Difference between revisions of "Physikalische Effekte bei Gleit- und Steckkontakten"
From Electrical Contacts
Doduco Admin (talk | contribs) (→Physikalische Effekte bei Gleit- und Steckkontakten) |
Doduco Admin (talk | contribs) (→Physikalische Effekte bei Gleit- und Steckkontakten) |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
===<!--6.4.5-->Physikalische Effekte bei Gleit- und Steckkontakten=== | ===<!--6.4.5-->Physikalische Effekte bei Gleit- und Steckkontakten=== | ||
| − | + | '''Mechanischer Verschleiß von Gleitkontakten''' | |
<table class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size:12px;width:40%"> | <table class="twocolortable" style="text-align: left; font-size:12px;width:40%"> | ||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| − | + | '''Kontaktverhalten von Steckkontakten''' | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<div class="multiple-images"> | <div class="multiple-images"> | ||
<figure id="fig:Contact resistance Rk as a function of the contact force Fk"> | <figure id="fig:Contact resistance Rk as a function of the contact force Fk"> | ||
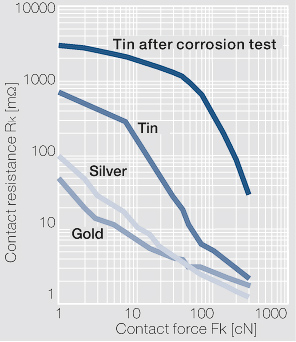
| − | [[File:Contact resistance Rk as a function of the contact force Fk.jpg| | + | [[File:Contact resistance Rk as a function of the contact force Fk.jpg|left|thumb|Figure 1: Abhängigkeit des Kontaktwiderstandes R<sub>k</sub> von der Kontaktkraft F<sub>k</sub> für verschieden Beschichtungswerkstoffe. Gemessen mit einer kugelförmigen Goldsonde; I=10 mA, U< 20 mV]] |
</figure> | </figure> | ||
| − | |||
<figure id="fig:Contact resistance Rk as a function of the fretting wear cycles"> | <figure id="fig:Contact resistance Rk as a function of the fretting wear cycles"> | ||
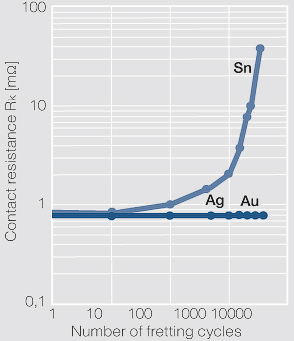
| − | [[File:Contact resistance Rk as a function of the fretting wear cycles.jpg| | + | [[File:Contact resistance Rk as a function of the fretting wear cycles.jpg|left|thumb|Figure 2: Abhängigkeit des Kontaktwiderstandes R<sub>k</sub> von der Anzahl der Reibzyklen für verschiedene Beschichtungswerkstoffe, Relativbewegung d=50μm]] |
| + | </figure> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <figure id="fig:Coefficient of frictional wear for the wear loss of sliding contacts Silver Silver"> | ||
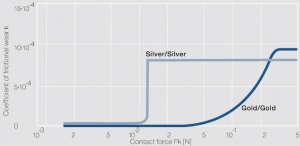
| + | [[File:Coefficient of frictional wear for the wear loss of sliding contacts Silver Silver.jpg|left|thumb|Figure 3: Verschleißkoeffizient für den Abrieb an Gleitkontakten Silber/Silber und Hartgold/Hartgold | ||
| + | in Abhängigkeit von der Kontaktkraft]] | ||
</figure> | </figure> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Latest revision as of 12:49, 11 January 2023
Physikalische Effekte bei Gleit- und Steckkontakten
Mechanischer Verschleiß von Gleitkontakten
| dV/dx = k x FK /3 HW |
| dV/dx Verschleißvolumen in mm3 pro Gleitlänge in mm |
| k Verschleißkoeffizient |
| HW Härte des weicheren Werkstoffes (Brinell- oder Vickerseinheiten) |
| FK Kontaktkraft in cN |
| Verschleißkoeffizient k bei Materialübertragung |
| Silber – Silber 120 x 10-4 |
| Platin – Platin 400 x 10-4 |
| Silber – Platin 1.3 x 10-4 |
| Verschleißkoeffizient k bei Abrieb |
| Silber – Silber 8 x 10-4 |
| Gold – Gold 9 x 10-4 |
| Platin – Platin 40 x 10-4 |
| Silber – Gold 9 x 10-4 |
| Silber – Platin 5 x 10-4 |
Kontaktverhalten von Steckkontakten
Table 1: Beschichtungswerkstoffe für Steckverbinder
| Herstellungsverfahren | Schichtwerkstoffe | Zwischenschicht | Härte HV | Reibwert |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Galvanische Beschichtung | Zinn Nickel Nickel-phosphorus (NiP 6 - 15) Silver Hartgold (< 0,3 Massen-% Ni oder Co) Palladium mit Goldflash (<0,2μm) Palladium - Nickel mit Goldflash (<0.2μm) |
bei Messing: Kupfer oder Nickel Nickel, Nickel - Phosphor Nickel Nickel |
50 - 90 300 - 600 500 - 1100 70 - 100 100 - 200 250 - 300 300 - 400 |
0.5 - 1 0.5 - 0.8 0.2 - 0.5 0.2 - 0.5 0.2 - 0.5 |
| Mechanische Plattierung | Gold-Nickel (AuNi 5 -10) Silber-Palladium (AgPd 10 - 30) |
Nickel Nickel |
160 - 200 120 - 170 |
0.2 - 0.5 0.2 - 0.5 |
| Feuerverzinnung | Zinn | Intermetallische Verbindung (1) Zinn - Kupfer | 400 - 500 |
(1) entsteht beim Verzinnungsprozess