- Hole corrosion (pitting corrosion):
Local narrowly limited corrosion growing by dissolving material in small pin holes or craters to a depth that can lead to holes all the way through the material.
- Inter-crystalline corrosion:
Corrosion along the grain boundaries with the danger for the material to lose all its mechanical strength by decomposition (for example: at weld seams in austenitic stainless steels).
- Selective corrosion:
Preferred corrosion in specific microstructure areas (for example: loss of zinc in brasses with formation of copper enrichments).
- Air access corrosion:
Through differences in the amount of exposure to air or oxygen, surface areas of a metal are becoming cathodes at the more exposed spots and therefore corrode less than those protected (for example: gap corrosion in screw or press connections).
- Tension stress corrosion:
Crack formation of stress corrosion sensitive materials which are under mechanical pull stresses while exposed to corrosive media. Especially affected are zinc containing copper alloys (brasses) under the influence of ammonia or nitrates.
- Oxygen corrosion:
Cathodic reaction in aqueous solutions forms reduced molecular, in water dissolved oxygen. Corrosion occurs when the electrochemical potential of the metal is below that of oxygen.
- Hydrogen corrosion:
Cathodic reduction of H to H2 (in acidic solutions) under conditions where the potential of the metal is less precious.
- Fretting (frictional) corrosion:
Enrichment of oxide particles of non-precious metal (especially tinned) surfaces during relative movements at small amplitudes (< 100 μm). They occur through transfer of oscillation of thermal displacement energy because of the difference in thermal expansion of the two contacting metals. This effect can be especially detrimental in connectors with tin plated surfaces, such as for example in automotive applications.
- Fatigue corrosion:
Fatigue fracture during repeated mechanical stresses in corrosive environments. This effect is often observed in brittle electroplated surface coatings exposed to repeated alternations between mechanical stress and corrosive chemicals.
Electrochemical Potentials
Corrosion effects are mainly governed by the electrode potential of the respective metals. The electrochemical potential table gives a measure of the corrosion resistance. Non-precious (corrosion prone) metals are characterized by a negative, precious (corrosion resistant) metals by a positive normal potential against hydrogen.
| Metal | Reaction | Potential [V] |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | AI → AI+++ +3e | - 1.71 |
| Zinc | Zn → Zn++ +2e | - 0.76 |
| Chromium | Cr → Cr++ +2e | - 0.71 |
| Iron | Fe → Fe++ +2e | - 0.41 |
| Cadmium | Cd → Cd++ +2e | - 0.40 |
| Indium | In → In+++ +3e | - 0.34 |
| Cobalt | Co → Co++ +2e | - 0.27 |
| Nickel | Ni → Ni++ +2e | - 0.25 |
| Tin | Sn → Sn++ +2e | - 0.13 |
| Lead | Pd → Pd++ +2e | - 0.12 |
| Hydrogen | H2 → H2++ +2e | - 0.00 |
| Copper | Cu → Cu++ +2e Cu → Cu+ +e |
+ 0.34 + 0.52 |
| Silver | Ag → Ag+ +e | + 0.80 |
| Palladium | Pd → Pd++ +2e | + 0.83 |
| Platinum | Pt → Pt++ +2e | + 1.20 |
| Gold | Au → Au+++ +3e Au → Au+ +e |
+ 1.42 + 1.68 |
13.5.4 Corrosion Testing
The following pages describe test methods and procedures which are mainly related to the effects of environmental exposure of electrical contacts which are used in contact components for the telecommunication and information technology. Corrosion products on the surface of electrical contacts can reduce the reliability of contact making significantly by, for example, higher contact resistance, which will negatively affect the transmission of current and data signals. This can cause major problems in electromechanical contact components used in the information processing technology. Causes for the formation of tarnish film on electrical contacts include for example the presence of corrosive gases such as H2S, SO2, NOx, O3, Cl2 and NH3 (Table 2) in industrial environments.
