Difference between revisions of "General Rules for Dimensioning of Contacts"
From Electrical Contacts
Doduco Admin (talk | contribs) |
(→6.4.6 General Rules for Dimensioning of Contacts) |
||
| (18 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | === | + | ===6.4.6 General Rules for Dimensioning of Contacts=== |
| − | '''Recommended Minimum Contact Forces at Slightly Sliding Contact Make:''' | + | *'''Recommended Minimum Contact Forces at Slightly Sliding Contact Make:''' |
| − | + | {| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px;width:40%" | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | |Gold | |
| − | + | |0.03 N | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | |Silver | |
| − | + | |0.1 N | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | |Tungsten | |
| − | + | |0.5 N | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | |} | |
| − | '''Contact Force Recommendations:''' | + | *'''Contact Force Recommendations:''' |
{| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px;width:40%" | {| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px;width:40%" | ||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
| − | '''General Rules for Dimensioning of Contact Rivets''' | + | *'''General Rules for Dimensioning of Contact Rivets''' |
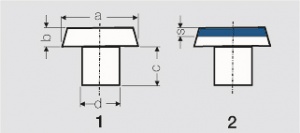
| − | [[File:General Rules for Dimensioning of Contact Rivets.jpg|left|thumb| | + | [[File:General Rules for Dimensioning of Contact Rivets.jpg|left|thumb|General Rules for Dimensioning of Contact Rivets]] |
{| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px;width:100%" | {| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px;width:100%" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | *'''Head diameter for electrical loads''' | ||
| + | {| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px;width:40%" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |For AC currents: | ||
| + | |approx. 1 – 1.5 A/mm² | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |For 1 A | ||
| + | |min. 2 mm head diameter | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |10 A | ||
| + | |approx. 3 – 3.5 mm head diameter | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |20 A | ||
| + | |approx. 5 mm head diameter | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |For DC currents: | ||
| + | |approx. 0.5 – 0.8 A/mm² | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | *'''Head radius R for electrical loads''' | ||
| − | + | {| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px;width:40%" | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | {| class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size: 12px;width: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | |for I < 1 A | |
| − | + | |R ≈ 1,5 mm | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | |I = 6 A | |
| − | + | |R ≈ 5 mm | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |I = 10 A |
| − | + | |R ≈ 10 mm | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |I = 20 A |
| − | | | + | |R ≈ 15 mm |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| + | *'''Failure Probability of Single and Double (Bifurcated) Contacts''' (according to Thielecke) | ||
| − | + | Fig. 6.18: Failure probability of a contact as a | |
| − | + | function of the voltage (according to Kirchdorfer); | |
| − | + | Ag/Ni10; 10 mA | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Fig. 6.19: Failure probability of a contact as a | |
| − | + | function of the current (according to | |
| − | + | Kirchdorfer); Ag/Ni10; F = 0.45 N; U = 24 V | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
[[Application Tables and Guideline Data for Use of Electrical Contact Design#References|References]] | [[Application Tables and Guideline Data for Use of Electrical Contact Design#References|References]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 11:00, 2 April 2014
6.4.6 General Rules for Dimensioning of Contacts
- Recommended Minimum Contact Forces at Slightly Sliding Contact Make:
| Gold | 0.03 N |
| Silver | 0.1 N |
| Tungsten | 0.5 N |
- Contact Force Recommendations:
| Signal relays | ≥ 3 cN |
| AC power relays | ≥ 20 cN |
| Automotive relays | ≥ 20 cN |
| Motor switches (Contactors) (Silver – Metal oxide contacts) |
0.05 - 0.08 N/A |
| Power switches | 0.1 - 0.2 N/A |
| Connectors (Gold coating) |
≥ 30 cN/contact element |
| Connectors (Silver coating) |
≥ 50 cN/contact element |
| Connectors (Tin coating) |
≥ 1 N/contact element |
- General Rules for Dimensioning of Contact Rivets
| Dimensioning | Solid Rivets (1) | Composite Rivets (2) |
|---|---|---|
| a : d | 1.5 : 1 bis 2.5 : 1 | 2 : 1 bis 2.5 : 1 |
| a : b | 2.5 : 1 bis 10 : 1 | 3 : 1 bis 5 : 1 |
| c : b | ≥ 1 : 1 | ≥ 1 : 1 |
| b : s | ≥ 2 : 1 | |
| smin | ≈ 0.3 mm |
- Head diameter for electrical loads
| For AC currents: | approx. 1 – 1.5 A/mm² |
| For 1 A | min. 2 mm head diameter |
| 10 A | approx. 3 – 3.5 mm head diameter |
| 20 A | approx. 5 mm head diameter |
| For DC currents: | approx. 0.5 – 0.8 A/mm² |
- Head radius R for electrical loads
| for I < 1 A | R ≈ 1,5 mm |
| I = 6 A | R ≈ 5 mm |
| I = 10 A | R ≈ 10 mm |
| I = 20 A | R ≈ 15 mm |
- Failure Probability of Single and Double (Bifurcated) Contacts (according to Thielecke)
Fig. 6.18: Failure probability of a contact as a function of the voltage (according to Kirchdorfer); Ag/Ni10; 10 mA
Fig. 6.19: Failure probability of a contact as a function of the current (according to Kirchdorfer); Ag/Ni10; F = 0.45 N; U = 24 V