| Industrial Atmosphere | SO2 | H2S | NO2 | CI2 | O3 | NH3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median value Extreme value |
0.04 0.22 |
0.01 0.4 |
0.1 1.0 |
0.005 |
0.02 0.2-0.6 |
0.2 0.2 |
| Smell threshold MAK-value1) Life threatening |
0.18 2.0 400 |
0.02 10.0 700 |
0.1 5.0 200 |
0.005 0.5 3 |
0.02 0.1 |
5 50 5000 |
Corrosion tests – also called environmental – on electrical contacts in natural environments must be critically evaluated because they are the rather time consuming.
During different times of the year, temperature and relative humidity changes as well as changes in the concentration of corrosive gases can have significant influences on the formation of corrosion products.
Therefore, research and quality assurance efforts have centered for many years on developing test methods for electrical contacts which can predict in an accelerated time frame the corrosion behavior of electrical contacts in different corrosive atmospheres with reasonable accuracy.
Single components corrosive test atmospheres and testing with two gas exposures following each other, provide only limited validity. Flowing gas test atmospheres with four components have proven to be the most likely ones to realistically simulate long term natural corrosive gas exposure (Table 3).
| Test Method | Corrosive Gas | Degree of Severity 1 [ppb] |
Degree of Severity 2 [ppb] |
Temperature [°C] | Relative Humidity [%] | Duration [d] | Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-component corrosive gas | SO2 H2S |
500 100 |
10000 10000 |
25 ± 1 25 ± 1 |
75 ± 3 75 ± 3 |
1, 4, 10 oder 21 1, 4, 10 oder 21 |
DIN 40046 Part 36 DIN 40046 Part 37 |
| 2-component corrosive gas (used sequential) |
SO2 + H2S |
500 100 |
25 ± 1 |
75 ± 3 |
1, 4, 10 oder 21 |
EC 68-2-60 TTD | |
| 4-component mixed corrosive gas | H2S CI2 NO2 SO2 |
10 ± 5 10 ± 5 200 ± 20 200 ± 20 |
25 ± 1 | 70 ± 3 | 10 | IEC 68-2-60 Part 2, Method 4 | |
| 4-component mixed corrosive gas | H2S CI2 NO2 SO2 |
10 ± 1,5 10 ± 1,5 200 ± 30 100 ± 15 |
30 ± 1 | 70 ± 2 | 10 | Telcordia GR-63-Core Section 5.5 Indoor | |
| 4-component mixed corrosive gas | H2S CI2 NO2 SO2 |
100 ± 15 20 ± 3 200 ± 30 200 ± 30 |
30 ± 1 | 70 ± 2 | 4 | Telcordia GR-63-Core Section 5.5 Outdoor |
The differences in the corrosive gas concentrations and the test durations are dependent on the end application of the contact components and the assessment of the exposure parameters. Battelle (the Battelle Institute) has, for different applications, defined four climate classes which reflect the corrosion behavior of porous electroplated gold surfaces. Such gold layers are often used in connectors for the telecommunications and information technology (Table 4 and Figure 1).
| Class | Application | Corrosion Effects | H2S [ppb] | CI2 [ppb] | NO2 [ppb] | Temporature [°C] | Relative Humidity [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | Controlled office climate | None | |||||
| Ⅱ | Office climate | Pore corrosion | 10 + 0/-4 | 10 + 0/-2 | 200 ± 25 | 30 ± 2 | 70 ± 2 |
| Ⅲ | Moderate industrial climate | Pore and creep corrosion | 100 ± 10 | 20 ± 5 | 200 ± 25 | 30 ± 2 | 75 ± 2 |
| Ⅳ | Corrosive industrial climate | Surface creep corrosion | 200 ± 10 | 50 ± 5 | 200 ± 25 | 50 ± 2 | 75 ± 2 |
The dominant corrosion effects for thin gold coatings are pore corrosion and at higher gas concentrations creep corrosion from the base materials onto the coating, starting at the boundary line between non-precious base metal and contact layer. The measurement of contact resistance allows an indirect classification of corrosion product layers. While the analysis of thicker corrosive product layers in the range of 0.1 – 1 μm can be performed by classic methods such as SEM and X-ray microprobe, thinner layers of 10 – 100 nm require the use of ionoptical analysis equipment.
References
Vinaricky, E. (Hrsg.): Elektrische Kontakte, Werkstoffe und Anwendungen. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York 2002
Nobel, F.J.; Ostrow, B.D.; Thomson, D.W.: Porosity Testing of Gold Deposits. Plating 52 (1965) 1001-1008
Bedetti, F.V.; Chiarenzelli, R.V.: Porosity Testing of Electroplated Gold. Plating 53 (1966) 305-308
Antler, M.: Gold-plated Contacts: Effect of Substrate Roughness on Reliability. Plating 56 (1969) 1139-1144
Huck, M.; Mayer, U.: Korrosionsbeständigkeit und Werkstoffeigenschaften galvanischer Legierungsniederschläge für die Elektroindustrie. Metalloberfläche 10, (1984) 427-434
Wund, K.; Schnabl, R.: Gold und seine Legierungen in der Galvanotechnik. Galvanotechnik 77(2) (1986) 312-324
DIN EN ISO 6507: Metallic materials - Vickers hardness test - Part 1: Test method
DIN ISO 4516: Metallic and other inorganic coating - Vickers and Knoop hardness test
Dengel, D.: Wichtige Gesichtspunkte für die Härtemessung nach Vickers und nach Knoop im Bereich der Kleinlast und Mikrolast.
Z. Werkstofftechnik 4 (1973) 292-298
Schnabl, R.: Herstellverfahren und Prüfungen für Kontaktschichten in der Nachrichtentechnik. Buchreihe „Kontakt & Studium“, Bd. 366: Werkstoffe für elektrische Kontakte und ihre Anwendungen, Expert-Verlag, Renningen,Bd
366, (1997) 279-310
Bogenschütz, A.F.; Jostan, J.L.; Mussinger, W.: Galvanische
Korrosionsschutzschichten für elektronische Anwendungen. Metalloberfläche 34 (1980) 45-53, 93-136, 163-168, 187-194 (mit J. Ruf), 229-235, 261-269
Huck, M.: Kontaktzuverlässigkeit von Steckverbindern. Metall 37 (1983) H.7,
685-690
Kaspar, F.: Drahtbonden zur Kontaktierung auf elektronischen Baugruppen, 13
Werkstoffen und Beschichtungen. VDE-Fachbericht 55, (1999) 97-103
Weiser,J.: Prüfverfahren in der Informationstechnik. In Vinaricky, E. (Hrsg.): Elektrische Kontakte, Werkstoffe und Anwendungen. Springer Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York (2002) 600 - 609
I Data Book I Testing Procedures I
Schäfer, E.: Zuverlässigkeit, Verfügbarkeit und Sicherheit in der Elektronik, Vogel-Verlag, (1979)
Siepmann, R.: Elektronische Lastnachbildung, Siemens Comp., (1990) 28
Johler, W.: Untere und obere Einsatzgrenzen von Signalrelais. VDE-Fachbericht 63 (2007) 31-40
IEC/EN 61810-2: Electromechanical elementary relays - Part 2: Reliability
IEC/EN 61810-7: Electromechanical elementary relays - Part 7: Test and measurement procedures
Braumann, P.; Koffler, A.: Einfluss von Herstellungsverfahren, Metalloxidgehalt und Wirkzusätzen auf das Schaltverhalten von AgSnO2 in Relais (1). VDE-Fachbericht 59 (2003) 133-142 Braumann, P.; Koffler, A.: Einfluss von Herstellungsverfahren, Metalloxidgehalt und Wirkzusätzen auf das Schaltverhalten von AgSnO2 in Relais (2). VDE-Fachbericht 61 (2005) 149-154
Schöpf, Th.: Silber/Zinnoxid und andere Silber/Metalloxidwerkstoffe in
Netzrelais. VDE-Fachbericht 51 (1997) 41-50
Behrens, V.; Honig, Th.; Kraus, A.; Michal, R.: Schalteigenschaften von verschiedenen Silber/Zinnoxid-Werkstoffen in Kfz-Relais.
VDE-Fachbericht 51 (1997) 51-57
Braumann, P.: Prüfung der elektrischen Lebensdauer von Kfz-Relais. VDE-Fachbericht 55 (1999) 49-59
Schröder, K.-H.: Prüfverfahren in der Energietechnik. In Vinaricky, E. (Hrsg.): Elektrische Kontakte, Werkstoffe und Anwendungen. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York (2002) 609-633
IEC/EN 60947-4-1: Low-voltage switchgear and controlgear - Part 4-1: Contactors and motor-starters-Electromechanical contactors and motor starters
IEC/EN 60947-5-1: Low-voltage switchgear and controlgear - Part 5-1: Control circuit devices and switching elements- Electromechanical control circuit devices
IEC/EN 60947-2: Low-voltage switchgear and controlgear - Part 2: Circuitbreakers
UL 489: „Molded Case Circuit Breakers, Molded Case Switches and Circuit Breaker enclosures“
Braumann, P.; Koffler, A.; Schröder, K.-H.: Analysis of Interrelation Between Mechanical and Eletrical Phenomena During Making Operations of Contacts: Proc. 17th Int. Conf. on Electrical Contacts, Nagoya, Japan, 1994
Braumann, P.; Koffler, A.: The Importance of Characterizing the Make and Break Operations to Allow Effective Contact Material Development. 19. ITK Nürnberg, VDE-Verlag, Berlin, Offenbach, (1998) 325-333
EN ISO 8044: Corrosion of metals and alloys - Basic terms and definitions. Berlin, Beuth-Verlag 1999
Abbott, W.H.: Contact Corrosion. in Slade, P.: Electrical Contacts, Principles and Applications: Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, Basel, (1999) 113 - 154
Slade, P.: Introduction to Contact Tarnishing and Corrosion. in Slade, P.: Electrical Contacts, Principles and Applications: Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, Basel, (1999) 89 - 112
Cosack, U.: Survey of Corrosion Tests with Pollutant Gases and their Relevance for Contact Material. Proc. of the 13th Intern. Conf. on Electr. Contacts, Lausanne, Switzerland, (1986) 316-325
Schnabl, R.; Paulsen, R.: Korrosionserscheinungen an Edelmetallen und
Trägerwerkstoffen. Metall 7 (1987) 696-701
Abbott, W.H.: The Development and Performance Characteristics of Flowing Mixed Gas Test Environments. IEEE Transactions on Components, Hybrids, and Manufacturing Technology, Vol. 2, No. 1, (1988) 22-35
Hienomen, R.; Rakkolainen, J.; Saarinen, T.; Aberg, M.: Nordic Project on Corrosion in Electronics. A Comparative Study on Field and Laboratory Test Results of Various Electronic Contacts. Proc. 14th Int. Conf. on Electric Contacts, Paris, (1988) 271-275
Leygraf, Ch.: Indoor Athmosperic Corrosion. VDE-Fachbericht 63 (2007) 39-52
ASTM Designation B 845-97: Standard Guide for Mixed Flowing Gas (MFG) Tests for Electrical Contacts, 1997
IEC Standard 68-2-60, Environmental Testing Part 2: Tests Flowing-Mixed Gas
Corrosion Test, 1995
Telcordia GR-63-CORE Issue 2, Section 5.5 : Airborne Contaminants Test
Methods, Nov. 2000